2AD-FHV problems
Rough Idling or Excessive Engine Vibrations
Description
| Malfunction Condition | Main Trouble Areas | Related Trouble Areas |
|
|
|
HINT:
- Rough idling and excessive engine vibrations are checked in this troubleshooting procedure.
- Specified values in the following troubleshooting flowchart are for reference only. Variations in the Data List result values may occur depending on the measuring conditions or the vehicle's age. Do not judge the vehicle to be normal even when the Data List values indicate a standard level. There are possibly some concealed factors of the malfunction.
- Check that the vehicle has not been modified in any way prior to the vehicle inspection.
Inspection procedure
NOTICE:
- After replacing the supply pump, the ECM needs initialization.
- After replacing the injector, the ECM needs registration.
HINT:
- Before troubleshooting, conduct the following:
- Check the fuel quality.
- Check the fuel for air.
- Check the fuel system for blockages.
- Check the air filter.
- Check the engine oil.
- Check the engine coolant.
- Check the engine idling speed and the maximum engine speed.
- Check the vacuum pump.
| 1.CHECK MALFUNCTION CONDITION |
-
Identify when shuddering occurs.
Result:Driving Condition Proceed to When idling A When engaging engine clutch at vehicle start B
(Clutch system shudders)
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 2.CHECK WIRE HARNESS AND CONNECTOR IN ENGINE COMPARTMENT |
-
Check the wire harness and connector connections of common rail system components.
HINT:
Check the following components and system:
- Sensors
- Supply pump
- Common rail
- Injectors
- EDU
- Turbocharger system
- Intake and exhaust system
OK:
The wire harnesses and connectors are connected securely.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 3.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN |
HINT:
Drive the vehicle according to the driving pattern below to allow the ECM to set DTCs relating to malfunctions of the fuel system, EGR system, and throttle valve. If DTCs are set, problem areas can be identified.
-
Start the engine (procedure "A").
-
Stop the engine and wait for at least 10 seconds (procedure "B").
-
Perform procedure "A" and procedure "B" again described above to allow the ECM to set pressure discharge valve malfunction DTCs.
-
Enter CHECK MODE.
-
Fully warm up the engine.
-
Allow the engine to idle for 5 minutes or more.
-
Drive the vehicle at more than 40 km/h (25 mph) for 1 minute or more (procedure "C").
-
Decelerate and stop the vehicle (procedure "D").
-
Repeat procedure "C" and procedure "D" 4 times or more.
-
Stop the engine and wait for at least 10 seconds (procedure "E").
-
Repeat procedure "C" and procedure "E" described above (to set DTCs relating to the EGR system and throttle valve).
-
Drive the vehicle at more than 70 km/h (43 mph) for at least 1 minute (to set DTCs relating to the supply pump).
| NEXT | |
| 4.CHECK OUTPUT DTC (RELATING TO ENGINE) |
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the ignition switch on (IG) and turn the tester ON.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
-
Read pending DTCs.
Result:Display (DTC Output) Proceed to No DTCs A Engine related DTCs B
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 5.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST BY INTELLIGENT TESTER (FUEL LEAK TEST) |
HINT:
By performing this Active Test, the engine speed is maintained at 2,000 rpm and the common rail internal fuel pressure is raised to the maximum operating pressure. As a result, a fuel leak check can be conducted while retaining the high common rail pressure.
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Test the Fuel Leak.
-
Visually check the supply pump, injector, and fuel line located between the supply pump and common rail for fuel leaks and fuel pressure leaks. Also, perform the same check on the fuel line between the common rail and the injector.
HINT:
There may be fuel leaks inside the components, such as the supply pump.
OK:
No fuel leakage.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 6.READ VALUE OF MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR, MAF METER, AND FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR |
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Start the engine and warm it up and turn the tester ON.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List.
-
Select the following menu items in order and read the values.
- MAP
- MAF
- Fuel Press
Standard value:
Item Engine Speed*1 Standard Range Description MAP*2 Ignition switch on (IG) (engine stopped) Same as atmospheric pressure Intake manifold internal pressure detected by manifold absolute pressure sensor Idling 85 to 93 kPa (690 to 765 mmHg, 27.17 to 30.13 in.Hg) 3,000 rpm (no engine load) 120 to 140 kPa (803 to 878 mmHg, 31.60 to 34.56 in.Hg) 3,000 rpm (driving with full throttle acceleration)*5 239 to 259 kPa (1,795 to 1,945 mmHg, 70.67 to 76.57 in.Hg) 3600 rpm (driving with full throttle acceleration)*5 245 to 265 kPa (1,840 to 1,990 mmHg, 57.00 to 62.91 in.Hg) MAF*2, *4 Ignition switch on (IG) (engine stopped) 0 g/sec. Intake air volume detected by mass air flow meter Idling 2.5 to 5.52 g/sec. 3,000 rpm (no engine load) 49 to 57 g/sec. 3,000 rpm (driving with full throttle acceleration)*5 124 to 136 g/sec. 3,600 rpm (driving with full throttle acceleration)*5 151 to 163 g/sec. Common Rail Pressure*3 Idling 37 to 43 MPa Common rail internal fuel pressure 2,000 rpm (no engine load) 47 to 53 MPa 3,000 rpm (no engine load) 60 to 66 MPa 3,000 rpm (driving with full throttle acceleration)*5 150 to 156 MPa 3,600 rpm (driving with full throttle acceleration)*5 175 to 185 MPa Result:Item Result Proceed to MAP, MAF and Fuel press Standard range A MAP and MAF Outside standard range B Only MAP Outside standard range C Only MAF Outside standard range D Only Fuel Press Outside standard range E HINT:
*1: The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be OFF with a fully warm engine.
*2: This value is indicated when the ambient temperature is 25°C (77°F), the atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa (758 mmHg, 29.83 in.Hg), and the stable boost pressure is maintained for approximately 10 seconds.
*3: This value is indicated when the ambient temperature is 25°C (77°F), the atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa (758 mmHg, 29.83 in.Hg), and the vehicle is accelerated for approximately 10 seconds.
*4: When the mass air flow meter malfunctions, the MAF output may deviate from the standard (referential) range when the engine idles and is accelerated from 3,000 to 4,000 rpm with full throttle acceleration.
*5: Fully depress the accelerator pedal with the vehicle creeping at idle speed in 2nd gear.
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 7.READ VALUE OF INJECTOR (INJECTION FEEDBACK VAL AND INJECTION VOLUME) |
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Start the engine, warm it up and turn the tester ON.
-
Select the following menu items in order and read the values.
- Injection Feedback Val #1, #2, #3, and #4
- Injection Volume
Standard value:
Item Engine Speed* Standard Range Description Injection Feedback Val #1 Idling -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 Value of injector fuel injection volume compensates for differences in combustion condition of cylinders - Positive values indicate control which corrects combustion degradation
- Negative values indicate control which corrects excessive combustion pressure
- If problems exist, "Injection Feedback Val" may deviate from the -3.0 and 3.0 mm3 range
Injection Feedback Val #2 Idling -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 Injection Feedback Val #3 Idling -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 Injection Feedback Val #4 Idling -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 Injection Volume Idling 3.9 to 7.0 mm3 Fuel injection volume value controlled by ECU - Controls NE signal, fuel temperature, engine coolant temperature, intake air temperature, boost pressure, atmospheric pressure, and EGR volume
- If problems exist, "Injection Volume" may be outside the standard range
Result:Result Proceed to Standard range A Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 and/or Injection Volume outside standard range B HINT:
*: The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be OFF with a fully warm engine.
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 8.CHECK INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE |
-
Read the injector compensation code.
HINT:
If the injector compensation code is not correctly registered, it may cause malfunctions.
-
Check the injector compensation code.
OK:
Compensation code of the installed injector is same as the code registered in the ECM.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 9.RESET ECM |
-
Disconnect the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal for at least 2 minutes.
-
Reconnect the cable to the negative (-) battery terminal.
-
Check whether the malfunction has been successfully repaired by performing a driving test using the freeze frame data recorded at the time the malfunction occurred.
OK:
Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
|
|
||||
| NG | |
| 10.CHECK ENGINE MOUNTING INSULATOR |
-
Visually check that the engine mounting insulator is installed correctly and is not crooked or twisted.
OK:
No abnormalities.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 11.CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM |
-
Check for air leakage and blockage between the air cleaner and turbocharger.
-
Check for air leakage and blockage between the turbocharger and intake manifold.
OK:
No air leakage or blockage.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 12.CHECK EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY |
-
Check the EGR valve assembly.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 13.INSPECT DIESEL THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY |
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the ignition switch on (IG) and turn the tester ON.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Diesel Throttle Angle.
-
Read the value.
Standard value:
Ignition switch on (IG):
0%
Idling (warmed up engine):
95%
Accelerator pedal fully depressed:
0%
|
|
||||
| NG | |
|
| 14.IDENTIFY MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER INJECTOR |
-
Follow the instructions in the table below according to the check result of the intelligent tester.
HINT:
This operation is based on the premise that the common rail pressure is normal.
Standard value:
Item Engine Speed* Reference Value Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 Idling -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 Injection Volume Idling 3.9 to 7.0 mm3 HINT:
*: The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be OFF, and the engine should be fully warmed up.
Result:Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 Injection volume Less than 3.9 mm3 Between 3.9 to 7.0 mm3 (Normal) More than 7.0 mm3 3.0 mm3 or more, -3.0 mm3 or less A B B Between -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 - Normal C* Proceed to Inspection Areas Descriptions A Inspect and repair cylinder injector with revised injection volume of less than -3.0 mm3: - Perform power balance inspection and identify malfunctioning cylinder
- Replace malfunctioning cylinder injector
Abnormal value cylinder injector injects excessively large quantity of fuel B Identify malfunctioning cylinders by conducting power balance inspection: - Perform power balance inspection to identify malfunctioning cylinders
- Clean malfunctioning cylinder injector, then check and repair it
Abnormal value cylinder injector injects excessively large quantity of fuel - Fuel injection volume too low due to injector nozzle being blocked by deposits
- Abnormal value cylinder injector compression decreases
- Abnormal value cylinder injector injects excessively large quantity of fuel
C Inspect and repair all cylinder injectors:
Clean all cylinder injectors, inspect, and repair themAll cylinder injectors inject excessively small quantity of fuel:
Fuel injection volume too low due to all cylinder injector nozzles being blocked by depositsHINT:
*: When the Injection Volume displayed on the tester is large despite the Fuel Press and Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 in the Data List being normal, the injector may be clogged. In this case, there may be deposits inside or outside the tip of the injector.
- Despite the injector functioning normally, the indicated Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 value may be outside the normal operating range due to compensation for other problems (such as low compression).
- Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 is the value used to correct the fuel injection volumes of each cylinder, in order to optimize (compensate for the unevenness between) all the cylinder combustion conditions. If any of the cylinders malfunction, the fuel injection volumes for the normal cylinders are corrected simultaneously. As a result, the Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 may deviate from the standard range.
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 15.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST BY INTELLIGENT TESTER (FUEL CUT FOR IDENTIFYING MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER) |
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Cylinder #1, #2, #3, and #4 Fuel Cut.
-
Check the four cylinders in sequence to identify any faulty cylinders by performing the power balance inspection.
HINT:
- If the engine idle does not change when an injector is disabled, the cylinder being tested is malfunctioning.
- If the cylinder being tested is normal, there will be a significant change of idle speed when the fuel injection is stopped for that cylinder.
| NEXT | |
|
| 16.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST BY INTELLIGENT TESTER (FUEL CUT FOR IDENTIFYING MALFUNCTION) |
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Cylinder #1, #2, #3, and #4 Fuel Cut.
-
Check the four cylinders in sequence to identify any faulty cylinders by performing the power balance inspection.
HINT:
- If the engine idle does not change when an injector is disabled, the cylinder being tested is malfunctioning.
- If the cylinder being tested is normal, there will be a significant change of idle speed when the fuel injection is stopped for that cylinder.
| NEXT | |
| 17.CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE |
-
Check the cylinder compression pressure.
Standard pressure:
2,700 kPa (27.5 kgf/cm2, 392 psi)
Minimum pressure:
2,200 kPa (22.4 kgf/cm2, 319 psi)
Difference between each cylinder:
500 kPa (5.1 kgf/cm2, 73 psi)
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 18.CHECK MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER'S INJECTOR FOR DEPOSITS |
HINT:
If an injector is contaminated with deposits, the fuel injection volume deviates from the standard range. This may cause malfunctions.
-
Check the injector for any deposits.
Result:Injector Condition Proceed to Deposits A No deposits B
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 19.CLEAN INJECTOR |
-
Wipe away deposits from the tips of the injectors.
HINT:
- Solvent or carbon removal agents help remove the deposits easily.
- Exercise extreme care not to damage the injectors while wiping off the deposits.
| NEXT | |
| 20.READ VALUE OF INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (INJECTION FEEDBACK VAL AND INJECTION VOLUME) |
-
Reinstall the injector to the cylinder head.
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the ignition switch on (IG) and turn the tester ON.
-
Start the engine and warm it up.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List.
-
Select the following menu items in order and read the values.
- Injection Feedback Val #1, #2, #3, and #4
- Injection Volume
Standard value:
Item Engine Speed* Reference Value Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 Idling -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 Injection Volume Idling 3.9 to 7.0 mm3 HINT:
*: The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be OFF, and the engine should be fully warmed up. When the values are outside the standard range, deposits inside the injector may be causing the problem.
OK:
Values are within the standard range.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
|
| 21.CHECK INJECTORS FOR DEPOSITS (EXCEPT FUEL ADDITION INJECTOR) |
HINT:
If an injector is contaminated with deposits, the fuel injection volume deviates from the standard range. This may cause malfunctions.
-
Check the injector for any deposits.
Result:Injector Condition Proceed to Deposits A No deposits B
|
|
||||
| A | |
| 22.CLEAN INJECTOR |
-
Wipe away deposits from the tips of the injectors.
HINT:
- Solvent or carbon removal agents help remove the deposits easily.
- Exercise extreme care not to damage the injectors while wiping off the deposits.
| NEXT | |
| 23.READ VALUE OF INJECTOR (INJECTION FEEDBACK VAL AND INJECTION VOLUME) |
-
Reinstall the injector to the cylinder head.
-
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
-
Turn the ignition switch on (IG) and turn the tester ON.
-
Start the engine and warm it up.
-
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List.
-
Select the following menu items in order and read the values.
- Injection Feedback Val #1, #2, #3, and #4
- Injection Volume
Standard value:
Item Engine Speed* Reference Value Injection Feedback Val #1 to #4 Idling -3.0 to 3.0 mm3 Injection Volume Idling 3.9 to 7.0 mm3 HINT:
*: The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be OFF, and the engine should be fully warmed up. When the values are outside the standard range, deposits inside the injector may be causing the problem.
OK:
Values are within the standard range.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
|
| 24.INSPECT COMMON RAIL ASSEMBLY (FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR) |
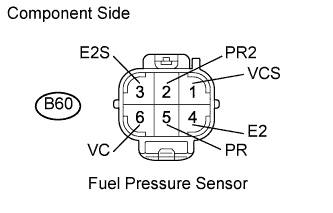
-
Disconnect the B60 fuel pressure sensor connector.
-
Measure the resistance of each terminal of the fuel pressure sensor.
Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition B60-5 (PR) - B60-4 (E2) 16.4 k? or less B60-2 (PR2) - B60-3 (E2S) 16.4 k? or less B60-5 (PR) - B60-6 (VC) 3 k? or less B60-2 (PR2) - B60-1 (VC2) 3 k? or less -
Reconnect the fuel pressure sensor connector.
|
|
||||
| OK | |
| 25.INSPECT SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY |
-
Measure the resistance of the suction control valve terminals.
Standard resistance:
Condition Specified Condition 20°C (68°F) 1.9 to 2.3 ?
|
|
||||
| OK | |
|