Engine. Lexus Gs430, Gs300. Uzs190 Grs190
3Uz-Fe Engine Control System. Lexus Gs430, Gs300. Uzs190 Grs190
CHECK OTHER DTC OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0420, P0430)
INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (RESISTANCE)
REPLACE CATALYST CONVERTER (BANK 1 OR BANK 2) AND FRONT EXHAUST PIPE
DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) |
DTC P0430 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2) |
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
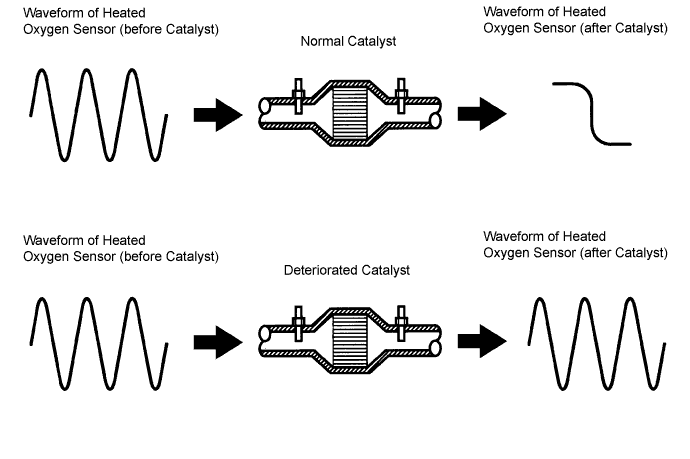
The ECM uses heated oxygen sensors mounted before and after the Three-Way Catalyst (TWC) to monitor its efficiency. The front sensor sends pre-catalyst air-fuel information to the ECM. The rear sensor sends post-catalyst information to the ECM. The ECM compares these 2 signals to judge the efficiency of the catalyst and the catalyst's ability to store oxygen. During normal operation, the TWC stores and releases oxygen as needed. The capacity to store oxygen results in a low variation in the post-TWC exhaust stream as shown below.If the catalyst is functioning normally, the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2) slowly switches between RICH and LEAN. If the catalyst is deteriorated, the waveform will alternate frequently between RICH and LEAN.
As the catalyst efficiency degrades, its ability to store oxygen is reduced and the catalyst output becomes more variable.
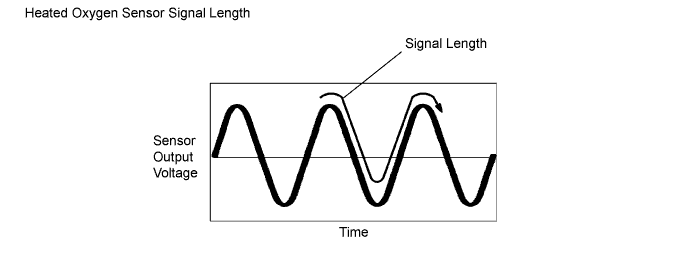
When running the catalyst monitor, the ECM begins to measure the signal length of the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) and heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2). The ECM calculates the rate of the signal length of the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) and heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2) (catalyst deterioration level). If the catalyst deterioration level exceeds the threshold, the ECM interprets this as a catalyst malfunction. The ECM illuminates the MIL (2 trip detection logic) and sets a DTC.
The monitor runs after:
- The engine is warmed up (Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is 75°C (167°F) or more).
- The vehicle is driven at approximately 60 to 100 km/h (37 to 63 mph) for 15 minutes.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P0420 P0430 |
|
|
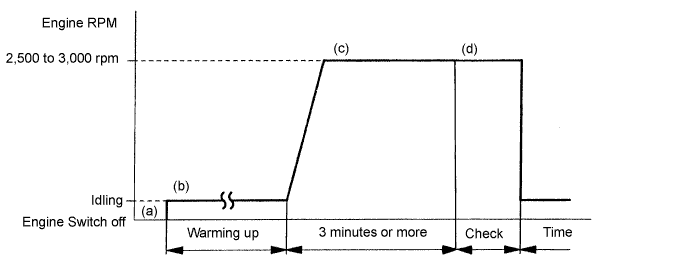
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Start the engine and warm it up with all the accessories switched OFF until the ECT becomes stable.
- Run the engine at 2,500 to 3,000 rpm for about 3 minutes.
- HINT:
- Control the engine RPM so that the calculated catalyst temperature can be between 550 and 800°C (1,022 and 1,472°F). The calculated catalyst temperatures of bank 1 and bank 2 can be read by viewing CAT TEMP B1 S1 and CAT TEMP B2 S1 of the Data List.
Confirm that heated oxygen sensor (bank 1 sensor 1 (OX1A) and bank 2 sensor 1 (OX2A)) have waveforms that are around 0.5 V during feedback to the ECM. Then check the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor (bank 1 sensor 2 (OX1B) and bank 2 sensor 2 (OX2B)) for the same waveforms (0.5 V during feedback).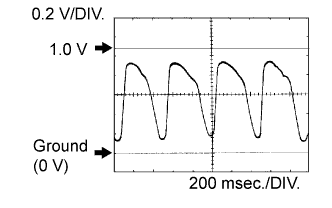
- HINT:
- If there is a malfunction in the catalyst, the waveform of the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2) (OX1B, OX2B) is almost the same as that of the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) (OX1A, OX2A), which is shown.
WIRING DIAGRAM
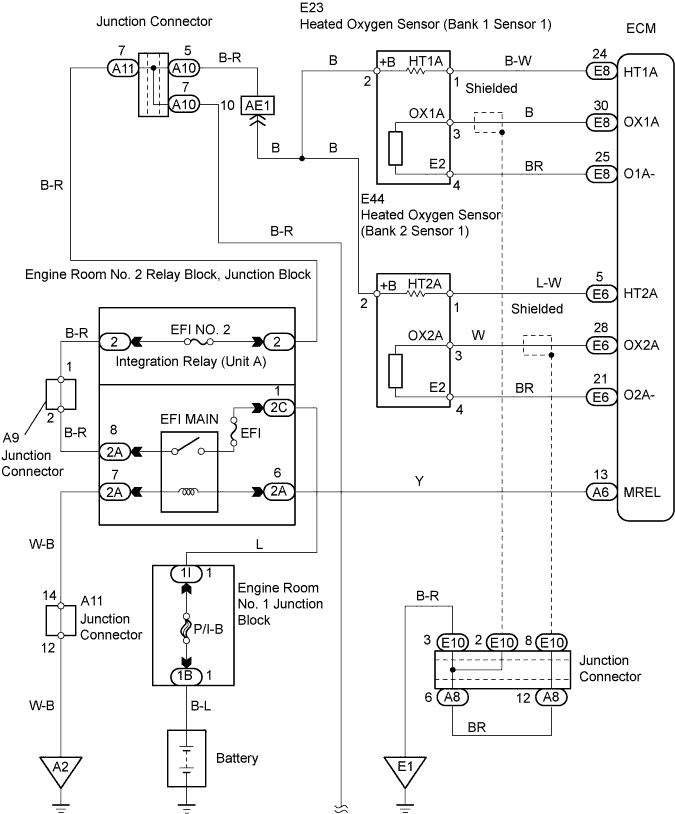
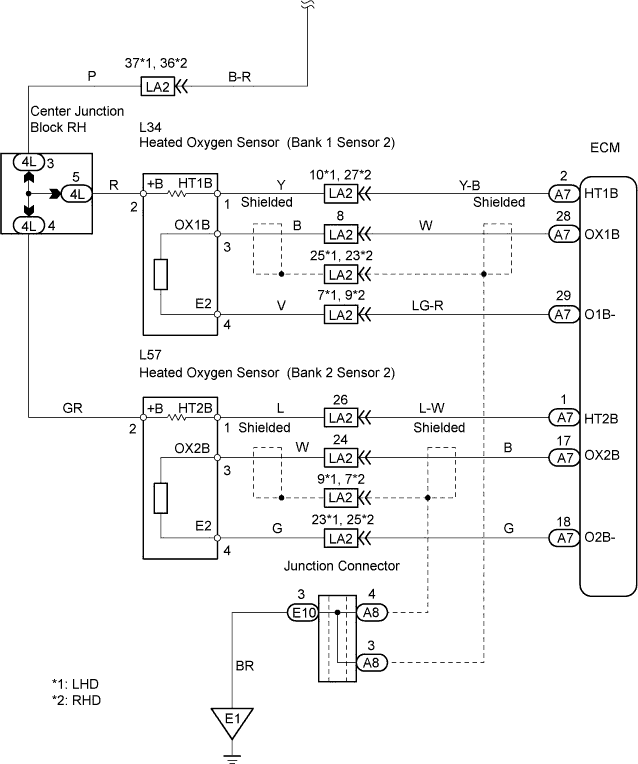
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was LEAN or RICH, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
- If DTC P0420 is displayed, check the bank 1 catalyst.
- If DTC P0430 is displayed, check the bank 2 catalyst.
- Bank 1 includes cylinder No. 1, but bank 2 does not. Cylinder No. 1 is located in the front part of the engine, opposite the transmission.
| 1.CHECK OTHER DTC OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0420, P0430) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG) and turn the tester ON.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
- Result:
Display (DTC output) Proceed to P0420 or P0430 A P0420 or P0430 and other DTCs B
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.CHECK FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAKAGE |
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 3.INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (RESISTANCE) |
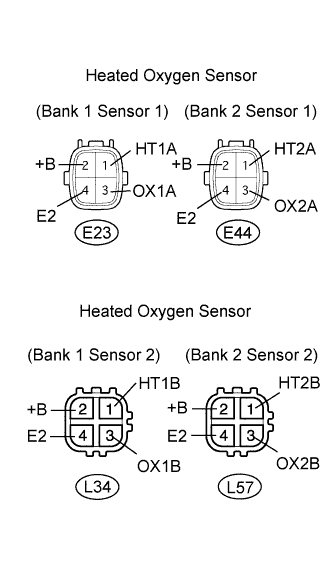 |
Disconnect the E23, E44, L34 and L57 sensor connectors.
Measure the resistance of the sensor.
- Standard resistance: Sensor 1:
Tester Connection Specified Condition 1 (HT1A) - 2 (+B) 11 to 16 Ω 1 (HT2A) - 2 (+B) 11 to 16 Ω 1 (HT1A) - 4 (E2) 10 kΩ or higher 1 (HT2A) - 4 (E2) 10 kΩ or higher
- Standard resistance: Sensor 2:
Tester Connection Specified Condition 1 (HT1B) - 2 (+B) 11 to 16 Ω 1 (HT2B) - 2 (+B) 11 to 16 Ω 1 (HT1B) - 4 (E2) 10 kΩ or higher 1 (HT2B) - 4 (E2) 10 kΩ or higher
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST |
- HINT:
- It is possible that the malfunctioning area can be found using the Active Test Control operation. The Active Test can determine if the heated oxygen sensor or other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning or not.
- The injection volume can be switched to -12.5% (decrease) or +25% (increase) by the Active Test.
- The Active Test procedure enables a technician to check and graph the voltage outputs of the heated oxygen sensors.
- Procedure:
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Turn the engine switch on (IG).
- Warm up the engine by running the engine at 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume.
- Perform the Active Test while the engine is idling.
- Standard:
- Heated oxygen sensor reacts in accordance with the increase and decrease of injection volume:
+25% → output: More than 0.55 V
-12.5% → output: Less than 0.4 V
- NOTICE:
- The heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) output has a few seconds of delay and the heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2) output has a maximum of 20 seconds of delay.
- If the vehicle is short on fuel, the air-fuel ratio becomes LEAN and the DTCs will be recorded.
| Case | Heated Oxygen Sensor (sensor 1) Voltage | Heated Oxygen Sensor (sensor 2) Voltage | Main Suspected Trouble Area | ||
| 1 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 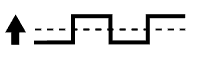 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 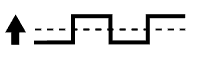 | - |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.55 V or more Below 0.4 V | 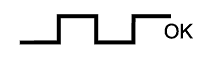 | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.5 V or more Below 0.4 V |  | ||
| 2 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 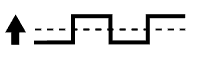 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 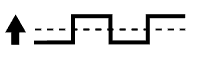 | Heated oxygen sensor (sensor 1) Heated oxygen sensor heater (sensor 1) |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.5 V or more Below 0.4 V |  | ||
| 3 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 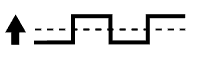 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 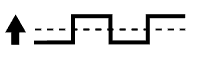 | Heated oxygen sensor (sensor 2) Heated oxygen sensor heater (sensor 2) |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage 0.55 V or more Below 0.4 V |  | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
| 4 | Injection volume +25% -12.5% | 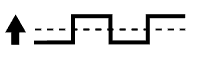 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 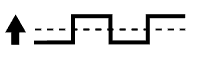 | Injector fuel pressure, Exhaust gas leak, etc. (air-fuel ratio is extremely LEAN or RICH) |
| Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Heated Oxygen Sensor Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 5.REPLACE CATALYST CONVERTER (BANK 1 OR BANK 2) AND FRONT EXHAUST PIPE |
- NOTICE:
- Replace both the front catalyst and rear catalyst (front exhaust pipe) of the damaged bank.
| NEXT | ||
| ||