Vehicle Stability Control System (W/ Vdim) -- System Description |
| VDIM (Vehicle Dynamics Integrated Management) DESCRIPTION |
This vehicle is equipped with VDIM. It is a concept of vehicle motion control that integrates brake control, drive force control and steering control.
Conventional vehicles use a combination of independent functions such as ABS, TRC, VSC and EPS. However VDIM integrates these systems to improve "drive, turn and stop," the motion performance of the vehicle in other words.
In conventional vehicles, control starts at the limit of the vehicle. However VDIM exercises control before the limit is reached, creating a smooth vehicle response. This expands the limits of the vehicle, and increases driving pleasure.
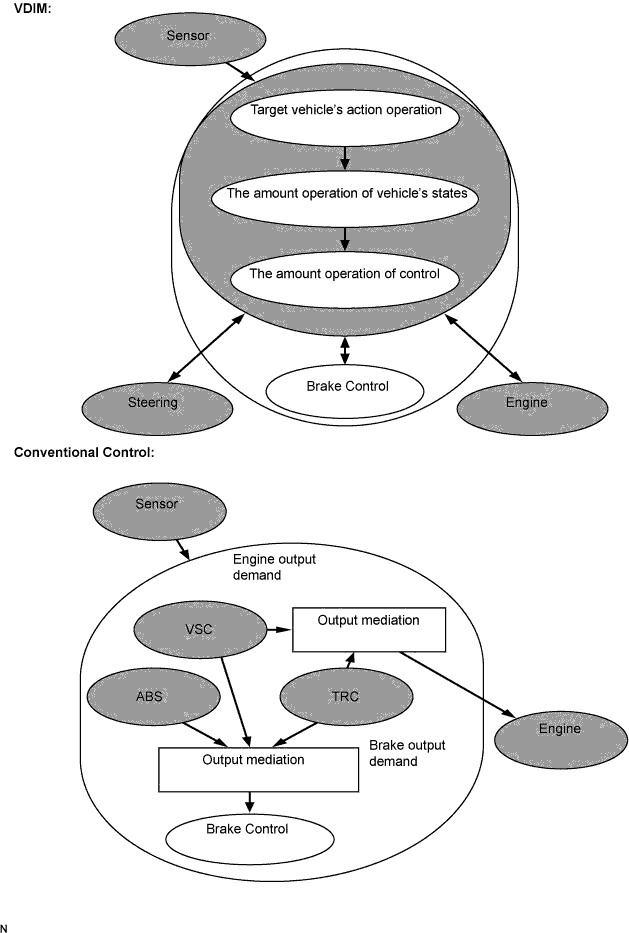
The VDIM manages all functions, such as the ABS with EBD, BA, the TRC, and the VSC. It is operated by the VSC system, which regulates a brake fluid pressure. The steering cooperative control function is also available. The VDIM is able to perform the comprehensive management.
Conventional brake control systems begin to control either the braking or motive force in order to stabilize the vehicle motion when it becomes unstable due to loss of tire traction. In contrast, in order to maintain stable vehicle control, the VDIM commences controlling the brake and steering systems in accordance with changes in balance before the vehicle becomes unstable. As a result, smooth vehicle control is achieved.
Conventional brake control systems manage all related functions, such as the ABS with EBD, BA, the TRC and the VSC independently, according to the vehicle dynamics. In contrast, the VDIM provides smooth control by seamlessly integrating all those functions.
| FUNCTION DESCRIPTION |
- HINT:
- The yaw rate sensor and acceleration sensor are combined in a single unit. This unit communicates with the skid control ECU via CAN communication.
ABS (Anti-lock Brake System)
The ABS helps prevent the wheels from locking when the brakes are applied firmly or when braking on a slippery surface.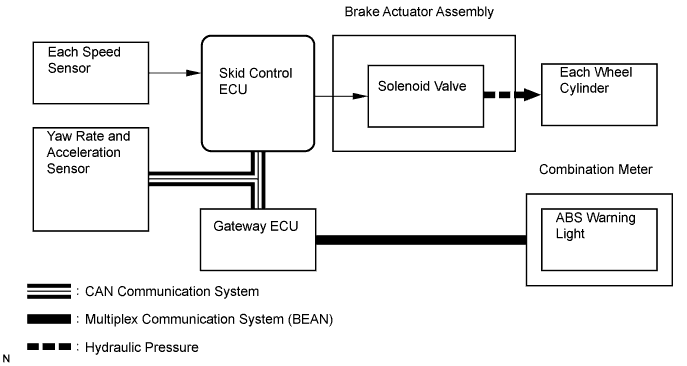
Operation description
The skid control ECU detects wheel lock condition by receiving vehicle speed signals from each speed sensor, and sends control signals to the solenoid valve. The solenoid valve avoid wheel lock by controlling the brake fluid pressure of each wheel cylinder.
The ABS warning light comes on when the ABS system is malfunctioning.
EBD (Electronic Brake force Distribution)
The EBD control utilizes ABS, and performs proper brake force distribution between the front and rear wheels in accordance with driving conditions.
When braking while cornering, it also controls the brake forces of the right and left wheels, helping to maintain vehicle behavior.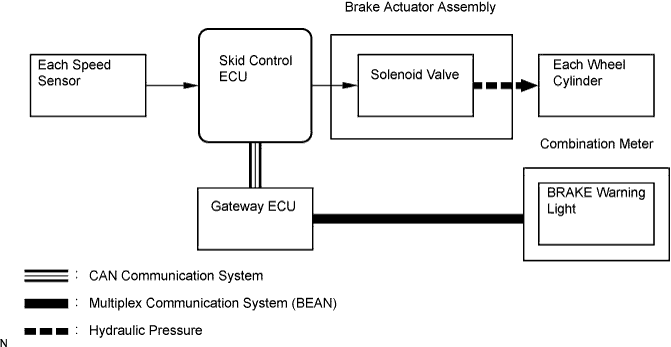
Operation description
The skid control ECU receives the speed signals from each speed sensor to detect the slip condition of the wheels and sends the control signals to the solenoid.
The solenoid valve controls the fluid pressure of each wheel cylinder and splits the control power properly between the front and rear wheels and the right and left wheels.
The BRAKE warning light comes on to indicate a malfunction in the EBD system.
BA (Brake Assist)
The primary purpose of the brake assist system is to provide auxiliary brake force to assist the driver who cannot generate a large enough brake force during emergency braking, thus helping to maximize the vehicle's brake performance.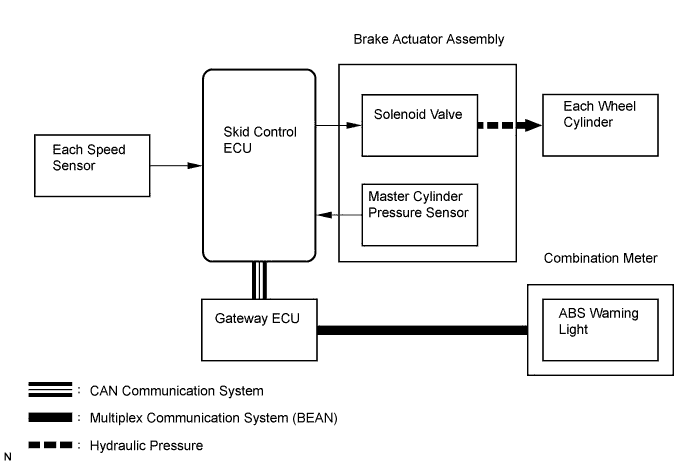
Operation description
The skid control ECU receives the speed signal from each speed sensor and the fluid pressure signal from the master cylinder pressure sensor to determine whether brake assist is necessary. If brake assist is necessary, the skid control ECU sends control signals to the pump motor and solenoid. The pump and the solenoid valve then control the pressure applied to each wheel cylinder.
The ABS warning light comes on to indicate a malfunction in the BA system.
TRC (Traction Control)
The TRC system helps prevent the drive wheels from slipping when the driver presses down on the accelerator pedal excessively when starting off or accelerating on a slippery surface.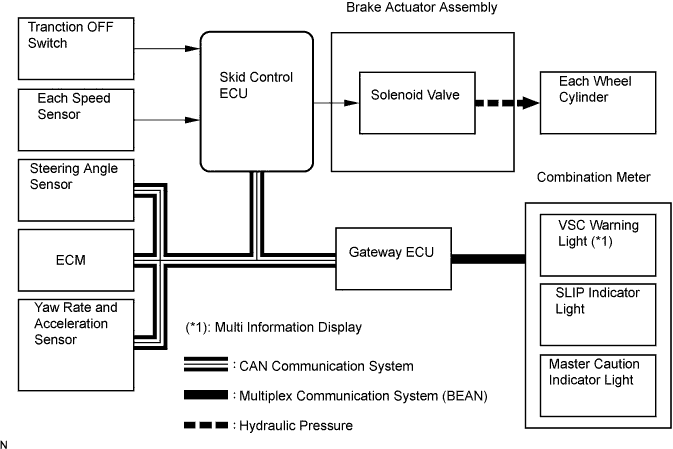
Operation description
The skid control ECU detects the vehicle's slip condition by receiving signals from each speed sensor and ECM via CAN communication. The skid control ECU controls engine torque with the ECM via CAN communication and oil pressure through the solenoid valve.
The SLIP indicator light blinks when the system is operating. When there is a malfunction in the TRC system, both master caution and SLIP indicator lights will come on and the DTC will be displayed on the multi information display.
Traction OFF switch stops traction control operation.
VSC (Vehicle Stability Control)
The VSC system helps prevent the vehicle from slipping sideways as a result of strong front or rear wheel skid during cornering.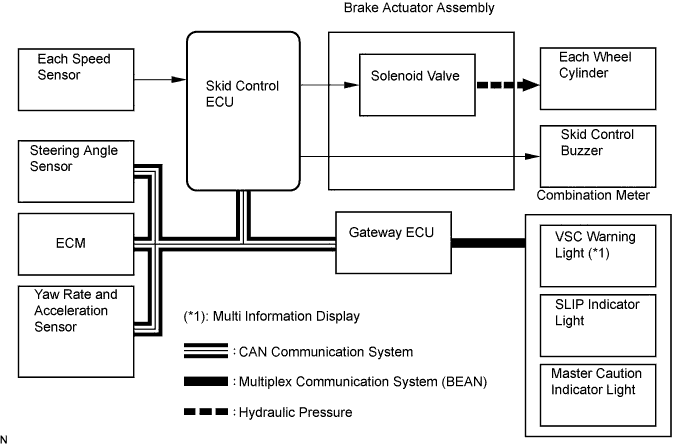
Operation description
The skid control ECU determines the vehicle condition by receiving signals from the speed sensor, yaw rate and acceleration sensor and steering angle sensor. The skid control ECU controls engine torque with the ECM via CAN communication and fluid pressure with the solenoid valve.
The SLIP indicator light blinks and the skid control buzzer sounds when the system is operating. When there is a malfunction in the VSC system, both master caution and SLIP indicator lights come on and the DTC will appear on the multi information display.
| LSD CONTROL |
Sometimes the wheels will spin when accelerating in a turn because the vehicle weight moves to the outside of the turn and it is difficult to transmit drive force to the inside.
The VSC system detects the turning conditions and the wheel spin, and applies the brakes to the drive wheel on the inside of the turn to restrict wheel spin. This transmits drive force to the wheels on the outside of the turn, so that the driver's intended acceleration is obtained.
| FAIL SAFE |
When a failure occurs in the ABS with BA, TRC and VSC systems, the ABS and VSC warning lights, and SLIP indicator light come on and ABS with BA, TRC and VSC operations are prohibited. In addition to this, when there is a failure that disables the EBD operation, the BRAKE warning light also comes on and the EBD operation is prohibited.
If control is prohibited due to a malfunction during operation, control will be disabled gradually.
This is to avoid sudden vehicle instability.
| INITIAL CHECK |
When the vehicle speed first becomes approximately 4 mph (6 km/h) or more after the engine switch is turned on (IG), each solenoid valve and motor of the brake actuator is sequentially activated to perform an electrical check. During the initial check, the operating sound of solenoid valve and motor can be heard from the engine compartment, but this is not a malfunction.
| SERVICE MODE |
VSC operation can be disabled by operating the intelligent tester.
- HINT:
- Refer to the intelligent tester operator's manual for further details.
| FUNCTION OF COMPONENTS |
| Components | Function |
| Speed sensor (Semiconductor type) | Detects the wheel speed and sends the signal to the skid control ECU. |
| Skid control ECU |
|
| Brake actuator assembly | Controls the hydraulic pressure of each of the four wheel cylinders using the output signal of the skid control ECU. |
| Solenoid relay | Supplies power to each solenoid. |
| Motor relay (ABS MOTOR2 relay) | Supplies power to the pump motor. |
| Fail safe relay (ABS MOTOR1 relay) | Cuts off power to the motor when the pump motor circuit malfunctions. |
| Steering angle sensor |
|
| Yaw rate and acceleration sensor |
|
| Master cylinder pressure sensor |
|
| Stop light switch | Detects the brake operating conditions and inputs the results to the skid control ECU. |
| Brake pedal load sensing switch |
|
| ECM | Controls the engine output when TRC and VSC are operating with the skid control ECU via CAN communication. |
| Skid control buzzer | Intermittently sounds to inform the driver that the VSC is operating. |
| ABS warning light |
|
| BRAKE warning light |
|
| SLIP indicator light |
|
| VSC warning light (Multi information display) |
|
| Master caution indicator light | Comes on to inform the driver that a malfunction has occurred. |
| Solenoid identification | Determines the identification signal using the skid control ECU, and specifies control characteristics of the actuator. |