READ VALUE USING GTS (THROTTLE POSITION NO.1 AND NO.2)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
REPLACE THROTTLE BODY WITH MOTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR DTCS)
DTC P0120 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A" Circuit Malfunction |
DTC P0121 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A" Circuit Range / Performance Problem |
DTC P0122 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A" Circuit Low Input |
DTC P0123 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A" Circuit High Input |
DTC P0220 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "B" Circuit |
DTC P0222 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "B" Circuit Low Input |
DTC P0223 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "B" Circuit High Input |
DTC P2135 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "A" / "B" Voltage Correlation |
DESCRIPTION
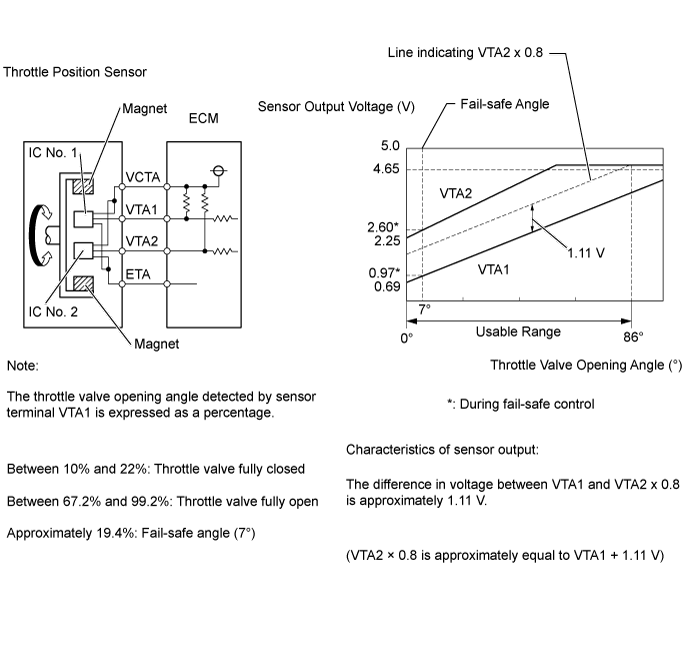
The throttle position sensor is mounted on the throttle body with motor assembly and detects the opening angle of the throttle valve. This sensor is a non-contact type. It uses Hall-effect elements in order to yield accurate signals even in extreme driving conditions, such as at high speeds as well as very low speeds.The throttle position sensor has 2 sensor circuits, each of which transmits a signal, VTA1 and VTA2. VTA1 is used to detect the throttle valve opening angle and VTA2 is used to detect malfunctions in VTA1. The sensor signal voltages vary between 0 V and 5 V in proportion to the throttle valve opening angle, and are transmitted to the VTA terminals of the ECM.
As the valve closes, the sensor output voltage decreases and as the valve opens, the sensor output voltage increases. The ECM calculates the throttle valve opening angle according to these signals and controls the throttle actuator in response to driver inputs. These signals are also used in calculations such as air-fuel ratio correction, power increase correction and fuel-cut control.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P0120 | Output voltage of VTA1 quickly fluctuates beyond the lower and upper malfunction thresholds for 2 seconds when the accelerator pedal is depressed (1 trip detection logic). |
|
| P0121 | Difference between VTA1 and VTA2 voltages is less than 0.8 V, or more than 1.6 V for 2 seconds (1 trip detection logic). |
|
| P0122 | Output voltage of VTA1 is 0.2 V or less for 2 seconds when the accelerator pedal is depressed (1 trip detection logic). |
|
| P0123 | Output voltage of VTA1 is 4.54 V or higher for 2 seconds when the accelerator pedal is depressed (1 trip detection logic). |
|
| P0220 | Output voltage of VTA2 quickly fluctuates beyond the lower and upper malfunction thresholds for 2 seconds when the accelerator pedal is depressed (1 trip detection logic). |
|
| P0222 | Output voltage of VTA2 is 1.75 V or less for 2 seconds when the accelerator pedal is depressed (1 trip detection logic). |
|
| P0223 | Output voltage of VTA2 is 4.8 V or higher, and VTA1 is between 0.2 V and 2.02 V for 2 seconds when the accelerator pedal is depressed (1 trip detection logic). |
|
| P2135 | Either condition is met (1 trip detection logic): (a) Difference between the output voltages of VTA1 and VTA2 is 0.02 V or less for 0.5 seconds or more. (b) Output voltage of VTA1 is 0.2 V or less, and VTA2 is 1.75 V or less for 0.4 seconds or more. |
|
- HINT:
- When any of these DTCs is stored, check the throttle valve opening angle by entering the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Throttle Position No.1 and Throttle Position No.2.
- Throttle Position No.1 is the VTA1 signal, and Throttle Position No.2 is the VTA2 signal.
- Reference (Normal Condition):
GTS Display Accelerator Pedal Fully Released Accelerator Pedal Fully Depressed Throttle Position No.1 0.5 to 1.1 V 3.3 to 4.9 V Throttle Position No.2 2.1 to 3.1 V 4.6 to 5.0 V
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses the throttle position sensor to monitor the throttle valve opening angle. There are several checks that the ECM performs to confirm that the throttle position sensor is operating properly.- A specific voltage difference is expected between the sensor terminals, VTA1 and VTA2, for each throttle valve opening angle. If the difference between VTA1 and VTA2 is incorrect, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the sensor and stores a DTC.
- VTA1 and VTA2 each have a specific voltage range. If VTA1 or VTA2 is outside the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the sensor and stores a DTC.
- VTA1 and VTA2 should never be close to the same voltage level. If VTA1 is within 0.02 V of VTA2, the ECM determines that there is a short circuit in the sensor and stores a DTC.
- The ECM uses the throttle position sensor to monitor the throttle valve opening angle.
This sensor transmits two signals: VTA1 and VTA2. VTA1 is used to detect the throttle opening angle and VTA2 is used to detect malfunctions in VTA1. The ECM performs several checks to confirm that the throttle position sensor and VTA1 are operating properly.
For each throttle opening angle, a specific voltage difference is expected between the outputs of VTA1 and VTA2. If the output voltage difference between the two signals deviates from the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction of the throttle position sensor. The ECM illuminates the MIL and stores the DTC.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, the DTC is stored 2 seconds after the engine is next started.
FAIL-SAFE
When any of these DTCs as well as other DTCs relating to ETCS (Electronic Throttle Control System) malfunctions are stored, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During fail-safe mode, the ECM cuts the current to the throttle actuator, and the throttle valve is returned to a 7° opening angle by the return spring. The ECM then adjusts the engine output by controlling the fuel injection (intermittent fuel-cut) and ignition timing in accordance with the accelerator pedal position to allow the vehicle to continue at a minimal speed. If the accelerator pedal is depressed firmly and gently, the vehicle can be driven slowly.The ECM continues operating in fail-safe mode until a pass condition is detected and the ignition switch is turned off.
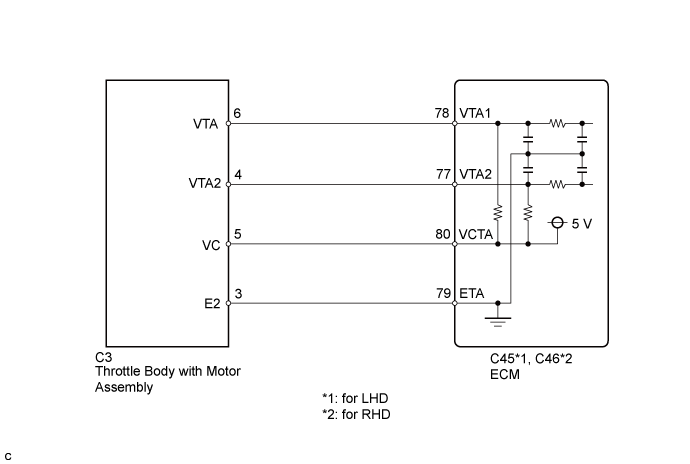
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- These DTCs relate to the throttle position sensor.
- Read freeze frame data using the GTS. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
| 1.READ VALUE USING GTS (THROTTLE POSITION NO.1 AND NO.2) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Throttle Position No.1 and Throttle Position No.2.
Check the values displayed on the GTS.
Result When Accelerator Pedal Released When Accelerator Pedal Depressed Trouble Area Proceed to Throttle Position No.1 Throttle Position No.2 Throttle Position No.1 Throttle Position No.2 0 to 0.2 V 0 to 0.2 V 0 to 0.2 V 0 to 0.2 V VC circuit open A 4.5 to 5.0 V 4.5 to 5.0 V 4.5 to 5.0 V 4.5 to 5.0 V ETA circuit open 0 to 0.2 V,
or 4.5 to 5.0 V2.4 to 3.4 V
(Fail-safe)0 to 0.2 V,
or 4.5 to 5.0 V2.4 to 3.4 V
(Fail-safe)VTA1 circuit open or shorted to ground 0.7 to 1.3 V
(Fail-safe)0 to 0.2 V,
or 4.5 to 5.0 V0.7 to 1.3 V
(Fail-safe)0 to 0.2 V,
or 4.5 to 5.0 VVTA2 circuit open or shorted to ground 0.5 to 1.1 V 2.1 to 3.1 V 3.3 to 4.9 V
(Not fail-safe)4.6 to 5.0 V
(Not fail-safe)TP sensor circuit normal B
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the throttle body with motor assembly connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for LHD Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition C3-5 (VC) - C45-80 (VCTA) Always Below 1 Ω C3-6 (VTA) - C45-78 (VTA1) Always Below 1 Ω C3-4 (VTA2) - C45-77 (VTA2) Always Below 1 Ω C3-3 (E2) - C45-79 (ETA) Always Below 1 Ω C3-5 (VC) or C45-80 (VCTA) - Body ground Always 10 kΩ or higher C3-6 (VTA) or C45-78 (VTA1) - Body ground Always 10 kΩ or higher C3-4 (VTA2) or C45-77 (VTA2) - Body ground Always 10 kΩ or higher for RHD Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition C3-5 (VC) - C46-80 (VCTA) Always Below 1 Ω C3-6 (VTA) - C46-78 (VTA1) Always Below 1 Ω C3-4 (VTA2) - C46-77 (VTA2) Always Below 1 Ω C3-3 (E2) - C46-79 (ETA) Always Below 1 Ω C3-5 (VC) or C46-80 (VCTA) - Body ground Always 10 kΩ or higher C3-6 (VTA) or C46-78 (VTA1) - Body ground Always 10 kΩ or higher C3-4 (VTA2) or C46-77 (VTA2) - Body ground Always 10 kΩ or higher
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 3.INSPECT ECM (VC VOLTAGE) |
 |
Disconnect the throttle body with motor assembly connector.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
Tester Connection Switch Condition Specified Condition C3-5 (VC) - C3-3 (E2) Ignition switch ON 4.5 to 5.5 V
Text in Illustration *a Front view of wire harness connector
(to Throttle Body with Motor Assembly)
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.REPLACE THROTTLE BODY WITH MOTOR ASSEMBLY |
Replace the throttle body with motor assembly (Click here).
| NEXT | |
| 5.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR DTCS) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Clear the DTCs (Click here).
Start the engine.
Allow the engine to idle for 15 seconds or more.
Read the output DTCs.
Result Result Proceed to P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222, P0223 and/or P2135 is output A No DTC is output B
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||