DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
READ OUTPUT DTC (RELATING TO ENGINE)
TAKE SNAPSHOT DURING IDLING AND 4000 RPM (PROCEDURE 2)
TAKE SNAPSHOT DURING LACK OF POWER (PROCEDURE 3)
CHECK SNAPSHOT (MAP AND MAF)
CHECK SNAPSHOT (FUEL PRESS, TARGET COMMON RAIL PRESSURE, MAP AND TARGET BOOSTER PRESSURE)
CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM
CLEAN FUEL FILTER CASE AND REPLACE FUEL FILTER
REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES OF ALL CYLINDERS
BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM
REGISTER INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE AND PERFORM PILOT QUANTITY LEARNING
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (MAP AND ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE)
CHECK AIR INTAKE SYSTEM
CHECK TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
REPLACE MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR
REPLACE ECM
REPAIR OR REPLACE AIR INTAKE SYSTEM
REPLACE TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
INSPECT CLOGGED FUEL PIPE
REPLACE FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE)
REPAIR OR REPLACE CLOGGED FUEL LINE
BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM
PERFORM FUEL SUPPLY PUMP INITIALIZATION
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
CHECK AIR INTAKE SYSTEM
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACTIVATE THE EGR VALVE CLOSE)
READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (MAF)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACTIVATE THE VSV FOR EGR COOLER BYPASS)
REMOVE DEPOSIT (ELECTRIC EGR CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY)
REPAIR OR REPLACE AIR INTAKE SYSTEM
REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER
REPLACE EGR COOLER
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACTIVATE THE VSV FOR EGR COOLER BYPASS)
CHECK FRONT EXHAUST PIPE ASSEMBLY (CATALYST CONVERTER)
INSPECT TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
REPLACE EGR COOLER
REPLACE FRONT EXHAUST PIPE ASSEMBLY (CATALYST CONVERTER)
REPLACE TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
COMPARE WITH SIMILAR VEHICLE WITH SAME ENGINE
EXPLAIN THE INVESTIGATION RESULT TO CUSTOMER
ECD SYSTEM (for DPF) - Lack of Power or Hesitation |
DESCRIPTION
Malfunction Condition
| Main Trouble Area
| Related Trouble Area
|
- Lack of power caused by abnormal fuel injection volume (fuel supply pump assembly malfunction, injector assembly malfunction, etc.)
- Lack of power caused by intake air volume shortage (turbocharger malfunction, or front exhaust pipe or exhaust manifold converter blocked)
| (a) Injector assembly malfunctions
- Injector sliding malfunction
- Injector stuck closed
- Injector stuck open
- Deposits in injector
- Injector circuit malfunction
(b) Abnormal common rail pressure
- Suction control valve
(c) Abnormal intake air volume
- Intake air system leakage or clogged
- Turbocharger
- Front exhaust pipe blockage
- Exhaust manifold converter blockage
- EGR valve does not close
- Throttle valve does not open
| - Pressure discharge valve (P1271 stored simultaneously)
- Intake air system blockage
- EGR system
- Fuel filter element sub-assembly is clogged
- Throttle valve
- Mass air flow meter
- Compression pressure
- Injector compensation code
- Fuel leak
- Glow plug
- Fuel pressure sensor
- Manifold absolute pressure sensor
- Vacuum hose connection for manifold absolute pressure sensor
- Injector driver (P062D stored simultaneously)
- Vehicle modifications
- Clutch disc wear
- Low quality fuel
- Frozen fuel
- ECM
|
- HINT:
- Specified values in the following troubleshooting flowchart are for reference only. Variations in the Data List values may occur depending on the measuring conditions or the vehicle's age. Do not judge the vehicle to be normal even when the Data List values indicate a standard level. There are possibly some concealed factors causing the malfunction.
- Check that the vehicle has not been modified in any way prior to the vehicle inspection.
- This troubleshooting procedure checks for the cause of an obvious lack of engine power while the vehicle is being driven (such as the maximum speed being extremely low).
| Faults and Symptoms of Common Rail Diesel Components |
Engine Control
Mass Air Flow MeterMain fault
| Decrease in performance (foreign matter is stuck)
|
Symptoms
| Lack of power, black smoke
|
Data List
| MAF
|
- HINT:
- The maximum fuel injection volume is controlled according to the output from the mass air flow meter.
|
Intake SystemSymptom and Corresponding Main Fault
| - Lack of power (no black smoke) due to air filter blockage or crushed or leaking air duct
- Black smoke (no lack of power) due to leakage between the turbo and intake manifold
|
Data List
| - MAP
- Target Booster Pressure
When the accelerator is fully depressed, if MAP is 20 kPa lower than Target Booster Pressure for more than 5 seconds, then a lack of power will be felt.
- MAF
|
Turbocharger SystemMain fault
| - Air leak in the turbocharged air passage
- Turbocharger (turbine, bearing, variable nozzle)
|
Symptoms
| Lack of power (when vehicle is starting, under heavy load)
(Black smoke is not emitted when racing while vehicle is stopped)
|
Data List
| MAP, Target Booster Pressure
- When the accelerator is fully depressed, if MAP is 20 kPa lower than Target Booster Pressure for more than 5 seconds, then a lack of power will be felt.
- With the ignition switch ON or during idling, MAP = atmospheric pressure (standard atmospheric pressure = 101 kPa). When the engine speed is about 1500 rpm or more, the turbocharger starts to take effect and MAP becomes higher than atmospheric pressure.
- Atmospheric pressure decreases by 1 kPa each time elevation increases by 100 m, and is also affected by the current weather conditions.
|
Exhaust SystemMain fault
| Blockage
|
Symptoms
| Lack of power (high engine speed, under heavy load)
|
Data List
| MAP, Target Booster Pressure
When the accelerator is fully depressed, if MAP is 20 kPa lower than Target Booster Pressure for more than 5 seconds, then a lack of power will be felt.
|
Glow SystemMain fault
| Glow system malfunction
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle, knocking, white smoke (when cold)
|
Data List
| Check the glow plug indicator light
|
Diagnostic Point
| Measure the resistance of the glow plug
|
Engine - 1Main fault
| Damaged, seized up
|
Symptoms
| Cannot crank, crank speed is low, strange noise
|
Engine - 2Main fault
| Loss of compression
|
Symptoms
| Rough idle (lack of power always)
|
Data List
| Engine Speed of Cyl#
- When cranking during the "Check the Cylinder Compression" Active Test, if there is a high speed cylinder, approx. 100 rpm more than the other cylinders, that cylinder may lose compression.
Injection Feedback Val
- When an Injector Feedback Val is more than 3 mm3/st, there may be a malfunction in the corresponding cylinder.
|
Diesel Injection
Fuel Supply Pump AssemblyMain fault
| -
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, engine stalling, rough idle, lack of power
|
Data List
| Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure, Target Pump SCV Current
- Fuel Press is within 5000 kPa of Target Common Rail Pressure during idling with the engine warmed up (engine coolant temperature is higher than 70°C (158°F)).
- If the fuel pressure is 20000 kPa below the target pressure, then a lack of power will be felt.
- If the fuel pressure is below 25000 kPa, then idling will be rough.
- If Target Pump SCV Current is 3000 mA or higher, the suction control valve may be stuck.
- HINT:
- The fuel pressure changes at engine start, but is approx. 25000 kPa at engine start after the engine is warmed up.
- When Target Pump SCV Current is 3000 mA or higher, the suction control valve has a tendency to become stuck.
|
Diagnostic Trouble Code
| Even if Fuel Press is below Target Common Rail Pressure, a DTC will not be stored.
|
Fuel Filter Element Sub-assemblyMain fault
| Blockage
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, engine stalling, rough idle, lack of power
|
Data List
| Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure
- Fuel Press is within 5000 kPa of Target Common Rail Pressure during idling with the engine warmed up (engine coolant temperature is higher than 70°C (158°F)).
- If the fuel pressure is 20000 kPa below the target pressure, then a lack of power will be felt.
- If the fuel pressure is below 25000 kPa, then idling will be rough.
- HINT:
- The fuel pressure changes at engine start, but is approx. 25000 kPa at engine start after the engine is warmed up.
|
Diagnostic Trouble Code
| Even if Fuel Press is below Target Common Rail Pressure, a DTC will not be stored.
|
Injector AssemblyMain fault
| Blockage
|
Symptoms
| Rough idle, lack of power, black smoke, white smoke, knocking
|
Data List
| Injection Feedback Val
- When an Injector Feedback Val is more than 3 mm3/st, there may be a malfunction in the corresponding cylinder. This value can be read after idling for 1 minute.
|
Injector DriverMain fault
| Circuit fault: The injector assembly does not open.
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle, lack of power, black smoke, white smoke, knocking
|
Data List
| Same as injector assembly
|
Diagnostic Trouble Code
| When the injector driver has a fault, some DTCs may be stored.
|
Fuel Pressure SensorMain fault
| Open circuit, decrease in performance (foreign matter is stuck)
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle, engine stall, lack of power
|
Data List
| Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure
- Fuel Press is within 5000 kPa of Target Common Rail Pressure during idling with the engine warmed up (engine coolant temperature is higher than 70°C (158°F)).
|
Diagnostic Code
| When the fuel pressure sensor has a fault, some DTCs may be stored.
|
Irregular FuelMain fault
| -
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle (especially when cold)
|
Diesel EGR
EGR SystemMain fault
| - Does not move smoothly
- Does not close fully
|
Symptoms
| - Rough Idle
- EGR valve stuck closed: A loud turbocharger sound.
- EGR valve stuck open: Difficult to start (does not stall), black smoke, white smoke (when engine is cold), lack of power, jerking (If there is an excess in the quantity of EGR and there is a heavy load, when the vehicle starts moving, a lack of power will be felt. Also, when racing the engine, there will be some black smoke).
|
Data List
| Actual EGR Valve Pos., Target EGR Position
- Generally, Actual EGR Valve Pos. = Target EGR Position +/-5% (fully closed: 0%, fully open: 100%).
- Using the EGR valve Active Test, check whether Actual EGR Valve Pos. follows Target EGR Position (the engine coolant temperature and intake air temperature should be considered when a malfunction occurs).
- EGR valve is fully closed when the ignition switch ON (engine stopped).
- EGR valve opens to the halfway point at idling after the engine is warmed up.
- When the EGR valve does not close, MAF (Mass Air Flow) decreases when the vehicle is accelerated at full throttle. MAP also decreases in comparison to Target Booster Pressure, however there is not a large difference.
EGR Close Lrn. Val., EGR Close Lrn. Status
- When leaving the vehicle idling, when EGR Close Lrn. Status is OK, the normal range of EGR Close Lrn. Val. is 0 to 1 V.
- In cases when EGR Close Lrn. Status. is NG or EGR Close Lrn. Val. is out of the normal range (0 to 1 V), it is possible that the EGR valve cannot completely close.
|
Diesel Throttle
Diesel Throttle SystemMain fault
| Stuck, does not move smoothly
|
Symptoms
| - Stuck closed: Lack of power, difficult to start, rough idle, engine stall, black smoke. These may occur when stuck almost fully closed.
- Stuck open: Turbocharger sound increases. When the engine is stopped, engine vibrations may occur.
|
Data List
| - Actual Throttle Position (fully closed: 100%, fully open: 0%)
- When the ignition switch ON (engine stopped), the diesel throttle is fully open. When idling, the diesel throttle is at the halfway point. When the ignition switch is turned from ON to off, the throttle is fully closed temporarily.
|
| Data List Related to Lack of Power |
- Engine Speed
- MAP
- MAF
- Intake Air
- Coolant Temp
- Target Common Rail Pressure
- Fuel Press
- Target Pump SCV Current
- Injection Feedback Val #1 (to #4)
- Injection Volume
- Actual Throttle Position
- Target EGR Position
- Actual EGR Valve Pos.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Lack of Power
| The power of the diesel engine is determined by the quantity of injected fuel and the quantity of intake air.
The quantity of injected fuel is determined by the fuel pressure and the amount of time the injector assembly is open. Basically, the fuel pressure is controlled so that it reaches the target fuel pressure. The throttle valve does not restrict air flow volume, so the manifold absolute pressure is almost the same as atmospheric pressure when idling. At more than approximately 1500 rpm, the turbo starts to operate causing the manifold absolute pressure to become higher than atmospheric pressure.
The manifold absolute pressure is controlled so that it reaches the Target Booster Pressure when accelerating the vehicle at full throttle. Also, when accelerating the vehicle at full throttle, the throttle is fully open and the EGR valve is fully closed, preserving the mass air flow.
|
- NOTICE:
- After replacing the ECM, the new ECM needs registration (HILUX_TGN26 RM0000012XK07EX.html) and initialization (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000TIN056X.html).
- After replacing the fuel supply pump assembly, the ECM needs initialization (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000TIN056X.html).
- After replacing an injector assembly, the ECM needs registration (HILUX_TGN26 RM0000012XK07EX.html).
| 1.READ OUTPUT DTC (RELATING TO ENGINE) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read the pending DTCs.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
No DTCs are output
| A
|
Engine related DTCs are output
| B
|
- HINT:
- If only DTC P1608 is output, proceed to step 2.
| 2.TAKE SNAPSHOT DURING IDLING AND 4000 RPM (PROCEDURE 2) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Lack of power.
With no load after the engine is warmed up, take a snapshot when idling and at 4000 rpm.
Text in Illustration*1
| Snapshot Button
|
- HINT:
- A snapshot can be used to compare vehicle data from the time of the malfunction to normal data and is very useful for troubleshooting.
- Graphs can be displayed by transferring the stored snapshot data from the tester to a PC. Intelligent Viewer must be installed on the PC.
- The shift lever should be in neutral and the A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off.
| 3.TAKE SNAPSHOT DURING LACK OF POWER (PROCEDURE 3) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data.
Check for a lack of power during the driving test.
Text in Illustration*1
| Snapshot Button
|
- HINT:
- A snapshot can be used to compare vehicle data from the time of the malfunction to normal data and is very useful for troubleshooting.
- Graphs can be displayed by transferring the stored snapshot data from the tester to a PC. Intelligent Viewer must be installed on the PC.
- Move the shift lever to 2nd gear and accelerate the vehicle with the accelerator pedal fully depressed (obey all laws and regulations, and pay attention to traffic conditions while driving the vehicle). Then, check the Data List with the engine warmed up and idling (the shift lever should be in neutral and the A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off).
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Apparent lack of power is present
| A
|
Apparent lack of power is not present
| B
|
| 4.CHECK SNAPSHOT (MAP AND MAF) |
Check MAP and MAF in the snapshot taken in procedure 2 when the engine was running at 4000 rpm with no load.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
MAP is 105 kPa or higher and MAF is 84 gm/s or more*1
| A
|
MAP is below 90 kPa*2
| B
|
Except above*3
| C
|
- HINT:
- The above values were measured under standard atmospheric pressure. The values are influenced by elevation, weather conditions, etc.
- Standard atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa. For every 100 m increase in elevation, pressure drops by 1 kPa. This varies by weather.
- *1: There may be a problem in the fuel injection system or intake system.
- *2: There may be a problem in the turbocharger system.
- *3: There may be a problem in the intake system or a problem with the EGR valve (valve stuck open or valve does not close).
| 5.CHECK SNAPSHOT (FUEL PRESS, TARGET COMMON RAIL PRESSURE, MAP AND TARGET BOOSTER PRESSURE) |
Check Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure, MAP and Target Booster Pressure in the snapshot taken in procedure 3 when the vehicle was accelerating with the accelerator pedal fully depressed in 2nd gear.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
MAP is below 190 kPa at an engine speed of 3000 rpm
| A
|
Difference between Fuel Press and Target Common Rail Pressure is 20000 kPa or more
| B
|
Except above
| C
|
- HINT:
- The above values were measured under standard atmospheric pressure. The values are influenced by elevation, weather conditions, etc.
Standard atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa. For every 100 m increase in elevation, pressure drops by 1 kPa. This varies by weather.
- The engine speed must be 1500 rpm or less before performing the inspection in which the accelerator pedal is fully depressed and the engine is accelerated to a speed of 3000 rpm.
- If the turbocharger movement is not smooth, etc., the value of MAP in the snapshot taken during lack of power will not reach the target value.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed and the engine speed is 3000 rpm, the MAP should be higher than 195 kPa.
Check for air leaks and blockages between the air cleaner case and turbocharger, and between the turbocharger and intake manifold.
- HINT:
- Inspect the air intake system, especially hoses and pipes between the air cleaner and turbocharger.
- Check for abnormal disconnections, pipe and hose squashing, and any damage in the intake system.
- Using your hand, check whether the pipes and hoses in the intake system are securely connected.
- By applying soapy water and revving up the engine, air leaks from the intake system can be checked by checking for bubbles.
- Check for any modifications in the intake system made by the user.
- OK:
- No leakage or blockage.
| 7.CLEAN FUEL FILTER CASE AND REPLACE FUEL FILTER |
Clean the fuel filter case and replace the fuel filter.
- HINT:
- Be sure to clean the inside of the fuel filter case as the fuel injectors may not operate properly if the fuel filter is installed with foreign matter remaining inside the fuel filter case.
| 8.REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES OF ALL CYLINDERS |
Replace the injector assemblies (HILUX_TGN26 RM0000044TN00PX.html).
- NOTICE:
- When replacing the injector assembly for a cylinder, always be sure to use a new injection pipe.
- Follow the procedure in the repair manual and temporarily install the injection pipes and nozzle leakage pipe, and then correctly position the injector assemblies. After that, tighten parts according to the torque specifications.
- If the installation procedure is not performed correctly, injector assemblies may become out of position, which may cause the injector assemblies to deteriorate, resulting in malfunctions.
- If an injector assembly deteriorates and malfunctions, other problems such as knocking, rough idle, etc. may occur.
- If an injector assembly becomes out of position, it is possible that the seal between the injector assembly and injection pipe may become incomplete, resulting in a fuel leak.
| 9.BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |
Bleed the air from the fuel system (HILUX_TGN26 RM000002SY802GX_01_0002.html).
| 10.REGISTER INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE AND PERFORM PILOT QUANTITY LEARNING |
Register the injector compensation code (HILUX_TGN26 RM0000012XK07EX_02_0003.html).
Perform the injector pilot quantity learning (HILUX_TGN26 RM0000012XK07EX_02_0009.html).
| 11.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
| 12.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (MAP AND ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / MAP and Atmosphere Pressure.
Compare MAP to Atmosphere Pressure when the ignition switch ON (do not start the engine).
- Standard:
- Difference between MAP and Atmosphere Pressure is less than 8 kPa.
- HINT:
- If MAP and Atmosphere Pressure have the same value, both are normal. If there is a difference of 8 kPa or more, compare the values to the atmospheric pressure for that day. The sensor whose deviation is the greatest is malfunctioning.
- Standard atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa. For every 100 m increase in elevation, pressure drops by 1 kPa. This varies by weather.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
MAP and Atmosphere Pressure have same value
| A
|
MAP is different from actual atmospheric pressure
| B
|
Atmosphere Pressure is different from actual atmospheric pressure
| C
|
| 13.CHECK AIR INTAKE SYSTEM |
Check for air leaks and blockages between the air cleaner case and turbocharger, and between the turbocharger and intake manifold.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Leaks and/or blockages exist in the intake system
| A
|
No leaks or blockages in the intake system
| B
|
- HINT:
- Inspect the air intake system, especially hoses and pipes between the air cleaner and turbocharger.
- Check for abnormal disconnections, pipe and hose squashing, and any damage in the intake system.
- Using your hand, check whether the pipes and hoses in the intake system are securely connected.
- When inspecting for a clogged intake system (cause of low MAP), check the following points:
- Clogged air cleaner
- Clogged intake hose
- Diesel throttle valve stuck in closed position
- Check for any modifications in the intake system made by the user.
| 14.CHECK TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY |
Check for turbocharger sub-assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM000003TBT00ZX.html).
| 15.CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS |
Check for intermittent problems (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000PDQ0YRX.html).
| 16.REPLACE MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR |
Replace the manifold absolute pressure sensor.
Replace the ECM (HILUX_TGN26 RM0000013Z001IX.html).
| 18.REPAIR OR REPLACE AIR INTAKE SYSTEM |
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part in the air intake system.
| 19.REPLACE TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY |
Replace the turbocharger sub-assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM000002S6F00NX.html).
| 20.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
| 21.INSPECT CLOGGED FUEL PIPE |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Diesel Injection.
With no load after the engine is warmed up, take a snapshot when idling and vehicle was accelerating with the accelerator pedal fully depressed in 2nd gear.
Check the Target Common Rail Pressure and Fuel Press value.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
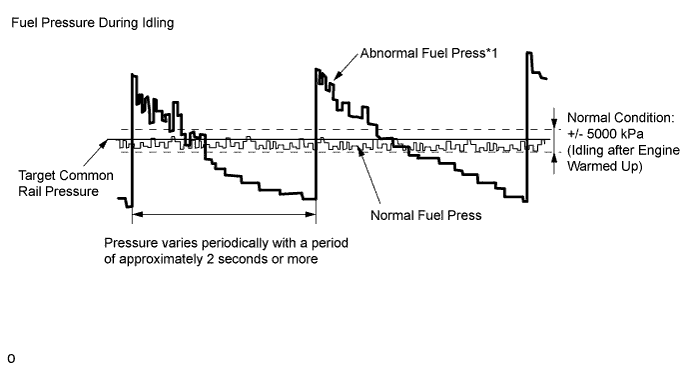
While idling the vehicle, "Fuel Press" deviates from the normal range and varies periodically with a period of approximately 2 seconds or more*1
| A
|
"Fuel Press" is normal while idling the vehicle, but "Fuel Press" does not follow "Target Common Rail Pressure" when the accelerator pedal is fully depressed in 2nd gear*2
|
Except above
| B
|
- NOTICE:
- *1: The cause may be a squashed or blocked fuel pipe or hose.
- *2: The cause may be a clogged fuel filter.
| 22.REPLACE FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE) |
Replace the fuel supply pump assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM0000014FO028X.html).
| 23.REPAIR OR REPLACE CLOGGED FUEL LINE |
Repair or replace the clogged (including frozen fuel) fuel pipe.
Replace the fuel filter element sub-assembly.
- HINT:
- If "Fuel Press" does not follow "Target Common Rail Pressure" when the accelerator pedal is fully depressed in 2nd gear, replace the fuel filter element sub-assembly.
| 24.BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |
Bleed the air from the fuel system (HILUX_TGN26 RM000002SY802GX_01_0002.html).
| 25.PERFORM FUEL SUPPLY PUMP INITIALIZATION |
Perform fuel supply pump initialization (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000TIN056X.html).
| 26.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Test the Fuel Leak / Data List / Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure.
Take a snapshot with the intelligent tester during the Active Test.
Text in Illustration*1
| Snapshot Button
|
- HINT:
- Detailed graphs can be displayed by transferring the stored snapshot from the tester to a PC (personal computer) with Intelligent Viewer installed.
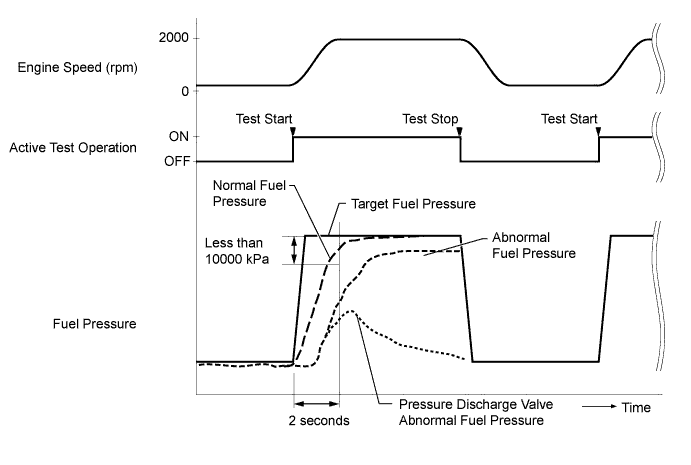
Measure the difference between the target fuel pressure (Target Common Rail Pressure) and the actual fuel pressure (Fuel Press) when the "Test the Fuel Leak" Active Test is performed.
- HINT:
- In order to obtain an exact measurement, perform the Active Test 5 times and measure the difference once each time the Active Test is performed.
- OK:
- The difference between the target fuel pressure and the actual fuel pressure 2 seconds after the Active Test starts is less than 10000 kPa.
- HINT:
- "Target Common Rail Pressure" is the target fuel pressure controlled by the ECM.
- "Fuel Press" is the actual fuel pressure.
| 27.CHECK AIR INTAKE SYSTEM |
Check for air leaks and blockages between the air cleaner case and turbocharger, and between the turbocharger and intake manifold.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
No leaks or blockages in the intake system
| A
|
Leaks and/or blockages exist in the intake system
| B
|
- HINT:
- Inspect the air intake system, especially hoses and pipes between the air cleaner and turbocharger.
- Check for abnormal disconnections, pipe and hose squashing, and any damage in the intake system.
- Using your hand, check whether the pipes and hoses in the intake system are securely connected.
- By applying soapy water and revving up the engine, air leaks from the intake system can be checked by checking for bubbles.
- Make sure that the hose between the manifold absolute pressure sensor and intake manifold is not loose or disconnected.
- Check for any modifications in the intake system made by the user.
| 28.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACTIVATE THE EGR VALVE CLOSE) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and warm it up, and make sure the A/C switch and all accessory switches are off.
Turn the ignition switch off. Wait for 30 seconds, and then restart the engine.
Turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / MAF.
Read the MAF value displayed on the tester while the engine is idling.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Activate the EGR Valve Close.
Read the MAF value when the EGR valve is closed using the Active Test function.
- HINT:
- If idling continues for 20 minutes or more, the EGR valve target opening angle becomes 0% (EGR valve fully closed). As this makes diagnosis impossible, it becomes necessary to drive the vehicle or restart the engine.
- Before performing the diagnosis, confirm that the EGR valve target opening angle is not 0%.
ResultActive Test
| Result
| Proceed to
|
Activate the EGR Valve Close:
Off (Open) to On (Closed)
| MAF value does not change
| A
|
MAF value changes
| B
|
- NOTICE:
- As the measured values may differ from those shown below due to factors such as differences in measuring environments and changes in vehicle condition due to aging, do not use these values to determine whether the vehicle is malfunctioning or not.
- HINT:
- The problem may be a temporary one, due to the entry of deposits or foreign matter. Check that there are no deposits or foreign matter in the electric EGR control valve assembly or mass air flow meter.
ReferenceEGR Valve Condition (Opening)
| Measuring Condition
| MAF (Reference)
|
Open (55%)
| - Atmosphere pressure: 101 kPa
- Intake air temperature: 30°C (86°F)
- Engine coolant temperature: 88°C (190°F)
| 3 to 10 gm/s
|
Closed (0%)
| 12 to 21 gm/s
|
| 29.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (MAF) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / MAF.
Read the value.
- Standard:
Tester Display
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
MAF
| Engine not running
| Less than 0.35 gm/s
|
| 30.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACTIVATE THE VSV FOR EGR COOLER BYPASS) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and warm it up, and make sure the A/C switch and all accessory switches are off.
Turn the ignition switch off and wait for 30 seconds.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / MAF.
Read the MAF value displayed on the tester while the engine is idling.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Activate the VSV for EGR Cooler Bypass / Data List / EGR Cooler Bypass Position.
- HINT:
- Whether the EGR is passing through the bypass side or cooler side during the Active Test can be confirmed by checking EGR Cooler Bypass Position.
Using the Active Test function, switch the EGR valve bypass switching valve between "Cooler" and "Bypass" a few times, and then check whether the MAF value changes after switching the valve from "Cooler" to "Bypass".
- HINT:
- If idling continues for 20 minutes or more, the EGR valve target opening angle becomes 0% (EGR valve fully closed). As this makes diagnosis impossible, it becomes necessary to drive the vehicle or restart the engine.
ResultTester Display
| Result
| Proceed to
|
Activate the VSV for EGR Cooler Bypass:
Cooler to Bypass
| MAF value does not change
| A
|
MAF value changes
| B
|
- HINT:
- If the EGR cooler is clogged, the mass air flow changes.
| 31.REMOVE DEPOSIT (ELECTRIC EGR CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY) |
Remove the electric EGR control valve assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM000004QWK00HX.html).
Visually check the electric EGR control valve assembly for deposits.
If there are deposits, clean the electric EGR control valve assembly.
- NOTICE:
- When cleaning the electric EGR control valve assembly, make sure the valve is completely closed.
- When cleaning the electric EGR control valve assembly, perform initialization procedure (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000TIN056X.html).
- Do not forcibly open the valve, as it may be damaged or deformed.
- When cleaning the electric EGR control valve assembly, use a piece of cloth soaked with cleaning solvent. Spraying the solvent directly onto these parts or soaking the parts in the solvent may damage the parts.
- HINT:
- If the EGR valve does not open properly or is stuck closed, the amount of intake air increases and combustion sounds and engine vibration may increase.
- If the EGR valve does not close properly or is stuck open, EGR becomes excessive and combustion becomes unstable. Also, there may be a lack of power. In this case, clean the electric EGR control valve assembly.
Reinstall the electric EGR control valve assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM000004QWH00HX.html).
| 32.REPAIR OR REPLACE AIR INTAKE SYSTEM |
Repair or replace the malfunctioning part in the air intake system.
| 33.REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER |
Replace the mass air flow meter (HILUX_TGN26 RM000002WMW01FX.html).
- HINT:
- If foreign matter is stuck inside the mass air flow meter, the output characteristics of the mass air flow meter may change, resulting in a malfunction.
- Before replacing the mass air flow meter, perform a wire harness inspection and if there are any problems with the wire harness, repair or replace it.
Replace the EGR cooler (HILUX_TGN26 RM000004QWO00HX.html).
| 35.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
| 36.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACTIVATE THE VSV FOR EGR COOLER BYPASS) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and warm it up, and make sure the A/C switch and all accessory switches are off.
Turn the ignition switch off and wait for 30 seconds.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / MAF.
Read the MAF value displayed on the tester while the engine is idling.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Activate the VSV for EGR Cooler Bypass / Data List / EGR Cooler Bypass Position.
- HINT:
- Whether the EGR is passing through the bypass side or cooler side during the Active Test can be confirmed by checking EGR Cooler Bypass Position.
Using the Active Test function, switch the EGR valve bypass switching valve between "Cooler" and "Bypass" a few times, and then check whether the MAF value changes after switching the valve from "Cooler" to "Bypass".
- HINT:
- If idling continues for 20 minutes or more, the EGR valve target opening angle becomes 0% (EGR valve fully closed). As this makes diagnosis impossible, it becomes necessary to drive the vehicle or restart the engine.
ResultTester Display
| Result
| Proceed to
|
Activate the VSV for EGR Cooler Bypass:
Cooler to Bypass
| MAF value does not change
| A
|
MAF value changes
| B
|
- HINT:
- If the EGR cooler is clogged, the mass air flow changes.
| 37.CHECK FRONT EXHAUST PIPE ASSEMBLY (CATALYST CONVERTER) |
Remove the front exhaust pipe assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM00000456A00CX.html).
Visually check for catalyst clogging or carbon deposits adhering to the inner wall of the exhaust pipe upstream of the catalyst.
- OK:
- Less than 10% of the cells are clogged.
Reinstall the front exhaust pipe assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM00000456800CX.html).
| 38.INSPECT TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY |
Inspect the turbocharger sub-assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM000003TBT00ZX.html).
| 39.CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS |
Check for intermittent problems (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000PDQ0YRX.html).
Replace the EGR cooler (HILUX_TGN26 RM000004QWO00HX.html).
| 41.REPLACE FRONT EXHAUST PIPE ASSEMBLY (CATALYST CONVERTER) |
Replace the front exhaust pipe assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM00000456A00CX.html).
| 42.REPLACE TURBOCHARGER SUB-ASSEMBLY |
Replace the turbocharger sub-assembly (HILUX_TGN26 RM000002S6F00NX.html).
| 43.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
| 44.COMPARE WITH SIMILAR VEHICLE WITH SAME ENGINE |
Confirm the situation in which the lack of power was experienced by the customer again, and compare the driving feeling under the same conditions using a similar vehicle with the same engine while collecting data with the intelligent tester.
- HINT:
- Confirm the state of the following conditions when the lack of power was experienced.
- Accelerator pedal position (vehicle load)
- Vehicle speed
- Engine coolant temperature
- Ambient temperature
- Driving conditions before the lack of power occurred
- Climate
- Road and traffic conditions
- When (what day) the problem was noticed
- Whether the problem occurs suddenly or gradually
- How often the problem occurs
- Why the customer felt there is a lack of power (e.g. the customer compared their vehicle with another vehicle, somebody told the customer that their vehicle has a lack of power, etc.)
- Level of lack of power (slight or drastic)
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Significant difference is found
| A
|
Significant difference is not found
| B
|
| 45.EXPLAIN THE INVESTIGATION RESULT TO CUSTOMER |
Vehicle performance is normal.
There is no problem at this point in time. However, if the problem reoccur, ask the customer to explain in detail the situation in which the problem occurred.
The best course may be to have the customer ride in another vehicle with the same specifications to understand that there is no problem with the customer's vehicle.