READ OUTPUT DTC (CHECK KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT)
CHECK WIRE HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CONNECTOR - ECM)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CONNECTOR - KNOCK SENSOR)
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor) |
DTC P0328 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit High Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor) |
DTC P0332 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Low Input (Bank 2) |
DTC P0333 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit High Input (Bank 2) |
DESCRIPTION
A flat type knock sensor (non-resonant type) has a structure that can detect vibrations over a wide band of frequencies: between approximately 6 kHz and 15 kHz.Knock sensors are fitted onto the engine block to detect engine knocking.
The knock sensor contains a piezoelectric element which generates a voltage when it becomes deformed.
The voltage is generated when the engine block vibrates due to knocking. Any occurrence of engine knocking can be suppressed by delaying the ignition timing.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P0327 P0332 | Output voltage of knock sensor 1 or 2 is 0.5 V or less (1 trip detection logic) |
|
| P0328 P0333 | Output voltage of knock sensor 1 or 2 is 4.5 V or more (1 trip detection logic) |
|
- HINT:
- When any of DTCs P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 are set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During fail-safe mode, the ignition timing is delayed to its maximum retardation. Fail-safe mode continues until the engine switch is turned to OFF.
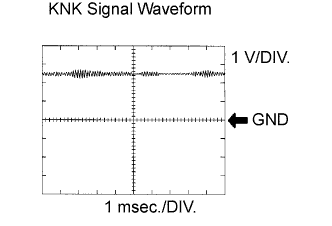
The correct waveform is as shown.
| Item | Content |
| Terminals | KNK1 - EKNK or KNK2 -EKN2 |
| Equipment Settings | 0.01 to 10 V/DIV., 0.01 to 10 msec./DIV. |
| Conditions | Keep engine speed at 4,000 rpm with warm engine |
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The knock sensor, located on the cylinder block, detects spark knock. When spark knock occurs, the piezoelectric element of the sensor vibrates. When the ECM detects a voltage in this frequency range, it retards the ignition timing to suppress the spark knock.The ECM also senses background engine noise with the knock sensor and uses this noise to check for faults in the sensor. If the knock sensor signal level is too low for more than 10 seconds, or if the knock sensor output voltage is outside the normal range, the ECM interprets this as a fault in the knock sensor and sets a DTC.
WIRING DIAGRAM
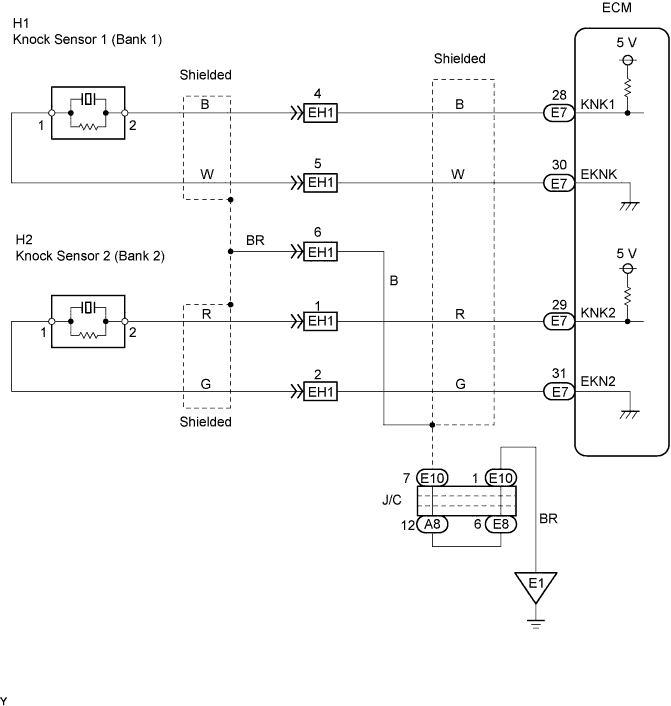
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- DTCs P0327 and P0328 are for the bank 1 knock sensor circuit.
- DTCs P0332 and P0333 are for the bank 2 knock sensor circuit.
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
| 1.READ OUTPUT DTC (CHECK KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT) |
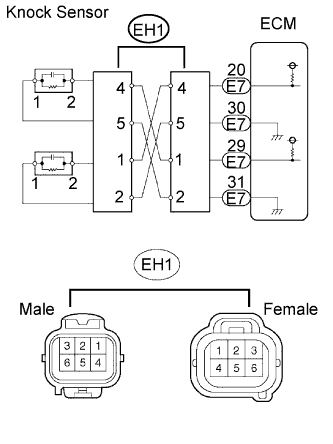 |
Disconnect the EH1 connector.
Using lead wires, connect the connectors as follows.
Male Connector - Female Connector Terminal 4 - Terminal 1 Terminal 5 - Terminal 2 Terminal 1 - Terminal 4 Terminal 2 - Terminal 5
Warm up the engine.
Run the engine at 3,000 rpm for 10 seconds or more.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG) and turn the intelligent tester ON.
Enter the following menus: Power train / Engine / DTC.
Read DTCs.
- Result:
Display Proceed to DTCs same as when vehicle brought in P0327, P0328 → P0327, P0328 or P0332, P0333 → P0332, P0333 A DTCs different from when vehicle brought in P0327, P0328 → P0332, P0333 or P0332, P0333 → P0327, P0328 B
Reconnect the EH1 connector.
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.CHECK WIRE HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CONNECTOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the EH1 connector.
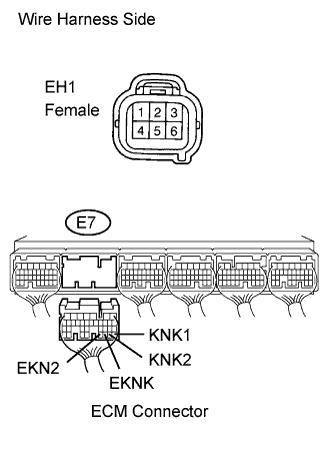 |
Disconnect the E7 ECM connector.
Measure the resistance.
- Standard resistance (Check for open):
Tester Connection Specified Condition EH1 female connector 4 - KNK1 (E7-28) Below 1 Ω EH1 female connector 5 - EKNK (E7-30) Below 1 Ω EH1 female connector 1 - KNK2 (E7-29) Below 1 Ω EH1 female connector 2 - EKN2 (E7-31) Below 1 Ω
- Standard resistance (Check for short):
Tester Connection Specified Condition EH1 female connector 4 or KNK1 (E7-28) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher EH1 female connector 5 or EKNK (E7-30) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher EH1 female connector 1 or KNK2 (E7-29) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher EH1 female connector 2 or EKN2 (E7-31) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the EH1 connector.
Reconnect the ECM connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 3.INSPECT ECM |
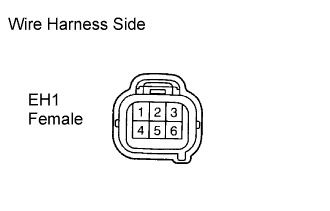 |
Disconnect the EH1 connector.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage between the EH1 terminals.
- Standard voltage:
Tester Connection Specified Condition EH1 female connector 4 - 5 4.5 to 5.5 V EH1 female connector 1 - 2 4.5 to 5.5 V
Reconnect the ECM connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||
| 4.INSPECT KNOCK SENSOR |
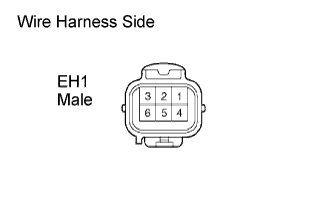 |
Disconnect the EH1 connector.
Measure the resistance between the terminals of the EH1 male connector.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition EH1 male connector 4 - 5 120 to 280 kΩ EH1 male connector 1 - 2 120 to 280 kΩ
Reconnect the EH1 connector.
|
| ||||
| NG | |
| 5.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CONNECTOR - KNOCK SENSOR) |
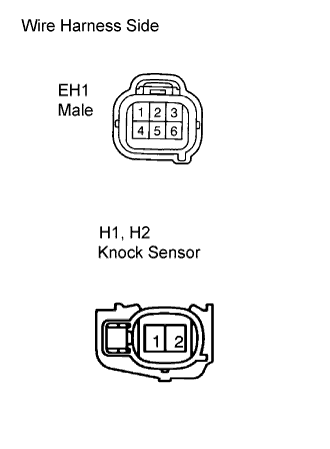 |
- HINT:
- If DTC P0327 or P0328 has changed to P0332 or P0333, check the knock sensor circuit on the right bank side.
- If DTC P0332 or P0333 has changed to P0327 or P0328, check the knock sensor circuit on the left bank side.
Disconnect the EH1 connector.
Disconnect the H1 and H2 knock sensor connectors.
Measure the resistance.
- Standard resistance (Check for open):
Tester Connection Specified Condition EH1 male connector 4 - H1-2 Below 1 Ω EH1 male connector 5 - H1-1 Below 1 Ω EH1 male connector 1 - H2-2 Below 1 Ω EH1 male connector 2 - H2-1 Below 1 Ω
- Standard resistance (Check for short):
Tester Connection Specified Condition EH1 male connector 4 or H1-2 - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher EH1 male connector 5 or H1-1 - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher EH1 male connector 1 or H2-2 - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher EH1 male connector 2 or H2-1 - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the EH1 connector.
Reconnect the knock sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||