DTC P2047 Reductant Injector Circuit / Open (Bank 1 Unit 1)
DTC P2048 Short to GND in Reductant Injector Circuit (Bank 1)
DTC P2049 Short to B+ in Reductant Injector Circuit (Bank 1)
Description
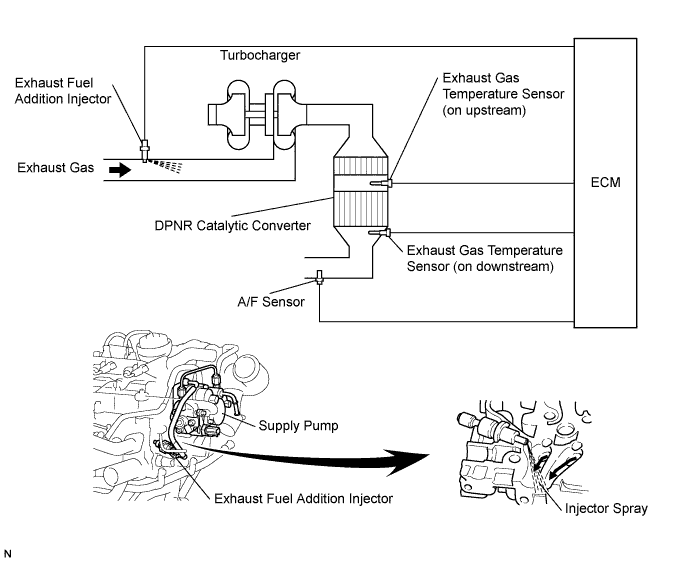
The exhaust fuel addition injector is mounted on the exhaust port of the cylinder head, and low pressure is provided to the injector by the feed pump in the supply pump. This injector adds fuel by a control signal from the ECM.
This injector is used for two different controls: DPNR catalyst regeneration and nitrogen oxide (NOx) reduction.
Under the DPNR catalyst regeneration control, the injector adds fuel to raise a catalyst temperature.
In the other control, the injector helps the air-fuel ratio become RICH. As a result, NOx in the exhaust gas will be reduced in response to the RICH air-fuel ratio.
HINT:
- For more information on the exhaust fuel addition injector and TOYOTA D-CAT*1, refer to the following procedures
- If P2047, P2048 and P2049 are present, refer to the DTC table for TOYOTA D-CAT.
*1: Diesel Clean Advanced Technology.
Toyota fault code list DTC P2047 DTC P2048 DTC P2049
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P2047 | With the exhaust fuel addition injector off, the FIVM1 output is High and the FIVM2 output is Low for 3 seconds. (1 trip detection logic) |
|
| P2048 | With the exhaust fuel addition injector off, the FIVM1 output is High and the FIVM2 output is High for 0.16 seconds. (1 trip detection logic) |
|
| P2049 | With the exhaust fuel addition injector on, the FIVM1 output is Low and the FIVM2 output is Low for 7 or more times. (1 trip detection logic) |
HINT:
DTC P1386 (injector for exhaust fuel addition) will be present if there is an open malfunction in the exhaust fuel addition injector circuit.
Monitor description
In order to detect abnormality in the fuel addition injector, an internal CPU of the ECM monitors injection command (FIV) signals and injection confirmation (FIVM) signals. The FIV signal is sent from the CPU to the (exhaust) fuel addition injector via a drive circuit inside the ECM. The FIVM signal, which is originally output from the internal drive circuit of the ECM, is transmitted to the CPU via a monitor circuit. By receiving the FIVM signal, the ECM judges that the current has been applied to the (exhaust) fuel addition injector.
This DTC will be set if the ECM judges that the number of signals of the FIV and the FIVM are inconsistent.
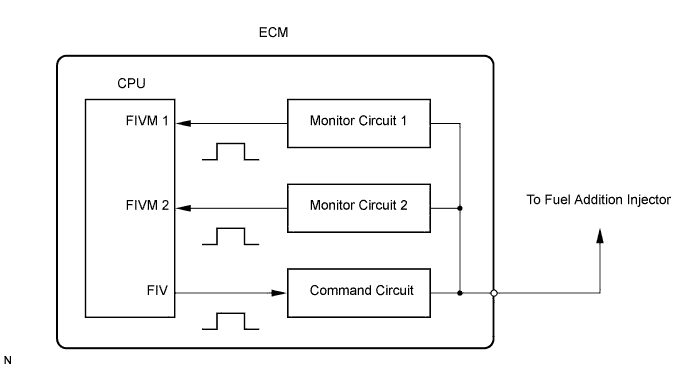
Wiring diagram
Inspection procedure
NOTICE:
After replacing the ECM, the new ECM needs registration and initialization.
| 1.INSPECT EXHAUST FUEL ADDITION INJECTOR (RESISTANCE) |
-
Inspect exhaust fuel addition injector.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 2.CHECK WIRE HARNESS (EXHAUST FUEL ADDITION INJECTOR - ECM) |
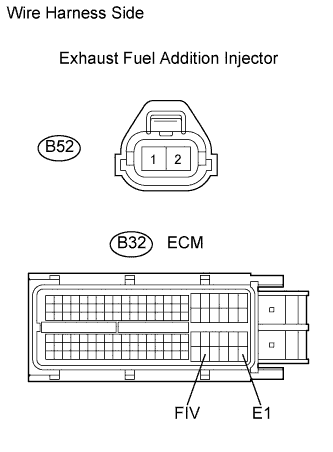
-
Disconnect the B52 exhaust fuel addition injector connector.
-
Disconnect the B32 ECM connector.
-
Check the resistance of the wire harness side connectors.
Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition B52-1 - B32-105 (FIV) Below 1 ? B52-2 - B32-109 (E1) Below 1 ? B52-1 or B32-105 (FIV) - Body ground 10 k? or higher -
Reconnect the exhaust fuel addition injector connector.
-
Reconnect the ECM connector.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
|