Intake System -- On-Vehicle Inspection |
| 1. CHECK INTAKE AIR SYSTEM |
Check that there is no air suction or leaks at the points shown in the illustration.

Text in Illustration *1 Air Cleaner *2 Mass Air Flow Meter *3 Turbocharger *4 Intercooler *5 Intake Air Temperature Sensor *6 Diesel Throttle Body *7 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor *8 EGR Valve *9 Electric Vacuum Regulating Valve
(for EGR Valve)*10 Vacuum Switching Valve
(for Swirl Control Valve)*11 Swirl Control Valve *12 Vacuum Pump
Check for leakage or clogging between the air cleaner housing and turbocharger inlet, and between the turbocharger outlet and cylinder head.
Condition Operation Clogged air cleaner Clean or replace Collapsed or deformed hoses Repair or replace Leakage from connections Check each connection and repair Cracks in components Check and replace
| 2. CHECK EXHAUST SYSTEM |
Check for leakage or clogging between the cylinder head and turbocharger inlet, and between the turbocharger outlet and exhaust pipe.
Condition Operation Deformed components Repair or replace Foreign matter in passages Remove Leakage from components Repair or replace Cracks in components Check or replace
| 3. CHECK BOOST PRESSURE |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Warm up the engine.
- HINT:
- Be sure to perform the inspection when the engine coolant temperature is between 75 and 90°C (167 and 194°F).
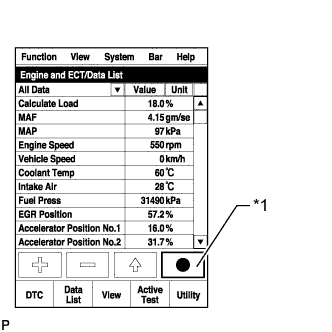
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data.
Take a snapshot of the Data List items with the intelligent tester shown in the illustration.
Text in Illustration *1 Snapshot Record Button - HINT:
- Graphs can be displayed by transferring the stored snapshot from the tester to a PC. Intelligent Viewer must be installed on the PC.
- The condition of the turbocharger can be determined by fully depressing the accelerator pedal while driving at 15 km/h (9 mph) in 2nd gear to accelerate the vehicle (obey all laws and regulations, and pay attention to driving conditions while driving the vehicle), and then comparing MAP with Target Booster Pressure at an engine speed of 3000 rpm.
 |
Compare MAP with Target Booster Pressure.
- Standard:
- MAP is within 30 kPa of Target Booster Pressure when accelerating with accelerator pedal fully depressed.
- HINT:
- The specification above denotes the difference between the absolute pressure values.
- The inspection above is only for vehicles equipped with a manual transmission.
Warm up the engine.
- HINT:
- Be sure to perform the inspection when the engine coolant temperature is between 75 and 90°C (167 and 194°F).
Using a 3-way connector, connect SST (turbocharger pressure gauge) between the manifold absolute pressure sensor and the gas filter.
- SST
- 09992-00242
Text in Illustration *1 Gas Filter *2 3-Way Connector Fully apply the parking brake and chock the 4 wheels.
While depressing the clutch pedal, fully depress the accelerator pedal. Measure the boost pressure at maximum engine speed (approximately 4600 rpm).
- Standard pressure (Gauge pressure):
- 10 to 40 kPa (0.10 to 0.41 kgf/cm2, 1.5 to 5.8 psi)
- The intake system or exhaust system has leakage or blockage.
- The turbocharger sub-assembly or turbo motor driver is malfunctioning.
- The EGR valve does not close.
- The diesel throttle body does not open.
- The vacuum hose connected to the diesel turbo pressure sensor (manifold absolute pressure sensor) is cracked or disconnected.
- The mass air flow meter is malfunctioning.
- A fuel injector is malfunctioning.
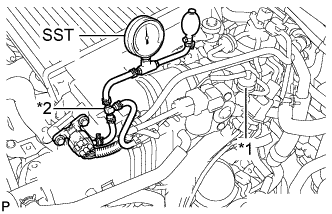
Chart showing the suspected trouble areas when the pressure is lower than the standard.
- HINT:
- ○: If a problem listed in the leftmost column of the chart exists, or if the part in the leftmost column of the chart has a malfunction, the value of the Data List item in the uppermost row of the chart will meet the conditions shown in the row labeled "Value which represents a malfunction".
- The values in the chart are applicable when the engine coolant temperature is between 75 and 90°C (167 and 194°F).
- The values in the chart are valid in an area with an absolute atmospheric pressure higher than 95 kPa. (Standard atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa. Atmospheric pressure decreases by 1 kPa for every 100 m increase in altitude, and is also affected by the current weather conditions.)
- When the altitude increases, atmospheric pressure and MAP decrease.
Item MAP
(Absolute pressure inside intake manifold)MAF
(Intake air flow rate)Accel Position Actual Throttle Position Actual EGR Valve Pos. EGR Close Lrn. Status
(EGR valve fully closed position learning status)Fuel Pressure Injection Feedback Val #1 (to #4) Values taken from an actual normal vehicle
*1- 90 g/sec. 99% or more 0% 0% OK - -3 to +3 mm3/st Values which represent a malfunction
*1MAP is below Target Booster Pressure by 30 kPa or more MAF is less than 81 g/sec. Accel Position is not fully depressed position
*2Actual Throttle Position is not fully open position Actual EGR Valve Pos. is not valve fully closed position
*3NG
(Determined after performing learning)Fuel Pressure is below Target Common Rail Pressure by 10 MPa or more (Check while condition steady) Outside of above range Turbocharger ○ ○ - - - - - - EGR valve does not close or has problem with movement ○ ○ - - ○
(Problem with EGR valve movement)
*4○
(EGR valve does not close)
*4- - Problem with diesel throttle movement ○
(Intake airflow decreases)○ - ○ - - - - Accelerator pedal cannot be fully depressed or problem with accelerator pedal position sensor exists - ○ ○ - - - - - Intake air system leakage or blockage ○ ○ - - - - - - Exhaust gas leakage before turbocharger or blockage ○ ○ - - - - - - Manifold absolute pressure sensor ○ ○ - - - - - - Manifold absolute pressure sensor hose is disconnected ○ ○ - - - - - - Mass air flow meter sub-assembly - ○ - - - - - - Fuel system (injector, supply pump or common rail) ○ ○ - - - - ○
(Fuel injector leakage, decrease in pressure discharge valve relief pressure or valve is stuck)○
*5- HINT:
- *1: These values are measured when the transmission is in 2nd gear, the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the vehicle is accelerating, and the engine speed is 3000 rpm.
- *2: The Accel Position is the accelerator opening angle (%) for engine control use. The value indicates around 100% when the accelerator pedal fully depressed. If the value does not indicate around 100% when the accelerator pedal fully depressed, the accelerator pedal position sensor circuit or the pedal itself is malfunctioning. When the MIL is illuminated, even with the accelerator pedal fully depressed and an Accel Position of below 70%, it means the fail-safe is restricting the accelerator.
- *3: Check that the Actual EGR Valve Pos. is always following the Target EGR Position value (e.g. the Actual EGR Valve Pos. is around fully closed position when the Target EGR Position value indicates 0%). The EGR valve may be malfunctioning if the value is stuck or does not fluctuate smoothly. However, in some cases the EGR valve may be malfunctioning even if the Actual EGR Valve Pos. and EGR Lift Sensor Volt % values are normal. Inspect the EGR valve for any defects (deposits, valve stuck, poor movement, etc.) if necessary.
- *4: DTC P0400 may be stored at this time. If the actual EGR valve position follows the target EGR valve position slowly, a feeling of hesitation may occur.
- *5: If Injection Feedback Val # of a cylinder is not within -3 to +3 mm3/st, the corresponding cylinder may have a malfunction (injector or compression). However, in some cases the cylinder may be malfunctioning even if the value is within -3 to +3 mm3/st because these values are injection volume correction values calculated by the ECM at the engine idling and not correction values for the high engine load condition related to the boost pressure control and engine output performance.
| 4. INSPECT MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR |
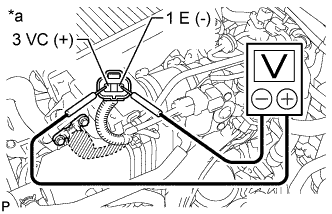
Inspect the power source voltage.
Disconnect the manifold absolute pressure sensor connector.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
Tester Connection Switch Condition Specified Condition 3 VC(+) - 1 E(-) Ignition switch ON 4.75 to 5.25 V
If the result is not as specified, inspect the wire harness or ECM (Toyota Fortuner RM0000013FU047X.html).Text in Illustration *a Front view of wire harness connector
(to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor)Connect the manifold absolute pressure sensor connector.
Check the power supply.
Text in Illustration *a Component harness connected
(ECM)Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Disconnect the vacuum hose from the manifold absolute pressure sensor.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition E6-28 (PIM +) - E7-28 (E2 -) 13.3 kPa (100 mmHg, 3.94 in.Hg) 0.0 to 0.3 V 26.6 kPa (199 mmHg, 7.85 in.Hg) 0.1 to 0.4 V 40 kPa (300 mmHg, 11.81 in.Hg) 0.3 to 0.6 V
Text in Illustration *1 Vacuum Pump 
Vacuum - HINT:
- The values in the "Condition" column are gauge pressures.
Using SST, measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- SST
- 09992-00242
- Standard Voltage:
Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition E6-28 (PIM +) - E7-28 (E2 -) 19.6 kPa (0.20 kgf/cm2, 2.84 psi) 0.05 to 0.3 V 39.2 kPa (0.40 kgf/cm2, 5.68 psi) 0.25 to 0.55 V 58.8 kPa (0.60 kgf/cm2, 8.53 psi) 0.45 to 0.75 V 78.5 kPa (0.80 kgf/cm2, 11.4 psi) 0.65 to 0.95 V 98.0 kPa (1.00 kgf/cm2, 14.2 psi) 0.9 to 1.2 V
Text in Illustration 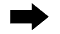
Pressure - HINT:
- The values in the "Condition" column are gauge pressures.

 |
| 5. CHECK MOTOR FOR TURBOCHARGER CONTROL OPERATION |
- CAUTION:
- Wear protective gloves to prevent injuries and burns when checking the turbocharger.
- The engine compartment becomes hot when the engine is running.
Remove the No. 1 exhaust manifold heat insulator (Toyota Fortuner RM00000143U00UX_01_0012.html) and No. 1 turbo insulator (Toyota Fortuner RM00000143U00UX_01_0011.html).
Check the stroke.
- NOTICE:
- Make sure the connectors of the DC motor are properly installed.
Turn the ignition switch from ON to off.
Check the operation of the DC motor. Check that the motor rod stroke is as shown in A to D in the illustration below.
After the DC motor operates, visually check that the vane activation link contacts the fully closed stopper.
- NOTICE:
- Never loosen or tighten the lock nut of the fully closed stopper.

If the result is not as specified, check the ECM(Toyota Fortuner RM0000013FU047X.html) and turbo motor driver (Toyota Fortuner RM000002PPM01VX.html).Text in Illustration *1 Motor Rod *2 Lock Nut *3 Fully Closed Stopper *4 Ignition Switch *a Motor Rod Stroke *b Fully Closed Stopper Contact *c Ignition Switch OFF Time - -
| 6. CHECK TURBO MOTOR DRIVER |
Check the voltage of the turbo motor driver.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
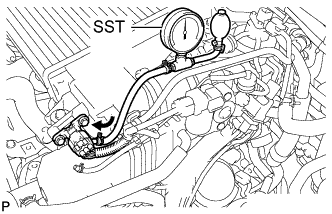
Tester Connection Specified Condition T34-3 (+B) - Body ground 9 to 14 V
If the result is not as specified, refer to the following procedures (Toyota Fortuner RM000002PPN02LX.html).Text in Illustration *a Component with harness connected
(Turbo Motor Driver)
 |
Check the resistance of the wire harness side connector.
Turn the ignition switch off.
Disconnect the turbo motor driver connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
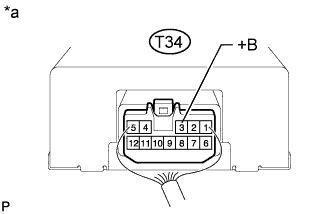
Tester Connection Specified Condition T34-4 (GND) - Body ground Below 1 Ω
If the result is not as specified, refer to the following procedures (Toyota Fortuner RM000002PPN02LX.html).Text in Illustration *a Front view of wire harness connector
(to Turbo Motor Driver)
 |
Connect the turbo motor driver connector.
Check the turbo motor signal.
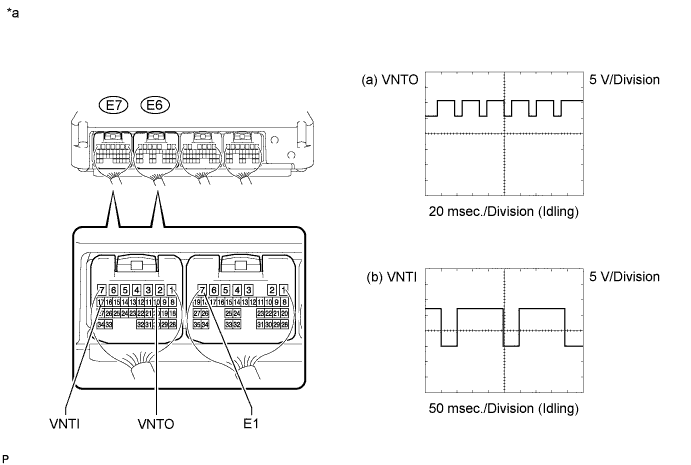
Text in Illustration *a Component with harness connected
(ECM)- - - OK:
Tester Connection Tool Setting Condition Specified Condition (a) Between E7-10 (VNTO) and E6-7 (E1)
(b) Between E7-17 (VNTI) and E6-7 (E1)(a) 5 V/Division, 20 msec./Division
(b) 5 V/Division, 50 msec./DivisionIdling with warm engine Refer to illustration
Connect an oscilloscope to the terminals of the ECM.
While idling the engine, check the waveform of the ECM.
- HINT:
- The waveform varies depending on the turbocharger operation.