READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACCELERATOR POSITION NO. 1, ACCELERATOR POSITION NO. 2)
CHECK WIRE HARNESS (ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK ECM (VCPA, VCP2 VOLTAGE)
REPLACE ACCELERATOR PEDAL ROD ASSEMBLY
CHECK IF DTC OUTPUT RECURS (ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR DTCS)
DTC P2120 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" Circuit |
DTC P2122 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" Circuit Low Input |
DTC P2123 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" Circuit High Input |
DTC P2125 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "E" Circuit |
DTC P2127 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "E" Circuit Low Input |
DTC P2128 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "E" Circuit High Input |
DTC P2138 Throttle / Pedal Position Sensor / Switch "D" / "E" Voltage Correlation |
DESCRIPTION
- HINT:
- The Electronic Throttle Control System (ETCS) does not use a throttle cable.
- These DTCs are related to the accelerator pedal position sensor. The troubleshooting procedures for the accelerator pedal position sensor are in the flowchart below.
- The ETCS does not use a throttle cable.
The Accelerator Pedal Position sensor is mounted on the accelerator pedal to detect the angle of the accelerator pedal. This sensor is electronically controlled and uses Hall-effect elements.
In the accelerator pedal position sensor, the voltage applied to the terminals VPA and VPA2 of the ECM changes between 0 and 5 V in proportion to the angle of the accelerator pedal. The VPA is a signal to indicate the actual accelerator pedal angle and is used for engine control. VPA2 is used to detect malfunctions of the sensor itself.
The ECM monitors the actual accelerator pedal angle from VPA and VPA2 signal outputs, and controls the throttle motor based on these signals.

| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P2120 | VPA quickly fluctuates up and down beyond upper and lower malfunction thresholds for 0.5 seconds |
|
| P2122 | Condition (a) continues for 0.5 seconds or more when accelerator pedal is fully released: (a) VPA is 0.2 V or less |
|
| P2123 | Condition (a) continues for 2.0 seconds or more: (a) VPA is 4.8 V or less |
|
| P2125 | Condition (a) continues for 0.5 seconds or more: (a) VPA2 quickly fluctuates up and down upper and lower malfunction thresholds |
|
| P2127 | Condition (a) continues for 0.5 seconds or more when accelerator pedal is fully released: (a) VPA2 is 0.5 V or less |
|
| P2128 | Conditions (a) and (b) continue for 2.0 seconds or more: (a) VPA2 is 4.8 V or more (b) VPA is 0.2 V or more and VPA is 3.45 V or less |
|
| P2138 | Condition (a) or (b) continues for 2.0 seconds or more: (a) Difference between VPA and VPA2 is 0.02 V or less (b) VPA is 0.2 V or less and VPA2 is 0.5 V or less |
|
- HINT:
- When DTC P2120, P2122, P2123, P2125, P2127, P2128 and/or P2138 is detected, check the output voltage of the accelerator pedal position sensor by entering the following menus on the intelligent tester: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Accelerator Position No. 1 and Accelerator Position No. 2.
| Suspected Area | Accelerator Position No. 1 When AP Released | Accelerator Position No. 2 When AP Released | Accelerator Position No. 1 When AP Depressed | Accelerator Position No. 2 When AP Depressed |
| VCP circuit open | 0 to 0.2 V | 0 to 0.2 V | 0 to 0.2 V | 0 to 0.2 V |
| Open or ground short in VPA circuit | 0 to 0.2 V | 1.2 to 2.0 V | 0 to 0.2 V | 3.4 to 5.0 V |
| Open or ground short in VPA2 circuit | 0.5 to 1.1 V | 0 to 0.2 V | 2.6 to 4.5 V | 0 to 0.2 V |
| EPA circuit open | 4.5 to 5.0 V | 4.5 to 5.0 V | 4.5 to 5.0 V | 4.5 to 5.0 V |
| Normal condition | 0.5 to 1.1 V | 1.2 to 2.0 V | 2.6 to 4.5 V | 3.4 to 5.0 V |
- HINT:
- The accelerator pedal position is expressed in terms of voltage.
- AP stands for Accelerator Pedal.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
When either output voltage of VPA or VPA2 deviates from the standard range, or the difference between the output voltage of the two sensors is less than the threshold, the ECM concludes that there is a defect in the accelerator pedal position sensor. The ECM illuminates the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) and sets a DTC.Example:
The output voltage of the VPA is below 0.2 V or exceeds 4.8 V.
This monitor runs for 2 seconds (the first 2 seconds of engine idle) after the engine is started (1 trip detection logic).
FAIL-SAFE
The accelerator pedal position sensor has a main circuit and associated circuit. When one circuit is malfunctioning, the accelerator pedal position is calculated by the output of the other circuit. When both of the circuits are malfunctioning, it is interpreted that the accelerator pedal is released. As a result, the throttle valve is closed and the engine idles.WIRING DIAGRAM
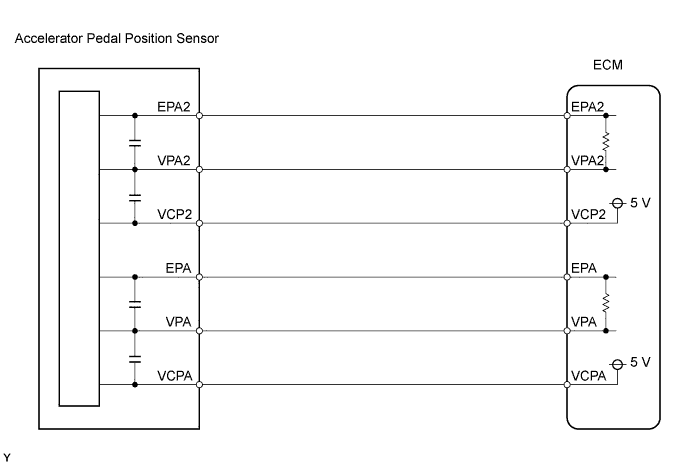
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
- These DTCs are related to the accelerator pedal position sensor.
| 1.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (ACCELERATOR POSITION NO. 1, ACCELERATOR POSITION NO. 2) |
 |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch ON and turn the tester ON.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Accelerator Position No. 1 and Accelerator Position No. 2.
Read the value.
- Standard voltage:
Accelerator Pedal No. 1 Accelerator Position No. 2 Accelerator Position Released 0.5 to 1.1 V 1.2 to 2.0 V Depressed 2.6 to 4.5 V 3.4 to 5.0 V
|
| ||||
| NG | |
| 2.CHECK WIRE HARNESS (ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
 |
Disconnect the A22 accelerator pedal position sensor connector.
Disconnect the E14 ECM connector.
Measure the resistance of the wire harness side connectors.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition A22-6 (VPA) - E14-18 (VPA) Below 1 Ω A22-5 (EPA) - E14-20 (EPA) Below 1 Ω A22-4 (VCPA) - E14-26 (VCPA) Below 1 Ω A22-3 (VPA2) - E14-19 (VPA2) Below 1 Ω A22-2 (EPA2) - E14-21 (EPA2) Below 1 Ω A22-1 (VCP2) - E14-27 (VCP2) Below 1 Ω A22-6 (VPA) or E14-18 (VPA) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A22-5 (EPA) or E14-20 (EPA) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A22-4 (VCPA) or E14-26 (VCPA) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A22-3 (VPA2) or E14-19 (VPA2) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A22-2 (EPA2) or E14-21 (EPA2) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A22-1 (VCP2) or E14-27 (VCP2) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 3.CHECK ECM (VCPA, VCP2 VOLTAGE) |
 |
Disconnect the A22 accelerator pedal position sensor connector.
Turn the ignition switch ON.
Measure the voltage of the E14 ECM connector.
- Standard voltage:
Tester Connection Specified Condition E14-26 (VCPA) - E14-20 (EPA) 4.5 to 5.5 V E14-27 (VCP2) - E14-21 (EPA2) 4.5 to 5.5 V
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.REPLACE ACCELERATOR PEDAL ROD ASSEMBLY |
| NEXT | |
| 5.CHECK IF DTC OUTPUT RECURS (ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR DTCS) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch ON and turn the tester ON.
Clear the DTCs (Toyota Fortuner RM0000010E700JX.html).
Start the engine.
Idle the engine for 15 seconds or more.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
- Result:
Display (DTC output) Proceed to P2120, P2122, P2123, P2125, P2127, P2128, and/or P2138 A No output B
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||