Engine Unit -- Inspection |
| 1. INSPECT CAMSHAFT (for Bank 1) |
Inspect the camshaft for runout.
Place the camshaft on V-blocks.
Using a dial indicator, measure the circle runout at the center journal.
- Maximum circle runout:
- 0.06 mm (0.0024 in.)
 |
Inspect the cam lobes.
Using a micrometer, measure the cam lobe height.
- Standard cam lobe height:
Camshaft Specified Condition Intake 44.168 to 44.268 mm (1.7389 to 1.7428 in.) Exhaust 44.580 to 44.680 mm (1.7551 to 1.7591 in.)
- Minimum cam lobe height:
Camshaft Specified Condition Intake 44.018 mm (1.7330 in.) Exhaust 44.430 mm (1.7492 in.)
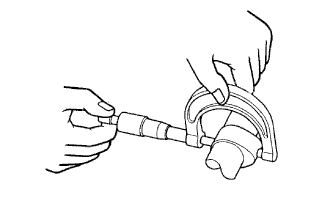 |
Inspect the camshaft journals.
Using a micrometer, measure the journal diameter.
- Standard journal diameter:
Journal Specified Condition No. 1 journal 35.971 to 35.985 mm (1.4162 to 1.4167 in.) Other journal 22.959 to 22.975 mm (0.9039 to 0.9045 in.)
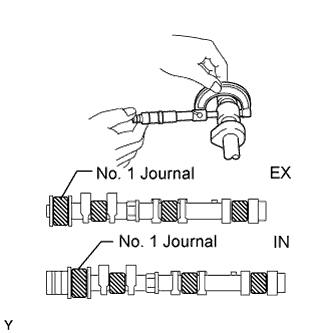 |
| 2. INSPECT CAMSHAFT TIMING GEAR (for Bank 1) |
Fix the intake camshaft with a vise.
- NOTICE:
- Be careful not to damage the camshaft.
Align the knock pin hole in the camshaft timing gear with the knock pin of the camshaft, and install the camshaft timing gear with the bolt.
- Torque:
- 100 N*m{1,020 kgf*cm, 74 ft.*lbf}
 |
Confirm that the camshaft timing gear is locked.
Release the lock pin.
Cover the 4 oil paths of the cam journal with vinyl tape as shown in the illustration.
- HINT:
- The 4 oil paths are in the groove of the camshaft. Plug 2 of the paths with rubber pieces.
Break through the tape of the advance side path and the retard side path on the opposite side of the groove.
Using air guns, apply air pressure of approximately 200 kPa (2.0 kgf/cm2, 28 psi) into the 2 broken paths (advance side path and retard side path).
- NOTICE:
- Cover the paths with cloth or equivalent to avoid oil splashing.
Confirm if the camshaft timing gear rotates in the timing advance direction when weakening the air pressure of the timing retard path.
- HINT:
- When the lock pin is released, the camshaft timing gear rotates in the advance direction.
When the camshaft timing gear comes to the most advanced position, remove the air gun from the retard side path, and then remove the air gun from the advance side path.
- NOTICE:
- The camshaft timing gear occasionally shifts to the retard side abruptly if the air compression of the advance side path is released before retard side path. If this abrupt shift occurs, the lock pin will break.
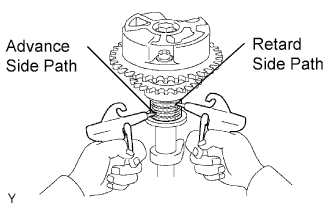
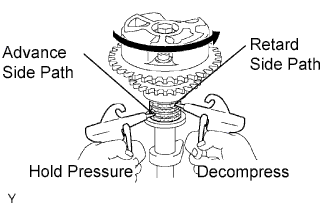
 |
Check the smooth revolution.
Except the position where the lock pin meets at the most retarded angle, let the camshaft timing gear turn back and forth. Check the movable range and that there is no disturbance.
- Standard:
- Movable range is about 31°.
- NOTICE:
- Be sure to perform this check by hand, instead of air pressure.
Check the lock in the most retarded position.
Confirm that the camshaft timing gear is locked at the most retarded position.
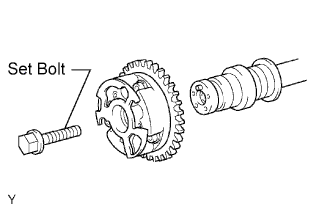
Remove the set bolt and camshaft timing gear.
- NOTICE:
- Be sure not to remove the other 3 bolts.
 |
| 3. INSPECT CAMSHAFT (for Bank 2) |
Inspect the camshaft for runout.
Place the camshaft on V-blocks.
Using a dial indicator, measure the circle runout at the center journal.
- Maximum circle runout:
- 0.06 mm (0.0024 in.)
 |
Inspect the cam lobes.
Using a micrometer, measure the cam lobe height.
- Standard cam lobe height:
Camshaft Specified Condition Intake 44.168 to 44.268 mm (1.7389 to 1.7428 in.) Exhaust 44.580 to 44.680 mm (1.7551 to 1.7591 in.)
- Minimum cam lobe height:
Camshaft Specified Condition Intake 44.018 mm (1.7330 in.) Exhaust 44.430 mm (1.7492 in.)
 |
Inspect the camshaft journals.
Using a micrometer, measure the journal diameter.
- Standard journal diameter:
Journal Specified Condition No. 1 journal 35.971 to 35.985 mm (1.4162 to 1.4167 in.) Other journal 22.959 to 22.975 mm (0.9039 to 0.9045 in.)
 |
| 4. INSPECT CAMSHAFT TIMING GEAR (for Bank 2) |
Fix the intake camshaft with a vise.
- NOTICE:
- Be careful not to damage the camshaft.
Align the knock pin hole in the camshaft timing gear with the knock pin of the camshaft, and install the camshaft timing gear with the bolt.
- Torque:
- 100 N*m{1,020 kgf*cm, 74 ft.*lbf}
 |
Confirm that the camshaft timing gear is locked.
Release the lock pin.
Cover the 4 oil paths of the cam journal with vinyl tape as shown in the illustration.
- HINT:
- The 4 oil paths are in the groove of the camshaft. Plug 2 of the paths with rubber pieces.
Break through the tape of the advance side path and the retard side path on the opposite side of the groove.
Using air guns, apply air pressure of approximately 200 kPa (2.0 kgf/cm2, 28 psi) into the 2 broken paths (advance side path and retard side path).
- NOTICE:
- Cover the paths with cloth or equivalent to avoid oil splashing.
Confirm if the camshaft timing gear rotates in the timing advance direction when weakening the air pressure of the timing retard path.
- HINT:
- When the lock pin is released, the camshaft timing gear rotates in the advance direction.
When the camshaft timing gear comes to the most advanced position, remove the air gun from the retard side path, and then remove the air gun from the advance side path.
- NOTICE:
- The camshaft timing gear occasionally shifts to the retard side abruptly if the air compression of the advance side path is released before retard side path. If this abrupt shift occurs, the lock pin will break.


 |
Check the smooth revolution.
Except the position where the lock pin meets at the most retarded angle, let the camshaft timing gear turn back and forth. Check the movable range and that there is no disturbance.
- Standard:
- Movable range is about 31° and gear moves smoothly.
- NOTICE:
- Be sure to perform this check by hand, instead of air pressure.
Check the lock in the most retarded position.
Confirm that the camshaft timing gear is locked at the most retarded position.
Remove the set bolt and camshaft timing gear.
- NOTICE:
- Be sure not to remove the other 3 bolts.
 |
| 5. INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD SET BOLT |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the thread outside diameter of the bolt.
- Standard outside diameter:
- 10.85 to 11.00 mm (0.4272 to 0.4331 in.)
- Minimum outside diameter:
- 10.7 mm (0.421 in.)
 |
| 6. INSPECT CHAIN |
Using a spring scale, pull the chain with a force of 147 N (15.0 kgf, 33.1 lbf). Using a vernier caliper, measure the length of 15 links of the chain.
- Maximum chain elongation:
- 146.8 mm (5.780 in.)
- NOTICE:
- Make the same measurements pulling at 3 or more places selected at random, and average the length.
 |
| 7. INSPECT NO. 2 CHAIN |
Using a spring scale, pull the chain with a force of 147 N (15.0 kgf, 33.1 lbf). Using a vernier caliper, measure the length of 15 links of the chain.
- Maximum chain elongation:
- 146.8 mm (5.780 in.)
- NOTICE:
- Make the same measurements pulling at 3 or more places selected at random, and average the length.
 |
| 8. INSPECT CAMSHAFT TIMING GEAR ASSEMBLY |
Wrap the No. 1 chain around the larger gear of the camshaft timing gear.
 |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the timing gear with the chain.
- Minimum gear diameter with chain:
- 115.5 mm (4.547 in.)
- NOTICE:
- The vernier caliper must contact the chain rollers for the measurement.
Wrap the No. 2 chain around the smaller gear of the camshaft timing gear.
 |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the timing gear with the chain.
- Minimum gear diameter with chain:
- 73.1 mm (2.878 in.)
- NOTICE:
- The vernier caliper must contact the chain rollers for the measurement.
| 9. INSPECT CAMSHAFT TIMING SPROCKET |
Wrap the No. 2 chain around the camshaft timing gear.
 |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the camshaft timing gear diameter with the chain.
- Minimum gear diameter with chain:
- 73.1 mm (2.878 in.)
- NOTICE:
- The vernier caliper must contact the chain rollers for the measurement.
| 10. INSPECT CRANKSHAFT TIMING SPROCKET |
Wrap the No. 1 chain around the crankshaft timing gear.
 |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the crankshaft timing gear diameter with the chain.
- Minimum gear diameter with chain:
- 61.0 mm (2.402 in.)
- NOTICE:
- The vernier caliper must contact the chain rollers for the measurement.
| 11. INSPECT NO. 1 IDLE GEAR |
Wrap the No. 1 chain around the idle gear.
 |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the idle gear with the chain.
- Minimum gear diameter with chain:
- 61.0 mm (2.402 in.)
- NOTICE:
- The vernier caliper must contact the chain rollers for the measurement.
| 12. INSPECT IDLE GEAR SHAFT OIL CLEARANCE |
Using a micrometer, measure the idle gear shaft diameter.
- Idle gear shaft diameter:
- 22.987 to 23.000 mm (0.9050 to 0.9055 in.)
 |
Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter of the idle gear.
- Standard idle gear inside diameter:
- 23.02 to 23.03 mm (0.9063 to 0.9067 in.)
 |
Subtract the idle gear shaft diameter measurement from the idle gear inside diameter measurement.
- Standard oil clearance:
- 0.020 to 0.043 mm (0.0008 to 0.0017 in.)
- Maximum oil clearance:
- 0.093 mm (0.0037 in.)
| 13. INSPECT NO. 1 CHAIN TENSIONER |
Check that the plunger moves smoothly when the ratchet pawl is raised with your finger.
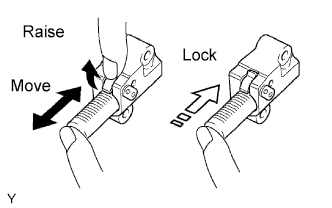 |
Release the ratchet pawl and check that the plunger is locked in place by the ratchet pawl and does not move when pushed with your finger.
| 14. INSPECT NO. 2 CHAIN TENSIONER |
Check that the plunger moves smoothly.
 |
Measure the worn depth of the chain tensioner.
- Maximum depth:
- 1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
| 15. INSPECT NO. 3 CHAIN TENSIONER |
Check that the plunger moves smoothly.
 |
Measure the worn depth of the chain tensioner.
- Maximum depth:
- 1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
| 16. INSPECT CHAIN TENSIONER SLIPPER |
Measure the worn depth of the chain tensioner slipper.
- Maximum depth:
- 1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
 |
| 17. INSPECT NO. 1 CHAIN VIBRATION DAMPER |
Measure the worn depth of the No. 1 chain vibration damper.
- Maximum depth:
- 1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
 |
| 18. INSPECT NO. 2 CHAIN VIBRATION DAMPER |
Measure the worn depth of the No. 2 chain vibration damper.
- Maximum depth:
- 1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
 |
| 19. CLEAN CYLINDER HEAD |
Using a gasket scraper, remove all the gasket material from the cylinder block contact surface.
- NOTICE:
- Be careful not to scratch the cylinder block contact surface.
 |
Using a wire brush, remove all the carbon from the combustion chambers.
- NOTICE:
- Be careful not to scratch the combustion chambers.
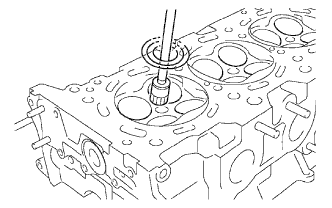 |
Using a valve guide bushing brush and solvent, clean all the valve guide bushes.
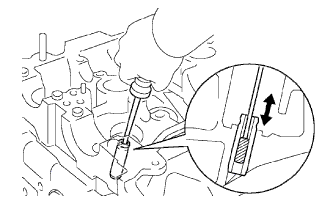 |
Using a soft brush and solvent, thoroughly clean the cylinder head.
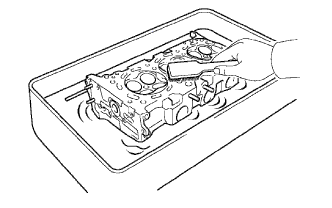 |
| 20. INSPECT CYLINDER HEAD |
Inspect the flatness.
Using a precision straightedge and feeler gauge, measure the warpage of the contact surfaces of the cylinder block and manifolds.
- Maximum warpage:
- 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
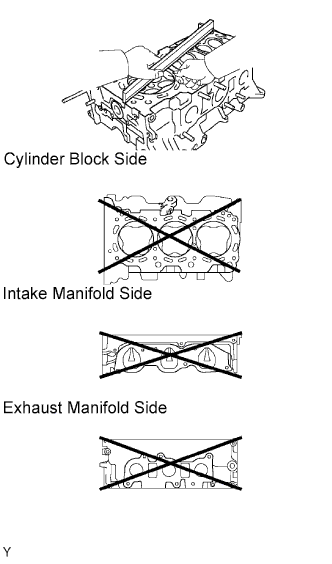 |
Inspect for cracks.
Using a dye penetrant, check the combustion chamber, intake ports, exhaust ports and cylinder block surface for cracks.
If cracked, replace the cylinder head.
 |
| 21. CLEAN VALVE |
Using a gasket scraper, chip off any carbon from the valve head.
 |
Using a wire brush, thoroughly clean the valve.
| 22. INSPECT VALVE |
Inspect the valve stem diameter.
Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of the valve stem.
- Standard valve stem diameter:
Item Specified Condition Intake 5.470 to 5.485 mm (0.2154 to 0.2159 in.) Exhaust 5.465 to 5.480 mm (0.2152 to 0.2158 in.)
 |
Inspect the valve face angle.
Grind the valve enough to remove pits and carbon.
Check that the valve is ground to the correct valve face angle.
- Standard valve face angle:
- 44.5°
 |
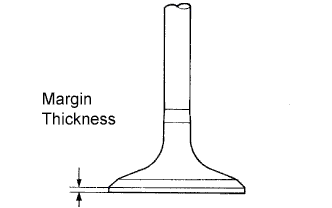
Inspect the valve head margin thickness.
Using a vernier caliper, check the valve head margin thickness.
- Standard margin thickness:
- 1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
- Minimum margin thickness:
- 0.5 mm (0.020 in.)
 |
Inspect the overall length.
Using a vernier caliper, check the overall length.
- Standard overall length:
Item Specified Condition Intake 106.95 mm (4.2106 in.) Exhaust 105.80 mm (4.1654 in.)
- Minimum overall length:
Item Specified Condition Intake 106.40 mm (4.1890 in.) Exhaust 105.30 mm (4.1457 in.)
 |
Inspect the valve stem tip.
Check the surface of the valve stem tip for wear.
If the valve stem tip is worn, resurface the tip with a grinder or replace the valve.- NOTICE:
- Do not grind off more than the minimum length.
 |
| 23. CLEAN VALVE SEAT |
Using a 45° carbide cutter, resurface the valve seats.
 |
Remove only enough metal to clean the valve seats.
| 24. INSPECT VALVE SEAT |
Apply a light coat of Prussian blue (or white lead) to the valve face.
 |
Lightly press the valve against the valve seat.
- NOTICE:
- Do not rotate the valve.
Check the valve face and seat according to the following procedure.
If blue appears 360° around the face, the valve is concentric.
If not, replace the valve.If blue appears 360° around the valve seat, the guide and face are concentric.
If not, resurface the valve seat.Check that the seat contact is in the middle of the valve face with the width below.
- Standard width:
- 1.0 to 1.4 mm (0.039 to 0.055 in.)
| 25. INSPECT COMPRESSION SPRING |
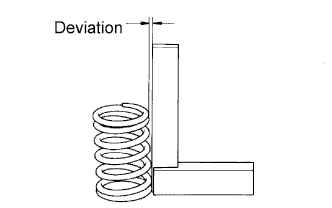
Inspect for deviation.
Using a steel square, measure the deviation of the inner compression spring.
- Maximum deviation:
- 2.0 mm (0.079 in.)
 |
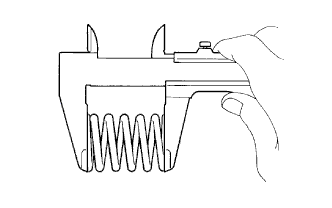
Inspect the free length.
Using a vernier caliper, measure the free length of the inner compression spring.
- Standard free length:
- 47.80 mm (1.8819 in.)
 |
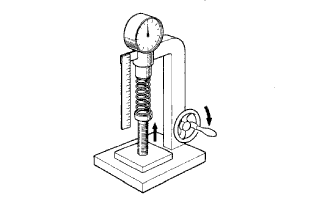
Inspect the tension.
Using a spring tester, measure the tension of the inner compression spring at the specified installed length.
- Standard installed tension:
- 186.2 to 205.8 N (19.0 to 21.0 kgf, 41.9 to 46.3 lbf) at 33.3 mm (1.311 in.)
 |
| 26. INSPECT VALVE GUIDE BUSH OIL CLEARANCE |
Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter of the valve guide bush.
- Standard inside diameter:
- 5.51 to 5.53 mm (0.2169 to 0.2177 in.)
 |
Subtract the valve stem diameter measurement (see "INSPECT VALVE: Inspect valve stem diameter" procedures above) from the valve guide bush inside diameter measurement.
- Standard oil clearance:
Item Specified Condition Intake 0.025 to 0.060 mm (0.0010 to 0.0024 in.) Exhaust 0.030 to 0.065 mm (0.0012 to 0.0026 in.)
- Maximum oil clearance:
Item Specified Condition Intake 0.08 mm (0.0031 in.) Exhaust 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
| 27. INSPECT VALVE LIFTER |
Using a micrometer, measure the valve lifter diameter.
- Standard valve lifter diameter:
- 30.966 to 30.976 mm (1.2191 to 1.2195 in.)
 |
| 28. INSPECT VALVE LIFTER OIL CLEARANCE |
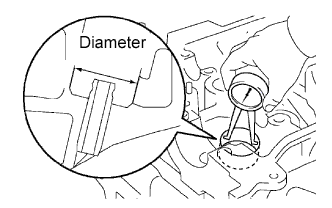
Using a caliper gauge, measure the lifter bore diameter of the cylinder head.
- Standard lifter bore diameter:
- 31.009 to 31.025 mm (1.2208 to 1.2215 in.)
 |
Subtract the valve lifter diameter measurement (see "INSPECT VALVE LIFTER" procedures above) from the lifter bore diameter measurement.
- Standard oil clearance:
- 0.033 to 0.059 mm (0.0013 to 0.0023 in.)
- Maximum oil clearance:
- 0.08 mm (0.0031 in.)
If necessary, replace the cylinder head.
| 29. INSPECT CAMSHAFT OIL CLEARANCE |
Clean the camshaft bearing caps, camshaft bearings and camshaft journals.
 |
Install the camshaft bearing.
Place the camshaft on the cylinder head.
Lay a strip of Plastigage across each of the camshaft journals.
Install the camshaft bearing caps (Toyota Fortuner RM000000YMM003X_01_0033.html).
- NOTICE:
- Do not turn the camshafts.
Remove the camshaft bearing caps.
Measure the Plastigage at its widest point.
- Standard oil clearance:
- Cylinder head for bank 1:
Item Specified Condition No. 1
(Intake)0.008 to 0.038 mm (0.0003 to 0.0015 in.) No. 1
(Exhaust)0.040 to 0.079 mm (0.0016 to 0.0031 in.) Others 0.025 to 0.062 mm (0.0010 to 0.0024 in.)
- Cylinder head for bank 2:
Item Specified Condition No. 1 0.040 to 0.079 mm (0.0016 to 0.0031 in.) Others 0.025 to 0.062 mm (0.0010 to 0.0024 in.)
- Cylinder head for bank 1:
Item Specified Condition No. 1 0.07 mm (0.0028 in.) Others 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
- cylinder head for Bank 2:
- 0.10 mm (0.0039 in.)
If necessary, replace the camshaft bearing caps and cylinder head as a set.- Reference:
Item Specified Condition Cylinder head journal bore diameter 40.009 to 40.017 mm (1.5752 to 1.5755 in.) Camshaft bearing center wall thickness (Mark "2") 2.004 to 2.008 mm (0.0789 to 0.0791 in.) Camshaft journal diameter 35.971 to 35.985 mm (1.4165 to 1.4167 in.)
 |
Remove the Plastigage completely.
Remove the camshafts.
Remove the camshaft bearing.
| 30. INSPECT CYLINDER BLOCK FOR FLATNESS |
Using a precision straightedge and feeler gauge, measure the surface contacting the cylinder head gasket for warpage.
- Maximum warpage:
- 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.)
 |
| 31. INSPECT CYLINDER BORE |
Using a cylinder gauge, measure the cylinder bore diameter at positions A and B in the thrust and axial directions.
- Standard diameter:
- 94.000 to 94.012 mm (3.7008 to 3.7013 in.)
- Maximum diameter:
- 94.132 mm (3.7060 in.)
 |
| 32. INSPECT PISTON |
Using a micrometer, measure the piston diameter at right angles to the piston pin center line, 27.7 mm (1.091 in.) from the piston head.
- Standard piston diameter:
- 93.910 to 93.920 mm (3.6972 to 3.6976 in.)
 |
| 33. INSPECT PISTON OIL CLEARANCE |
Subtract the piston diameter measurement from the cylinder bore diameter measurement.
- Standard oil clearance:
- 0.080 to 0.102 mm (0.0031 to 0.0040 in.)
- Maximum oil clearance:
- 0.13 mm (0.0051 in.)
| 34. INSPECT CONNECTING ROD |
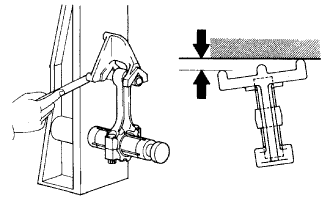
Using a rod aligner and feeler gauge, check the connecting rod alignment.
Check for out-of-alignment.
- Maximum out-of-alignment:
- 0.05 mm (0.0020 in.) per 100 mm (3.94 in.)
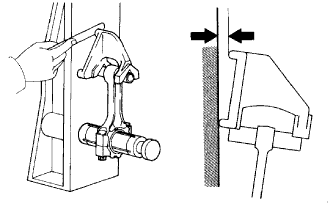
Check for twist.
- Maximum twist:
- 0.15 mm (0.0059 in.) per 100 mm (3.94 in.)
 |
| 35. INSPECT PISTON PIN OIL CLEARANCE |
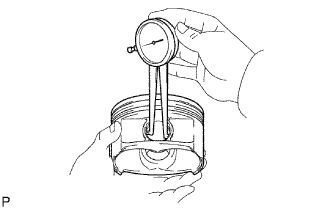
Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter of the piston pin hole.
- Standard piston pin hole inside diameter:
- 22.001 to 22.010 mm (0.8662 to 0.8665 in.)
- Standard piston pin hole inside diameter (Reference):
Mark Specified Condition A 22.001 to 22.004 mm (0.8662 to 0.8663 in.) B 22.005 to 22.007 mm (0.8663 to 0.8664 in.) C 22.008 to 22.010 mm (0.8665 to 0.8665 in.)
 |
Using a micrometer, measure the piston pin diameter.
- Standard piston pin diameter:
- 21.997 to 22.006 mm (0.8660 to 0.8664 in.)
- Standard piston pin diameter (Reference):
Mark Specified Condition A 21.997 to 22.000 mm (0.8660 to 0.8661 in.) B 22.001 to 22.003 mm (0.8661 to 0.8663 in.) C 22.004 to 22.006 mm (0.8663 to 0.8664 in.)
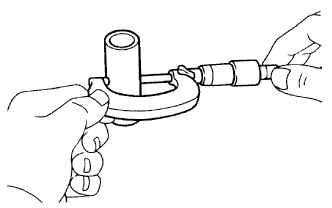 |
Using a caliper gauge, measure the inside diameter of the connecting rod bush.
- Standard bush inside diameter:
- 22.005 to 22.014 mm (0.8663 to 0.8667 in.)
- Standard bush inside diameter (Reference):
Mark Specified Condition A 22.005 to 22.008 mm (0.8663 to 0.8665 in.) B 22.009 to 22.011 mm (0.8665 to 0.8666 in.) C 22.012 to 22.014 mm (0.8666 to 0.8667 in.)
 |
Subtract the piston pin diameter measurement from the piston pin hole diameter measurement.
- Standard oil clearance:
- 0.001 to 0.007 mm (0.00004 to 0.00028 in.)
- Maximum oil clearance:
- 0.040 mm (0.0016 in.)
Subtract the piston pin diameter measurement from the bush inside diameter measurement.
- Standard oil clearance:
- 0.005 to 0.011 mm (0.0002 to 0.0004 in.)
- Maximum oil clearance:
- 0.050 mm (0.0020 in.)
 |
| 36. INSPECT PISTON RING GROOVE CLEARANCE |
Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between a new piston ring and the wall of the ring groove.
- Standard ring groove clearance:
Ring Groove Clearance No. 1 0.02 to 0.07 mm (0.0008 to 0.0028 in.) No. 2 0.02 to 0.06 mm (0.0008 to 0.0024 in.) Oil 0.07 to 0.15 mm (0.0028 to 0.0060 in.)
- If the clearance is not as specified, replace the piston.
 |
| 37. INSPECT PISTON RING END GAP |
Using a piston, push the piston ring a little beyond the bottom of the ring travel, 110 mm (4.33 in.) from the top of the cylinder block.
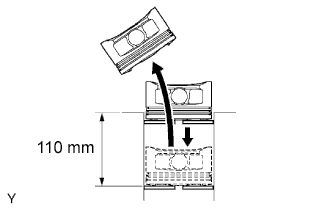 |
Using a feeler gauge, measure the end gap.
- Standard end gap:
Ring End Gap No. 1 0.22 to 0.32 mm (0.00866 to 0.0126 in.) No. 2 0.35 to 0.45 mm (0.0138 to 0.0177 in.) Oil (side rail) 0.10 to 0.40 mm (0.0039 to 0.0157 in.)
- Maximum end gap:
Ring End Gap No. 1 1.0 mm (0.039 in.) No. 2 1.1 mm (0.043 in.) Oil (side rail) 1.0 mm (0.039 in.)
- If the end gap is greater than the maximum, replace the piston ring. If the end gap is greater than the maximum, even with a new piston ring, replace the cylinder block.
 |
| 38. INSPECT CONNECTING ROD BOLT |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the tension portion diameter of the bolt.
- Standard diameter:
- 7.2 to 7.3 mm (0.283 to 0.287 in.)
- Minimum diameter:
- 7.0 mm (0.276 in.)
 |
| 39. INSPECT CRANKSHAFT BEARING CAP BOLT |
Using a vernier caliper, measure the tension portion diameter of the bolt.
- Standard diameter:
- 10.0 to 10.2 mm (0.393 to 0.402 in.)
 |
| 40. INSPECT CRANKSHAFT |
Using a dial indicator and V-blocks, measure the circle runout, as shown in the illustration.
- Maximum circle runout:
- 0.06 mm (0.0024 in.)
 |
Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of each main journal.
- Standard diameter:
- 71.988 to 72.000 mm (2.8342 to 2.8346 in.)
 |
Check each main journal for taper and out-of-round as shown.
- Maximum taper and out-of-round:
- 0.02 mm (0.0008 in.)
Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of each crank pin.
- Standard diameter:
- 55.992 to 56.000 mm (2.2044 to 2.2047 in.)
 |
Check each crank pin for taper and out-of-round as shown.
- Maximum taper and out-of-round:
- 0.02 mm (0.0008 in.)