DTC P1425 Differential Pressure Sensor Circuit
DTC P1427 Differential Pressure Sensor Circuit Low
DTC P1428 Differential Pressure Sensor Circuit High
Description
HINT:
- For more information on the differential pressure sensor and TOYOTA D-CAT*1, refer to the following procedures.
- If P1425, P1427 and/or P1428 is present, refer to the DTC chart for TOYOTA D-CAT.
*1: Diesel Clean Advanced Technology.
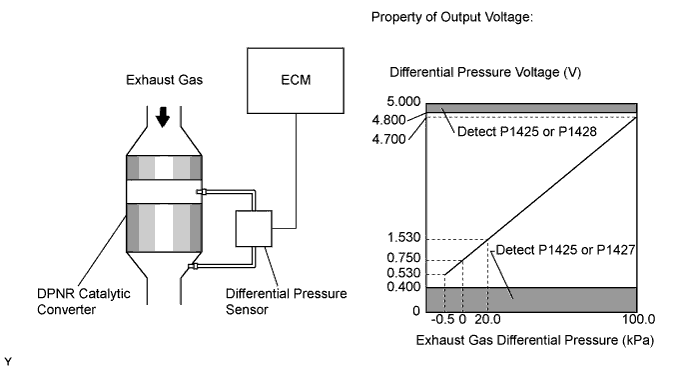
The two sensing chambers of the differential pressure sensor are mounted to monitor the pressure before and after the DPNR*2 catalytic converter. The sensor itself is not located on the engine assembly in order to reduce the influence of vibration. The sensor is a semiconductor-type that is not influenced by exhaust gases.
The ECM compares the exhaust gas pressure before and after DPNR catalytic converter by monitoring the pressure using the upstream and downstream sensing chambers of the differential pressure sensor. If the difference between the pressure before and after the catalytic converter exceeds a predetermined level, the ECM judges that the catalytic converter is clogged with particulate matter (PM). When the ECM judges that a partially clogged condition exists, the ECM begins to perform DPNR catalyst regeneration.
When the output voltage of the sensor deviates from the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction of the sensor circuit, and sets DTC P1425, P1427, or P1428 and illuminates the MIL.
*2: Diesel Particulate-NOx Reduction system
HINT:
If the vacuum hoses of the differential pressure sensor are incorrectly connected (crossed), the ECM interprets this as abnormal pressure difference, DTC P1426 (Differential Pressure Sensor [Installation]) will be set and the MIL will illuminate.
Toyota fault code list DTC P1425 DTC P1427 DTC P1428
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P1425 | Differential pressure sensor output voltage is less than 0.4 V, or more than 4.8 V for 3 seconds or more (1 trip detection logic) |
|
| P1427 | Differential pressure sensor output voltage is less than 0.4 V for 3 seconds or more (1 trip detection logic) |
|
| P1428 | Differential pressure sensor output voltage is more than 4.8 V for 3 seconds or more (1 trip detection logic) |
HINT:
- DTC P1426 (Differential pressure sensor [installation]) will be present if there is incorrect vacuum hose routing to the differential pressure sensor.
- After confirming DTC P1425, P1427 and P1428, check the differential pressure in the "Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / DPNR Differential Pressure" menu using the intelligent tester.
| Condition | Differential Pressure Output | Sensor Condition |
| Ignition switch on (IG) | Approximately 0 kPa | Normal |
| Always | 3 kPa | Open or short circuit |
| 3,000 rpm (No engine load) | Negative output | Incorrect arrangement of hose piping |
Monitor description
In order to detect abnormality in the differential pressure sensor at any time, the ECM always monitors output voltage from the sensor. When the sensor output voltage deviates from the normal operating range (between 0.4 V and 4.8 V) for more than 3 seconds, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the sensor circuit and illuminates the MIL.
Wiring diagram

Inspection procedure DTC P1425 DTC P1427 DTC P1428
| 1.READ VALUE OF DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE |
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the ignition switch on (IG) and turn the tester ON.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / DPNR Differential Pressure.
-
Check that differential pressure is within the specification below.
Result:Condition Differential Pressure Proceed to Always -5 kPa or less A Ignition switch on (IG) -4 kPa to 98 kPa B Always 99 kPa C
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 2.CHECK CONNECTION OF VACUUM HOSE (DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR - VACUUM TRANSMITTING PIPE) |
-
Check if the vacuum hose routing between the differential pressure sensor and the vacuum transmitting pipe is correct.
-
Check that there is no exhaust gas leakage between the differential pressure sensor and the vacuum transmitting pipe.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 3.CHECK BLOCKAGE OF VACUUM HOSE AND TRANSMITTING PIPE |
CAUTION:
Be careful of being burned by exhaust gases during the following inspection.
-
Disconnect the vacuum hose (both upstream and downstream) on the differential pressure sensor.
-
Start the engine.
-
Check if there are exhaust gas pulsations from both vacuum hoses during idling.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 4.CHECK WIRE HARNESS (DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR - ECM) |
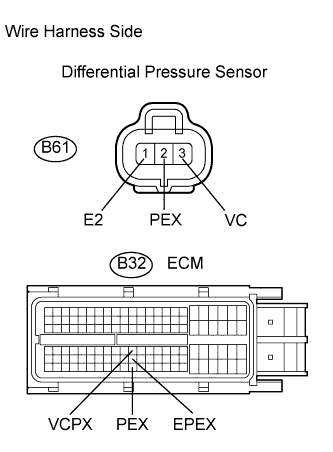
-
Disconnect the B61 differential pressure sensor connector.
-
Disconnect the B32 ECM connector.
-
Measure the resistance of the wire harness side connectors.
Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition B61-2 (PEX) - B32-120 (PEX) Below 1 ? B61-3 (VC) - B32-74 (VCPX) Below 1 ? B61-1 (E2) - B32-97 (EPEX) Below 1 ? B61-2 (PEX) or B32-120 (PEX) - Body ground 10 k? or higher B61-3 (VC) or B32-74 (VCPX) - Body ground 10 k? or higher -
Reconnect the differential pressure sensor connector.
-
Reconnect the ECM connector.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
|