Turbocharger -- System Description |
This section should be used as a guide for troubleshooting when the turbocharger is suspected as the cause of a problem.
| OUTLINE OF TURBOCHARGER FAILURE |
State of Turbocharger Failure Repair:
It is well known that turbocharger malfunctions cause many symptoms as shown below. However, the mechanisms resulting in these symptoms that indicate turbocharger malfunctions are not well understood. As a result, many unnecessary turbocharger replacements and other repairs are being performed due to lack of knowledge about the turbocharger and turbocharger failure. Therefore, knowing the facts regarding turbocharger malfunctions is useful for making effective repairs and saving time.Turbocharger Failure Classification:
Symptom Symptom Description See page Noise Whistling noise Continuous high pitch noise proportional to engine speed - "NOISE" listed below
- Flowchart "Turbocharger Noise" (Toyota Fortuner RM00000416S019X.html)
Whining noise Relatively low pitch noise compared to whistling noise Oil leak External oil leak Oil leak on surface of turbocharger visible from outside of turbocharger - "OIL LEAK AND WHITE SMOKE" listed below
- Flowchart "Turbocharger Oil Leak and White Smoke" (Toyota Fortuner RM00000416R018X.html)
Internal oil leak Oil leak from inside of bearing housing to inside of either compressor housing or turbine housing through seal ring White smoke Oil smoke Oil smoke is emitted from exhaust pipe Unburned fuel smoke Unburned fuel smoke is emitted from exhaust pipe Black smoke Black smoke is emitted from exhaust pipe - "BLACK SMOKE" listed below
- Flowchart "Black Smoke Emitted" (Toyota Fortuner RM000000TIR07YX.html)
Lack of power or hesitation Vehicle does not reach target speed - "LACK OF POWER AND HESITATION" listed below
- Flowchart "Lack of Power or Hesitation" (Toyota Fortuner RM000000W0E00FX.html)
Poor acceleration Shock during acceleration MIL turns on
DTC (SAE/TCCS)P0045/34 Boost Control Solenoid Circuit / Open Diagnostic Trouble Code Chart (Toyota Fortuner RM0000012WD005X.html) P0234/34 Overboost Condition P0299/34 Underboost P1251/34 Step Motor for Turbocharger Control Circuit (Intermittent) - HINT:
- This table shows only typical problems related to the turbocharger.
- "NOISE" listed below
| NOISE |
| Probable Cause | Probable Failed Component |
| Turbine shaft imbalance | Turbocharger |
| Leakage from intake line | Intake line |
| Gear noise (Mistaken for turbocharger noise) |
|
- HINT:
- It is easy to confirm whether the turbocharger is the cause of the noise or not, and confirming this before inspecting the turbocharger or removing it from the engine is an effective way to reduce troubleshooting time.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- HINT:
- The software version installed on the intelligent tester must be V2009.2 or later.
Start the engine and warm it up.
Turn the tester ON.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Activate the VN Turbo Open.
Perform the Active Test and rev the engine up several times.
Check whether the noise is reduced or not compared with the noise under the condition that the Active Test is not performed.
Result Result Cause of Noise The noise is reduced (or disappears) Turbocharger The noise does not change Not turbocharger (other parts) - HINT:
- Refer to the flowchart "Turbocharger Noise" (Toyota Fortuner RM00000416S019X.html).
| OIL LEAK AND WHITE SMOKE |
| Oil Leak Type | Description | Main Trouble Area |
| Internal oil leak (White smoke) |
|
|
| External oil leak |
|
|
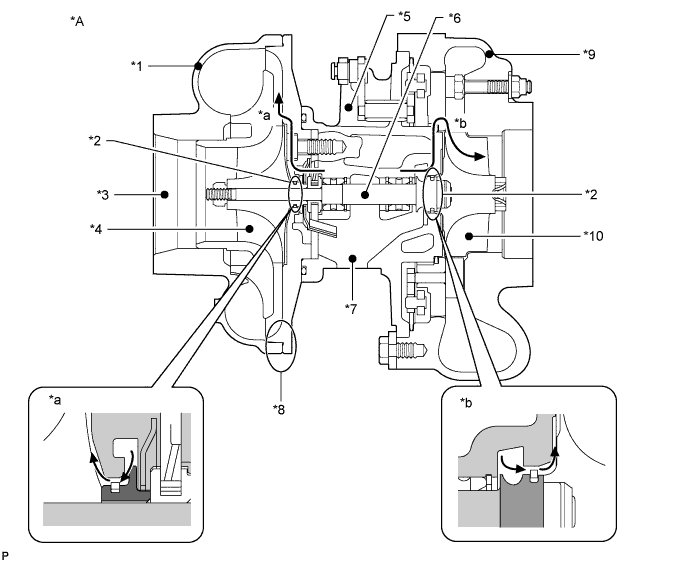
| *A | Variable Nozzle Type Turbocharger (motor controlled actuator) | - | - |
| *1 | Compressor Housing | *2 | Seal Ring |
| *3 | Compressor Inlet | *4 | Compressor Impeller |
| *5 | Bearing Housing | *6 | Turbine Shaft |
| *7 | Oil Drain (Outlet) | *8 | FIPG Sealing Part |
| *9 | Turbine Housing | *10 | Turbine Wheel |
| *a | Internal oil leak to compressor housing | *b | Internal oil leak to turbine housing |
- HINT:
- Above illustration is an example.
- When there is an internal oil leak, white smoke is emitted from the exhaust pipe and oil is consumed excessively. However, the cause of white smoke or excessive oil consumption can vary. Therefore, do not assume that the turbocharger is the cause of the failure when there is white smoke emission or excessive oil consumption.
- When there is an external oil leak, the sources of the oil leak are limited to the points mentioned in the table above. If oil leaks from a FIPG sealing part, replace the turbocharger. If oil leaks from an oil pipe flange or a hose connection, do not replace the turbocharger, but confirm and repair the flange or hose.
- Refer to the flowchart "Turbocharger Oil Leak and White Smoke" (Toyota Fortuner RM00000416R018X.html).
| BLACK SMOKE |
Malfunctions are classified into 2 types as shown below.
Description Malfunction Main Fault Intake air volume shortage Insufficient mass air flow due to, for example, excessively low boost pressure, which results in fuel injection volume being relatively excessive with respect to mass air flow. Excessive injection volume Excessive injection volume or incorrect injection timing due to fuel system trouble. Main Components Related to Black Smoke:
Possible Faulty Component Main Fault Turbocharger Abnormally low boost pressure Intake system Leakage between turbocharger and intake manifold Fuel system - Excessive fuel injection volume
- Incorrect fuel injection timing
EGR valve Stuck or does not close completely Diesel throttle Stuck or does not move smoothly - HINT:
- The components listed above are only the main ones. Not all the components potentially related to black smoke are listed. For details regarding the troubleshooting of black smoke, refer to the flowchart "Black Smoke Emitted" (Toyota Fortuner RM000000TIR07YX.html).
- Excessive fuel injection volume
Relation between Turbocharger and Black Smoke:
If the boost pressure is lower than normal due to a turbocharger failure, black smoke may occur due to a lack of mass air flow. However, abnormally low boost pressure can be caused by the failure of various components such as intake lines, the EGR valve, etc. Therefore, do not assume that the turbocharger is the cause of abnormally low boost pressure, but check all the components possibly related to abnormally low boost pressure. Components related to abnormal boost pressure are shown in a chart listed in the On-vehicle Inspection for Intake Air Control System (Toyota Fortuner RM0000014VF004X_01_0003.html). For simple and effective troubleshooting, refer to the chart before starting troubleshooting.
| LACK OF POWER AND HESITATION |
Malfunctions are classified into 2 types as shown below.
Description Malfunction Main Fault Intake air volume shortage Insufficient mass air flow due to, for example, excessively low boost pressure, which results in fuel injection volume being restricted. Abnormal injection volume Abnormal injection volume or timing due to fuel system trouble. Main Components Related to Lack of Power and Hesitation:
Possible Faulty Component Main Fault Turbocharger - Abnormal boost pressure
- VN does not move smoothly
Intake system - Leakage between turbocharger and intake manifold
- Clogging or blockage of intake line
Fuel system - Abnormal injection volume
- Incorrect fuel injection timing
EGR valve Stuck or does not close completely Diesel throttle Stuck or does not move smoothly Exhaust system Clogging of exhaust line - HINT:
- The components listed above are only the main ones. Not all the components potentially related to lack of power and hesitation are listed. For details regarding the troubleshooting of lack of power and hesitation, refer to the flowchart "Lack of Power and Hesitation" (Toyota Fortuner RM000000W0E00FX.html).
- If obvious malfunction (lack of power) has not been reproduced, perform test driving another vehicle, which is the same model and has the same engine, and compare the engine conditions and performance. If a great difference does not present in engine performance, explain to the customer that lack of power the customer mentioned is not abnormal.
- Abnormal boost pressure
Relation between Turbocharger and Abnormal Boost Pressure:
If the boost pressure is lower than normal due to a turbocharger failure, lack of power could occur due to an intake air volume shortage. However, abnormal boost pressure can be caused by the failure of various components such as intake lines, the EGR valve, etc. Therefore, do not assume that the turbocharger is the cause of abnormal boost pressure, but check all the components possibly related to abnormal boost pressure. Components related to abnormal boost pressure are shown in a chart listed in the On-vehicle Inspection for Intake Air Control System (Toyota Fortuner RM0000014VF004X_01_0003.html). For simple and effective troubleshooting, refer to the chart before starting troubleshooting.
| MIL TURNS ON |
| BRIEF OUTLINE OF TURBOCHARGER OPERATION AND CONSTRUCTION |
A turbocharger is a component used to supply a larger air volume to the cylinders by recovering exhaust gas energy using a turbine coaxially connected to a compressor.
Principle of Turbocharging:
Boost pressure is proportional to turbocharger speed, because the intake air is accelerated by centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the compressor and the increased kinetic energy, i.e. the velocity of the intake air, is converted to pressure energy by the diffuser located around the outlet of the compressor impeller. The compressor is driven by the turbine connected coaxially by the turbine shaft. The turbine is driven by exhaust gas energy. Therefore, when the turbocharger begins boosting the intake air, a larger air volume is supplied to the cylinders and more fuel can be injected. As a result, more exhaust energy will be available and the turbocharger boost increases.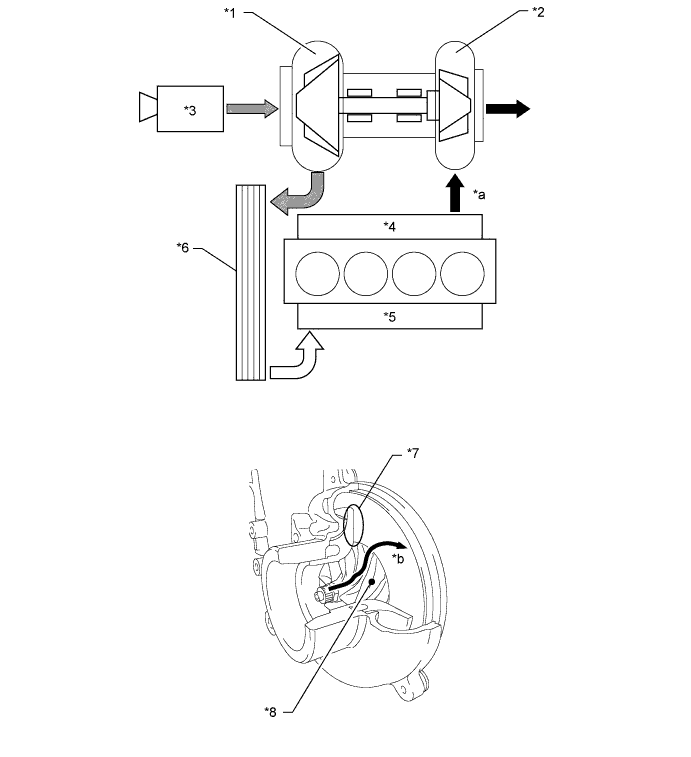
Text in Illustration *1 Compressor *2 Turbine *3 Air Cleaner *4 Exhaust Manifold *5 Intake Manifold *6 Intercooler *7 Diffuser *8 Compressor *a See HINT below *b Intake air flow - HINT:
- *a: If sufficient exhaust gas energy is not available, the turbocharger cannot generate the required boost pressure even when the turbocharger does not have a malfunction.
- Considering the fact that the turbocharger is driven by exhaust gas energy, if sufficient exhaust gas is not available due to abnormal injection volume, etc., the required boost pressure will not be available even when the turbocharger does not have a malfunction. Therefore, when boost pressure is abnormally low, checking all the related components using the correct troubleshooting procedure is necessary for simple and effective repair.
Boost Pressure Control:
The amount of energy the turbine can obtain from the exhaust gas is proportional to the expansion ratio, which is defined as the ratio of the turbine inlet exhaust gas pressure to the pressure at the turbine outlet.
To control boost pressure, a Variable Nozzle (VN) is used just upstream of the turbine wheel inlet, and controls the expansion ratio. If the VN is closed, the gap between neighboring vanes is narrowed and the turbine inlet exhaust gas pressure, and correspondingly the expansion ratio, increases. Therefore, when the VN is closed, the turbine receives more energy, and the turbine speed and boost pressure increase. On the other hand, if the VN is opened, the turbine inlet exhaust gas pressure decreases, and the turbine speed and boost pressure decrease. The VN is actuated by a DC motor. The ECM controls the VN opening angle through the turbo motor driver in accordance with the engine condition. When a high engine power is required, the actuation rod is moved by the actuator to close the VN and boost pressure increases.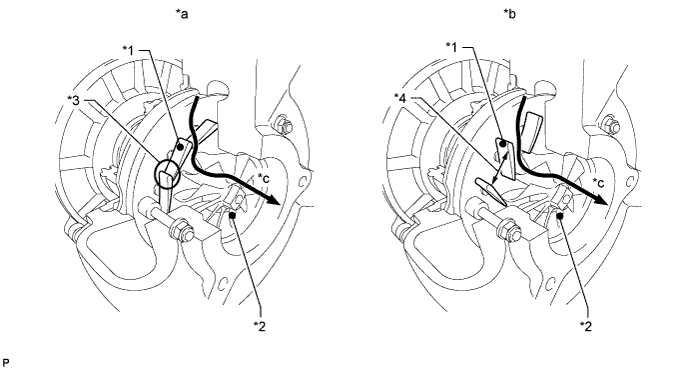
Text in Illustration *1 VN (Variable Nozzle) *2 Turbine Wheel *3 Narrow Gap *4 Wide Gap *a VN Closed *b VN Opened *c Exhaust Gas Flow - - - HINT:
- If the VN becomes stuck open, the necessary boost pressure will not be available. If the VN becomes stuck closed, overboost will occur.
Mechanical Construction of Turbocharger:
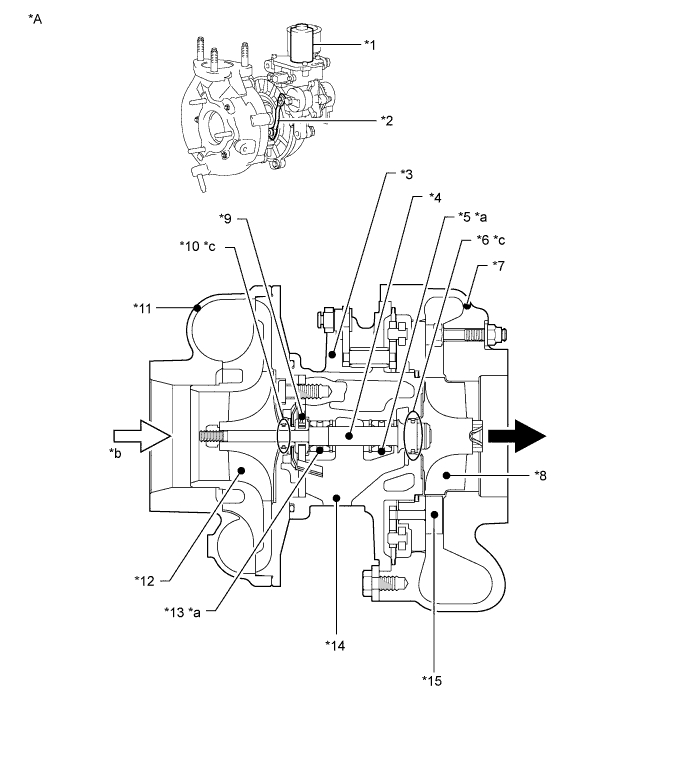
Text in Illustration 
Exhaust Gas Flow 
Intake Air Flow *A Variable Nozzle Type Turbocharger
(motor controlled actuator)- - *1 VN Actuator (DC Motor) *2 VN Actuating Rod *3 Bearing Housing *4 Turbine Shaft *5 Radial Bearing *6 Turbine Side Seal Ring *7 Turbine Housing *8 Turbine Wheel *9 Thrust Bearing *10 Compressor Side Seal Ring *11 Compressor Housing *12 Compressor Impeller *13 Radial Bearing *14 Oil Drain *15 VN (Variable Nozzle) - - *a See HINT below *b See HINT below *c See HINT below - - - HINT:
- Above illustration is an example.
- *a: The clearances of the radial bearing and thrust bearing are on the order of 100 μm, and for the accurate measurement of these clearances, an accurate process and accurate tools are essential.
- *b: A certain amount of oil mist from PCV gas is contained in the intake air. Therefore, a certain amount of oil at the inlet of the compressor is normal, and is not an oil leak.
- *c: The seal rings are C-shaped rings just like piston rings, and have a gap. Therefore, complete sealing is impossible by the seal rings alone. The oil is sealed in with the aid of the boost pressure in the compressor housing, and the exhaust gas pressure in the turbine housing. These pressures prevent oil from exiting the bearing housing through the gap of the seal rings. Therefore, if the turbine shaft is inclined from the horizontal, oil may flow out through the gap of a seal ring. This should not be interpreted as an oil leak due to seal ring failure.