READ DATA LIST (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (SENSOR 1) VOLTAGE)
INSPECT INTEGRATION RELAY (EFI MAIN)
CHECK WIRE HARNESS (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (SENSOR 1) - ECM)
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
DTC P0130 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P0150 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2195 Oxygen Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2196 Oxygen Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2197 Oxygen Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2198 Oxygen Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 2 Sensor 1) |
DESCRIPTION
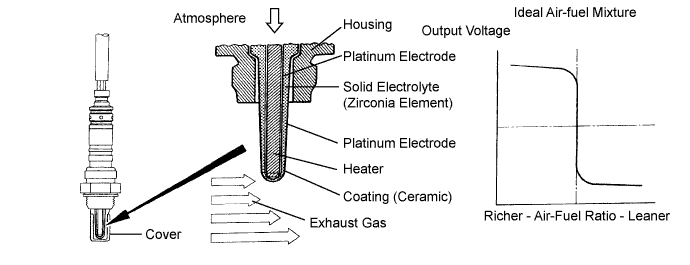
The heated oxygen sensor is used to monitor oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. For optimum catalytic converter operation, the air-fuel mixture must be maintained near the ideal stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. The heated oxygen sensor output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. The ECM adjusts the fuel injection time so that the air-fuel ratio is nearly stoichiometric. The heated oxygen sensor generates a voltage between 0.1 and 0.9 V in response to oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas.If the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas increases, the air-fuel ratio is called LEAN. The heated oxygen sensor voltage drops below 0.45 V, which informs the ECM of the LEAN condition.
If oxygen is not in the exhaust gas, the air-fuel ratio is called RICH. The heated oxygen sensor voltage increases above 0.45 V, which informs the ECM of the RICH condition.
- HINT:
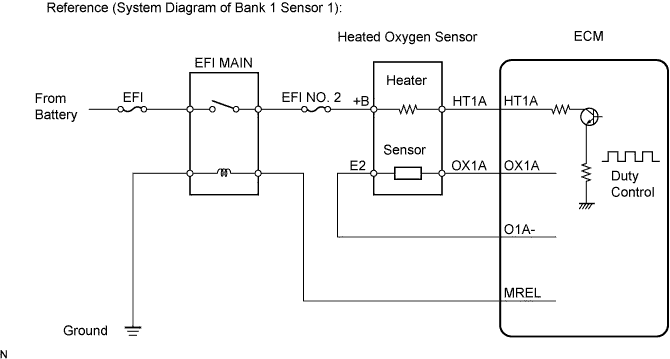
- The ECM provides a pulse width modulated control circuit to adjust current through the heater. The heated oxygen sensor heater circuit uses a relay on the +B side of the circuit.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P0130 P0150 |
|
|
| P2195 P2197 |
| Same as DTC No. P0130, P0150 |
| P2196 P2198 |
| Same as DTC No. P0130, P0150 |
MONITOR DESCRIPTION

The ECM uses the heated oxygen sensor information to regulate the air-fuel ratio close to a stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. This maximizes the catalytic converter's ability to purify the exhaust gases. The heated oxygen sensor detects oxygen levels in the exhaust gas and sends this signal to the ECM.
The inner surface of the sensor element is exposed to outside air. The outer surface of the sensor element is exposed to the exhaust gas. The sensor element is made of platinum coated zirconia and an integrated heating element. The heated oxygen sensor's output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity of the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio. The heated oxygen sensor generates output voltage between 0.1 V and 0.9 V in response to the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. When the front heated oxygen sensor voltage is 0.45 V or more, the ECM judges that the air-fuel ratio is RICH. When it is 0.45 V or less, the ECM judges that the air-fuel ratio is LEAN.
The heated oxygen sensor should indicate RICH and LEAN alternately at a regular cycle under the air-fuel ratio feedback control. If the heated oxygen sensor voltage remains at RICH or LEAN for about 20 seconds (x 3 times), the ECM interprets this as a malfunction of the heated oxygen sensor. The ECM illuminates the MIL (2 trip detection logic) and sets a DTC.
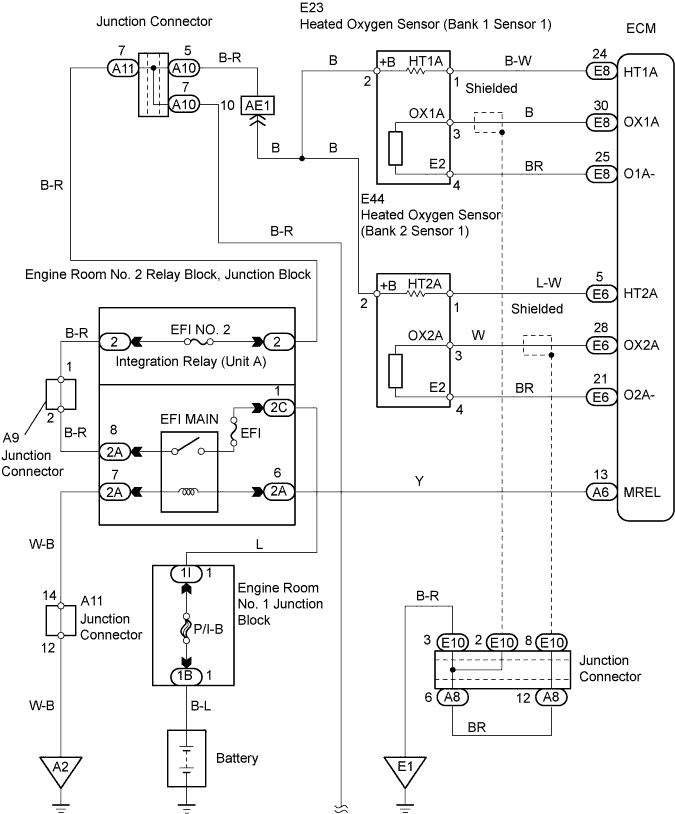
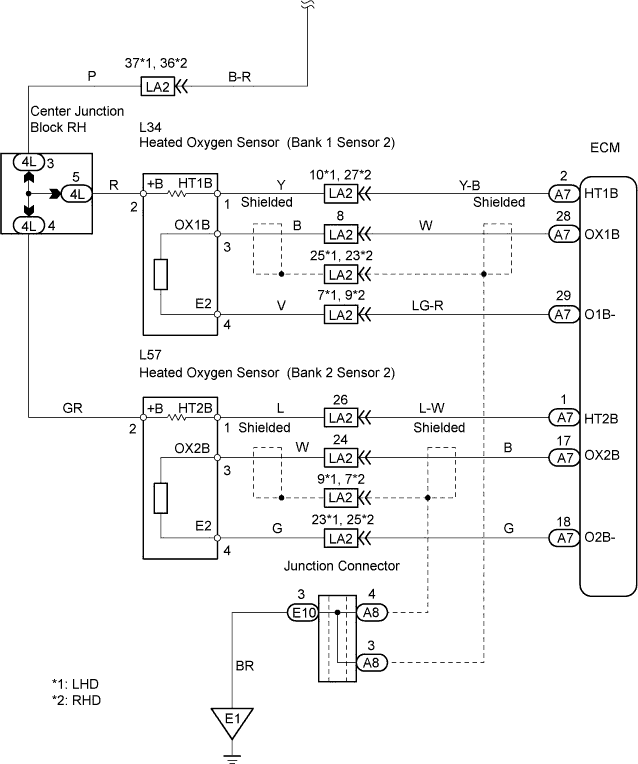
WIRING DIAGRAM
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
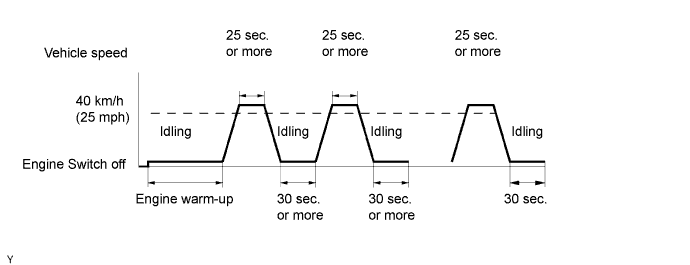
- (a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- (b) Switch the tester from normal mode to check mode (Click here).
- (c) Allow the engine to idle until the ECT reaches 75°C (167°F).
- (d) Allow the vehicle to run at 40 km/h (25 mph) or more for 25 seconds or more.
- (e) Allow the engine to idle for 30 seconds or more.
- (f) Perform the 2 previous steps at least 3 times.
- HINT:
- If a malfunction exists, the MIL will be illuminated on the multi-information display.
- (g) Allow the engine to idle for 30 seconds.
- NOTICE:
- If the conditions in this test are not strictly followed, you should perform steps "d" and "e".
- If you do not have the intelligent tester, turn the engine switch off after performing steps "c" to "g", and then perform steps "c" to "g" again.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- It is possible that the malfunctioning area can be found using the Active Test Control operation. The Active Test can determine if the heated oxygen sensor or other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning or not.
- The injection volume can be switched to -12.5% (decrease) or +25% (increase) by the Active Test.
- The Active Test procedure enables a technician to check and graph the voltage outputs of the heated oxygen sensors.
- Procedure:
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Turn the engine switch on (IG).
- Warm up the engine by running the engine at 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume.
- Perform the Active Test while the engine is idling.
- Standard:
- The heated oxygen sensor reacts in accordance with the increase and decrease of injection volume:
+25% → RICH output: More than 0.55 V
-12.5% → LEAN output: Less than 0.4 V
- NOTICE:
- The heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) output has a few seconds of delay and the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2) output has a maximum of 20 seconds of delay.
- If the vehicle is short on fuel, the air-fuel ratio becomes LEAN and the DTCs will be recorded.
| Case | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage (sensor 1) | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage (sensor 2) | Main Suspected Trouble Area | ||
| 1 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 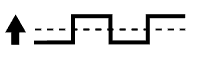 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 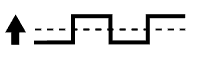 | - |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.55 V or more Below 0.4 V | 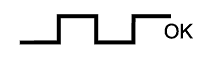 | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.5 V or more Below 0.4 V |  | ||
| 2 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 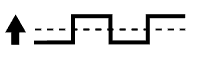 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 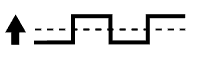 | Heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) Heated oxygen sensor heater (sensor 1) |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.5 V or more Below 0.4 V |  | ||
| 3 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 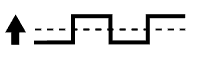 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 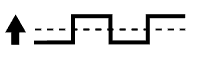 | Heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2) Heated oxygen sensor heater (sensor 2) |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.55 V or more Below 0.4 V |  | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
| 4 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | Injector fuel pressure, Exhaust gas leak, etc. (air-fuel ratio is extremely LEAN or RICH) |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
- HINT:
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was LEAN or RICH, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
- Bank 1 refers to the bank that includes cylinder No. 1.
- Bank 2 refers to the bank that does not include cylinder No. 1.
- Bank 1 includes cylinder No. 1, but bank 2 does not. Cylinder No. 1 is located in the front part of the engine, opposite the transmission.
- Sensor 1 refers to the sensor closest to the engine body.
- Sensor 2 refers to the sensor farthest away from the engine body.
| 1.CHECK OTHER DTC OUTPUT |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
- Result:
Display (DTC output) Proceed to P0130, P0150, P2195, P2196, P2197 or P2198 A P0130, P0150, P2195, P2196, P2197 or P2198 and other DTCs B
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.READ DATA LIST (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (SENSOR 1) VOLTAGE) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Data List / Primary / O2S B1 S1 (or O2S B2 S1).
Allow the engine to run for 90 seconds at 2,500 rpm.
Read the heated oxygen sensor voltage while the engine is idling.
- OK:
- The heated oxygen sensor voltage alternates between below 0.4 V and more than 0.55 V (see the following table).
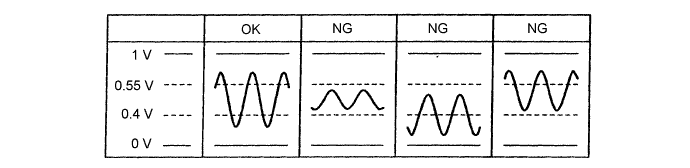
|
| ||||
| NG | |
| 3.INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
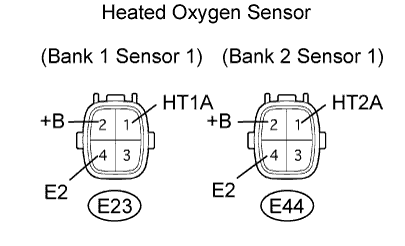 |
Disconnect the E23 and E44 sensor connectors.
Measure the resistance of the sensor.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition (HT1A) - 2 (+B) 11 to 16 Ω 1 (HT2A) - 2 (+B) 11 to 16 Ω 1 (HT1A) - 4 (E2) 10 kΩ or higher 1 (HT2A) - 4 (E2) 10 kΩ or higher
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.INSPECT INTEGRATION RELAY (EFI MAIN) |
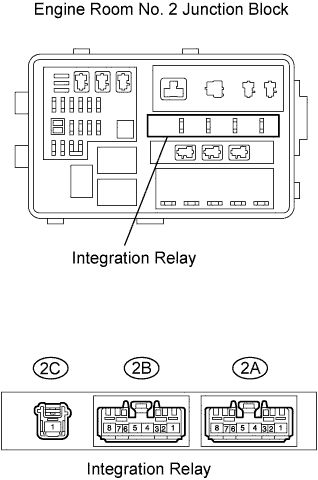 |
Remove the integration relay from the engine room No. 2 junction block.
Measure the resistance of the EFI MAIN relay.
- Standard resistance:
Terminal Connections Specified Condition 2A-8 - 2C-1 10 kΩ or higher 2A-8 - 2C-1 Below 1 Ω
(when battery voltage is applied to terminals 2A-6 and 2A-7)
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 5.CHECK WIRE HARNESS (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (SENSOR 1) - ECM) |
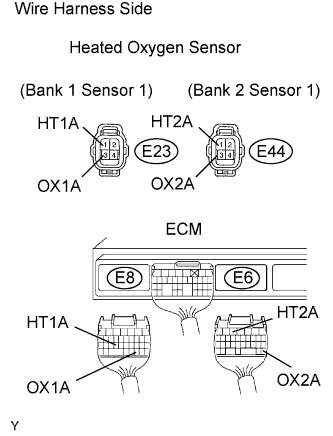 |
Disconnect the E23 and E44 sensor connectors.
Disconnect the E6 and E8 ECM connectors.
Measure the resistance of the wire harness side connectors.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition E23-1 (HT1A) - E8-24 (HT1A) Below 1 Ω E23-3 (OX1A) - E8-30 (OX1A) Below 1 Ω E44-1 (HT2A) - E6-5 (HT2A) Below 1 Ω E44-3 (OX2A) - E6-28 (OX2A) Below 1 Ω E23-1 (HT1A) or E8-24 (HT1A) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E23-3 (OX1A) or E8-30 (OX1A) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E44-1 (HT2A) or E6-5 (HT2A) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E44-3 (OX2A) or E6-28 (OX2A) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 6.CHECK AIR INDUCTION SYSTEM |
Check the air induction system for vacuum leaks.
- OK:
- There is no vacuum leaks in air induction system.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 7.CHECK FUEL PRESSURE |
Check the fuel pressure (Click here).
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 8.INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR |
Check the injector injection (whether fuel volume is high or low, and whether injection pattern is poor).
|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||
| 9.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN |
- HINT:
- Clear all DTCs before performing the confirmation driving pattern.
| NEXT | |
| 10.READ OUTPUT DTC |
Clear the DTC (Click here).
Start the engine and allow the engine to idle for 15 seconds or more.
Read the DTC.
- Result:
Display (DTC output) Proceed to P0130, P0150, P2195, P2196, P2197 or P2198 A P0130, P0150, P2195, P2196, P2197 or P2198 and other DTCs B
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||