DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
CHECK FOR ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT AND RECORD FREEZE FRAME DATA
CHECK ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM
CHECK MALFUNCTION CONDITION
CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA
CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA
CHECK SENSOR INSTALLATION
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED)
CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (FUEL INJECTOR POWER SOURCE)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED)
CHECK FUEL SYSTEM
CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA
INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK FUEL SYSTEM
CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM
PERFORM SIMULATION TEST
CONFIRM PROBLEM SYMPTOM
PERFORM SIMULATION TEST
INSPECT BATTERY
CHECK ENGINE ASSEMBLY
CHECK STARTER ASSEMBLY
INSPECT BATTERY
INSPECT STARTER ASSEMBLY
PERFORM SIMULATION TEST
INSPECT BATTERY
CHECK ENGINE
CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
CHECK SPARK PLUG AND SPARK
CONFIRM VEHICLE CONDITION
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK SPARK PLUG
READ VALUE USING GTS (ENGINE SPEED)
CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (IGNITION COIL POWER SOURCE)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL - ECM)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL - ECM)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED)
READ VALUE USING GTS (ENGINE SPEED)
CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (FUEL INJECTOR POWER SOURCE)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (FUEL INJECTOR - ECM)
CHECK MASS AIR FLOW METER ASSEMBLY
CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM
CHECK THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
CHECK THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE VVT SYSTEM)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE VVT EXHAUST LINEAR)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (MASS AIR FLOW METER - ECM)
INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK MASS AIR FLOW METER ASSEMBLY
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (MASS AIR FLOW METER - ECM)
READ VALUE USING GTS
PERFORM SIMULATION TEST
INSPECT AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR
PERFORM SIMULATION TEST
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
CHECK SPARK PLUG
CONFIRM VEHICLE CONDITION
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED)
CHECK MALFUNCTION CONDITION
INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (FUEL INJECTOR POWER SOURCE)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (FUEL INJECTOR - ECM)
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
READ VALUE USING GTS (ISC LEARNING VALUE)
CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
READ VALUE USING GTS (LONG FT)
PERFORM SIMULATION TEST
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED)
INSPECT FUEL PUMP
CHECK FUEL PRESSURE
READ VALUE USING GTS (LONG FT)
PERFORM SIMULATION TEST
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED)
INSPECT FUEL PUMP
CHECK PURGE VSV
CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
CHECK INTAKE VALVE
READ VALUE USING GTS (ISC LEARNING VALUE)
CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DTC P1604 Startability Malfunction
DESCRIPTION
This DTC is stored when the engine does not start even though the STA signal is input or when the engine takes a long time to start, and when the engine speed is low or the engine stalls just after the engine starts.
Using the GTS, the conditions present when the DTC was stored can be confirmed by referring to the freeze frame data. Freeze frame data records engine conditions when a malfunction occurs. This information can be useful when troubleshooting.
It is necessary to check if the vehicle ran out of fuel before performing troubleshooting, as this DTC is also stored when there is engine starting trouble due to running out of fuel.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P1604 | Either condition is met:
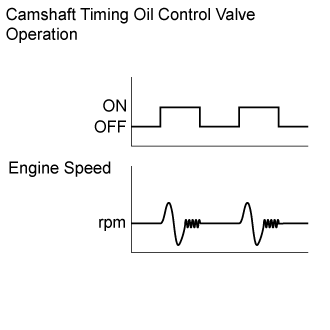
The engine speed is less than 500 rpm with the STA signal on for a certain amount of time (refer to the illustration below) (1 trip detection logic).
After the engine starts (engine speed is 500 rpm or more), the engine speed drops to 200 rpm or less within approximately 2 seconds (1 trip detection logic).
| Immobiliser system
Engine assembly (excess friction, compression loss)
Starter assembly
Crankshaft position sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Fuel pump
Fuel pump control system
Fuel pipes
Fuel injector assembly
Throttle body assembly
Fuel pressure regulator assembly
Battery
Drive plate
Spark plug
Ignition coil circuit
Intake system
Camshaft timing oil control valve assembly
Mass air flow meter assembly
Air fuel ratio sensor
Valve timing
Fuel
Purge VSV
Intake valve
Exhaust valve
ECM
|
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
In contrast to normal malfunction diagnosis for components, circuits and systems, DTC P1604 is used to determine the malfunctioning area from the problem symptoms and freeze frame data when the user mentions problems such as starting difficulty.
As these DTCs can be stored as a result of certain user actions, even if these DTCs are output, if the customer makes no mention of problems, clear these DTCs without performing any troubleshooting and return the vehicle to the customer.
If any other DTCs are output, perform troubleshooting for those DTCs first.
When the Data List item "Immobiliser Fuel Cut" is ON, the engine cannot be started.
Read freeze frame data using the GTS. Freeze frame data records engine conditions when a malfunction occurs. This information can be useful when troubleshooting.
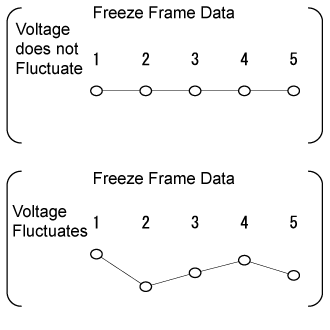
When confirming the freeze frame data, be sure to check all 5 sets of freeze frame data ().
When confirming freeze frame data, if there are multiple items related to the cause of the malfunction, perform troubleshooting for all related items.
Try to start the vehicle under the conditions recorded in the freeze frame data which were present when the malfunction occurred. Confirm the data at this time and compare it with the freeze frame data.
If the malfunction does not reoccur, carefully check the vehicle conditions from when the malfunction occurred using freeze frame data.
When performing inspections, jiggle the relevant wire harnesses and connectors in an attempt to reproduce malfunctions that do not always occur.
If the same inspection or replacement procedure appears 2 times when performing an inspection procedure, it is not necessary to repeat the procedure the second time.
| Malfunction Recurrence and Inspection Areas |
Freeze frame data exists, but the malfunction (starting difficulty) has not reoccurred and the malfunction conditions are unknown.
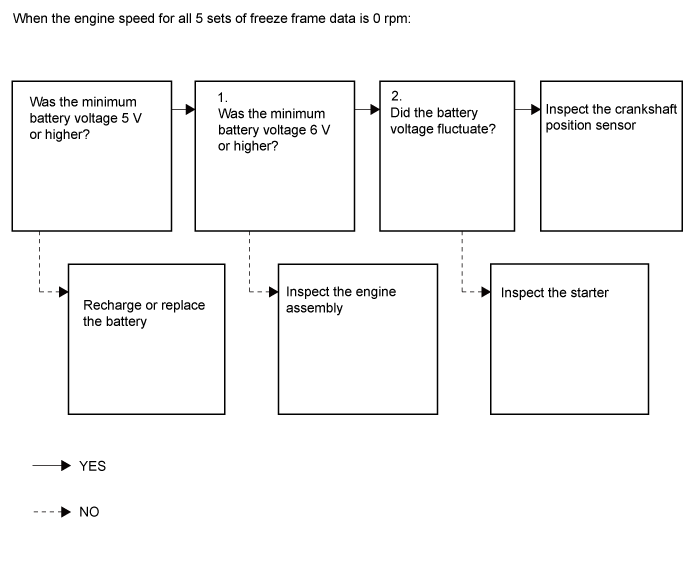
The engine speed recorded in the freeze frame data is 0 rpm (the engine does not crank).
- One of the following problems may be present: battery depletion, excess engine friction, a starter malfunction or a crankshaft position sensor malfunction.
If the battery voltage is less than 6 V during cranking, there is a high probability that engine friction is abnormal.
If the battery voltage drops to 5 V or less when starting the engine, the battery may be malfunctioning.
If the battery voltage fluctuates while cranking the engine, it can be concluded that cranking is being performed. When the engine speed is 0 rpm, the crankshaft position sensor and/or ECM may be malfunctioning.
All engine speeds recorded in the freeze frame data are between 100 and 250 rpm (the engine cranks but there is no combustion).
- If the engine speed is between 100 and 250 rpm (no initial combustion), there may be a wiring problem or a complete failure of an ignition or fuel system part.
Due to an engine coolant temperature sensor malfunction, the fuel injection volume is extremely high or low and the engine may not be able to be started.

The engine speed recorded in the freeze frame data is 250 rpm or higher (the initial combustion and starter turnoff timing is too late).
- If the engine speed is 250 rpm or higher (combustion occurs but the initial combustion and starter turnoff timing is too late), the fuel injection volume is often incorrect (too low or too high) and determining the cause of the malfunction is often difficult.
Due to an engine coolant temperature sensor malfunction, the fuel injection volume is extremely high or low and engine starting trouble may occur.
If Long FT is incorrect, there may be a fuel supply problem due to the injectors or fuel pump being clogged, etc.
If the engine cranking speed is too high, compression loss may have occurred due to carbon interfering with the valve operation.

When the malfunction (starting difficulty) can be reproduced, or malfunction conditions are known, perform the following inspections ("Problem Symptoms" and "Systems to Inspect").
Problem Symptoms
The engine does not crank.
- The starter is normal if a noise that indicates the starter pinion gear is extending is heard. The battery may be fully depleted or there may be excess engine friction.
The engine cranking speed is abnormal.
- If the engine cranking speed is too high (for example, 300 rpm or higher with no combustion), compression loss may have occurred because carbon interfered with valve operation, etc.
There is no initial combustion.
- If there is no initial combustion, there is probably a wiring problem or an ignition or fuel system part malfunction.
The engine stalls after starter turnoff.
- If the engine stalls after starter turnoff, the air-fuel ratio may be incorrect or the VVT may have a problem returning.
The initial combustion and starter turnoff occur late.
- If the initial combustion and starter turnoff occur late, the fuel injection volume is probably incorrect (too low or too high).
- Causes of fuel system malfunctions according to conditions present at the time of the malfunction.
When 2 to 3 minutes have elapsed after stopping the engine: Fuel pressure loss due to the pressure regulator failing to maintain the fuel pressure.
When 15 to 120 minutes have elapsed after stopping the engine: Problem with fuel injector fuel seal.
When a long time has elapsed after stopping the engine: Pressure regulator is stuck open.
Systems to Inspect
Intake system
Ignition system
Fuel system
Freeze frame data exists, but the malfunction (starting difficulty) has not reoccurred and the malfunction conditions are unknown.
| Freeze Frame Data Item | Result | Suspected Area | Procedure |
| Engine Speed | 0 rpm (no engine cranking at all) | Battery fully depleted
Engine assembly (excess friction)
Starter assembly
Immobiliser system
Crankshaft position sensor
ECM
| 4 to 9 |
| 100 to 250 rpm (engine cranks but no initial combustion*1) | Fuel pump control system
Ignition system
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Fuel injection system
| 10 to 14 |
| 250 rpm or higher (combustion occurs but initial combustion and starter turnoff*2 occur late) | Engine assembly (compression loss)
Fuel injection system
Fuel pump control system
| 15 to 23 |
*1: First combustion after cranking begins.
*2: Condition when engine speed increases and starter can be turned off.
When the malfunction (starting difficulty) can be reproduced, or when malfunction conditions are known.
Problem Symptoms
| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Suspected Component | Procedure |
| The engine does not crank | Battery malfunction | | 26 to 31 |
| Starting system | Starter assembly (includes pinion gear wear or tooth damage)
Starting system
|
| Immobiliser system | |
| Engine assembly | Engine assembly (excess friction)
Drive plate wear or tooth damage
|
| Cranking speed too low | Battery malfunction | | 32 to 34 |
| Starting system | |
| Engine assembly | Engine assembly (excess friction)
|
| Cranking speed too high | Engine assembly | Engine assembly (compression loss)
|
| There is no initial combustion | Fuel supply problem | Cannot maintain pressure due to pressure regulator malfunction
Fuel injector leak
Fuel leak from fuel line
Fuel pump control system
Fuel pump
| 35 to 50 |
| Ignition system malfunction | Spark plug
Crankshaft position sensor
Ignition coil assembly
|
| Engine stalls after starter turnoff | Air suction | Intake system connections
| 51 to 57 |
| Deposits in throttle body | |
| VVT valve does not return properly | Camshaft timing oil control valve assembly
|
| Mass air flow meter malfunction | Mass air flow meter assembly
|
| The initial combustion and starter turnoff occur late | Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunction | Engine coolant temperature sensor
| 58 to 71 |
| Mass air flow meter malfunction | Mass air flow meter assembly
|
| Abnormal A/F learned value | |
| Deviation from fuel injection characteristics | |
| Wet-fouled or dry-fouled spark plug | |
| Lack of fuel pressure | Fuel pressure regulator assembly
Fuel pump
Fuel pump control system
|
Systems to Inspect
| Troubleshooting by System | Suspected Area | Suspected Component | Procedure |
| Fuel system troubleshooting A | Abnormal A/F learned value | | 87 to 94
95 to 102 |
| Rough idling | Crankshaft position sensor
|
| Abnormal fuel pressure | Fuel
Fuel leak from fuel line
Fuel pump
Fuel pressure regulator assembly
|
| Fuel system troubleshooting B | Abnormal concentration of HC in surge tank | Purge VSV system
Fuel injector assembly
Intake valve
| 103 to 105 |
| Fuel system troubleshooting C | Injection signal system malfunction | Fuel injector assembly
Crankshaft position sensor
Camshaft position sensor
ECM
| 73 to 77 |
| Intake system troubleshooting | Difference between ISC target value and opening angle when idling | Engine assembly (compression loss)
Valve timing
Engine coolant temperature sensor
ECM
| 84 to 86
106 to 108 |
| Ignition system troubleshooting | Camshaft and/or crankshaft position sensor signal malfunction | Crankshaft position sensor system (including sensor installation)
Camshaft position sensor system (including sensor installation)
ECM
| 78 to 83
109 to 114 |
| 1.CHECK FOR ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT AND RECORD FREEZE FRAME DATA |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes.
Read the DTCs and record the freeze frame data.
This freeze frame data shows the actual engine conditions when engine starting trouble occurred.
When confirming the freeze frame data, be sure to check all 5 data sets of freeze frame data.
The fourth set of freeze frame data is the data recorded when the DTC is stored.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Only DTC P1604 is output | A |
| DTCs other than P1604 are output | B |
| 2.CHECK ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Immobiliser Fuel Cut.
Read the value displayed on the GTS.
- OK:
- Immobiliser Fuel Cut is OFF.
If the engine is started immediately after reconnecting the battery terminal, the engine may stall immediately after it starts due to the intercommunication process between each ECU. For this reason, when starting the engine after reconnecting the battery terminal, first turn the ignition switch to ON and then wait several seconds for the communication process to complete before starting the engine.
When this operation causes DTC P1604 to be stored, this is due to normal operation of the immobiliser system and does not indicate a malfunction, so clear the DTC and return the vehicle to the customer.
| | REPAIR ENGINE IMMOBILISER SYSTEM ()
|
|
|
| 3.CHECK MALFUNCTION CONDITION |
Confirm the problem symptoms.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Freeze frame data exists, but the starting difficulty cannot be reproduced and it is unknown what kind of starting difficulty occurred | A |
| The problem symptoms can be reproduced, or the malfunction conditions are known | B |
| 4.CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Using the GTS, confirm the vehicle conditions recorded in the freeze frame data which were present when the DTC was stored ().
Result| Freeze Frame Data Item | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Engine Speed | Battery Voltage |
| All 5 sets of freeze frame data are 0 rpm (no engine cranking at all) | Minimum voltage is below 5 V | Battery fully depleted | A |
| Minimum voltage is 5 V or higher | Starter malfunction
Crankshaft position sensor system
Excess engine friction
Immobiliser system
ECM
| B |
| 60 to 250 rpm (engine cranks but no initial combustion) | - | Fuel pump control system
Ignition system
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Immobiliser system
Fuel injection system
| C |
| 250 rpm or higher (combustion occurs but initial combustion and starter turnoff occur late) | - | Engine assembly
Fuel injection system
Fuel pump control system
| D |
- When DTC P1604 is stored, either "Engine Start Hesitation"*1 or "Low Rev for Eng Start"*2 in the freeze frame data will be ON. If "Low Rev for Eng Start" is ON, proceed to E.
- *1: This value turns ON when the engine speed does not reach a certain value for a certain period of time when starting the engine.
- *2: This value turns ON when the engine stalls immediately after starting the engine. If "Low Rev for Eng Start" is ON, as there is a possibility that the low engine speed or engine stall was caused by the user, confirm the following freeze frame data items.
Immobiliser Fuel Cut
Engine Speed (starter off)
Shift SW Status (R, D)
| A | |
| |
| CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY |
|
| 5.CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Using the GTS, confirm the vehicle conditions recorded in the freeze frame data which were present when the DTC was stored ().
Result| Freeze Frame Data Item | Result | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Battery Voltage | Minimum voltage is 6 V or higher and voltage does not fluctuate*1 | Starter system | A |
| Minimum voltage is 6 V or higher and voltage fluctuates*2, *3 | Crankshaft position sensor system
ECM
| B |
| Minimum voltage is 5 to 6 V*4 | Excess engine friction
Battery fully depleted
| C |
*1: The 5 sets of freeze frame data show approximately the same battery voltage.
*2: The 5 sets of freeze frame data show different battery voltages.
*3: If the voltage fluctuates, it can be determined that cranking is being performed. When the engine speed is 0 rpm, the crankshaft position sensor system and/or the ECM may be malfunctioning.
*4: There may be excess engine friction. Make sure that the crankshaft rotates smoothly when turning it by hand. Excess engine friction may have occurred temporarily. Remove the cylinder head cover and oil pan, and check for foreign matter such as iron fragments. If there is a malfunction or signs of a malfunction present, perform a detailed inspection by disassembling all the parts.
| |
|
| | CHECK AND REPAIR ENGINE OR BATTERY |
|
|
| A | |
| |
| CHECK STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT ()
|
|
| 6.CHECK SENSOR INSTALLATION |
Check the tightening and installation condition of the crankshaft position sensor bolt.
Check the connection of the crankshaft position sensor connector.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Normal | A |
| Abnormal | B |
| | SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 7.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector.
Check for oil on the connector terminals.
- OK:
- No oil on the terminals.
| | REPLACE CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 8.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C46-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C46-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C46-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C46-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C46-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C46-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C45-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C45-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C45-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C45-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C45-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C45-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 9.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the crankshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 10.CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Using the GTS, confirm the vehicle conditions recorded in the freeze frame data which were present when the DTC was stored ().
Result| Freeze Frame Data Item | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature, Intake Air | Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature | Fuel Pump/Speed Status |
| Difference between Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature and Intake Air is 10°C or more*1 | Coolant Temp is 125°C or higher, or below Ambient Temperature by 15°C or more | - | Engine coolant temperature sensor | A |
| Other than above | All 5 sets of freeze frame data are ON | - | B |
| At least 1 of the 5 sets of freeze frame data is OFF | Fuel pump control system | C |
| Difference between Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature and Intake Air is less than 10°C*2 | - | At least 1 of the 5 sets of freeze frame data is OFF | Fuel pump control system | C |
| All 5 sets of freeze frame data are ON | - | B |
*1: A long time had not elapsed after stopping the engine.
*2: A long time had elapsed after stopping the engine.
| |
|
| | CHECK FUEL PUMP CONTROL SYSTEM ()
|
|
|
| A | |
| |
| REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR ()
|
|
| 11.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Disconnect the connector from the fuel suction tube.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Fuel Pump / Speed.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
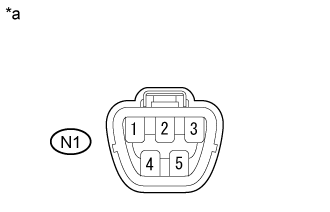
| N1-4 (B2) - Body ground | Active Test is being performed | 11 to 14 V |
Text in Illustration| *a | Front view of wire harness connector
(to Fuel Pump) |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR FUEL PUMP CONTROL SYSTEM ()
|
|
|
| 12.CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (FUEL INJECTOR POWER SOURCE) |
Disconnect the fuel injector connector.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
| Cylinder | Tester Connection | Switch Condition | Specified Condition |
| No. 1 | a5-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 2 | a1-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 3 | a6-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 4 | a2-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 5 | a7-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 6 | a3-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 7 | a8-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 8 | a4-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
Text in Illustration| *a | Front view of wire harness connector
(to Fuel Injector Assembly) |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR FUEL INJECTOR POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT |
|
|
| 13.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Fuel Pump / Speed.
When performing the Active Test, check for fuel leakage from the fuel pipes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage are present | A |
| No fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage | B |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
When performing the Active Test, if there is no operating noise from the fuel pump, the fuel pump system may be malfunctioning.
Check if the vehicle ran out of fuel, as engine starting trouble due to running out of fuel is also detected.
| A | |
| |
| REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL LINE |
|
Check for foreign matter, such as iron particles, around the fuel pump, fuel pump filter and inside the fuel tank, and for signs that the fuel pump was stuck.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| There is foreign matter or signs that fuel pump was stuck | A |
| There is no foreign matter and no signs that fuel pump was stuck | B |
| A | |
| |
| REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL SYSTEM |
|
| 15.CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Using the GTS, confirm the vehicle conditions recorded in the freeze frame data which were present when the DTC was stored ().
Result| Freeze Frame Data Item | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature, Intake Air | Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature | Long FT | Engine Speed |
| Difference between Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature and Intake Air is 10°C or more | Coolant Temp is 125°C or higher, or below Ambient Temperature by 15°C or more | - | - | Engine coolant temperature sensor | A |
| Other than above | -15% or less, or +15% or more | - | Fuel pump control system
Fuel injector assembly
| B |
| -15 to +15% | Minimum speed is 300 rpm or more*1 | Engine assembly | C |
| Minimum speed is less than 300 rpm | Fuel system
Intake air system
| D |
| Difference between Coolant Temp, Ambient Temperature and Intake Air is less than 10°C | - | -15% or less, or +15% or more | - | Fuel pump control system
Fuel injector assembly
| B |
| -15 to +15% | Minimum speed is 300 rpm or more*1 | Engine assembly | C |
| Minimum speed is less than 300 rpm | Fuel system
Intake air system
| D |
- *1: Compression loss may have occurred in the engine assembly.
| A | |
| |
| REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR ()
|
|
| 16.INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
Check that no carbon is stuck to the fuel injector.
| | REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
Check for foreign matter, such as iron particles, around the fuel pump, fuel pump filter and inside the fuel tank, and for signs that the fuel pump was stuck.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| There is foreign matter or signs that fuel pump was stuck | A |
| There is no foreign matter and no signs that fuel pump was stuck | B |
| A | |
| |
| REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL SYSTEM |
|
| 18.CHECK FREEZE FRAME DATA |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Using the GTS, confirm the vehicle conditions recorded in the freeze frame data which were present when the DTC was stored ().
Result| Freeze Frame Data Item | Result | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Coolant Temp | Engine coolant temperature is 40°C or less*1 | Fuel pressure regulator assembly | A |
| Engine coolant temperature is 40 to 90°C*2 | Fuel injector assembly | B |
| Engine coolant temperature is 90°C or higher*3 | Fuel pressure regulator assembly | A |
- *1: If the engine coolant temperature is 40°C or less (after stopping the engine and the vehicle has not been driven for a long period of time), the fuel pressure regulator may be stuck open. Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the ability of the system to maintain fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
- *2: If the engine coolant temperature is 40 to 90°C (15 to 120 minutes have passed after stopping the engine), there may be fuel leaking from a fuel injector.
- *3: If the engine coolant temperature is 90°C or more (2 to 5 minutes have passed after stopping the engine), there may be a problem with the fuel pressure regulator failing to maintain the fuel pressure. Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the ability of the fuel pressure regulator to maintain fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
- For the fuel pressure inspection, refer to the following procedures ().
Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
- Standard:
- 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) or higher (5 minutes after stopping the engine)
- If the engine cannot be started, read the values after cranking the engine.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Normal | A |
| Abnormal | B |
| |
|
| | REPLACE FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| 20.CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
Clean the inside of the surge tank with compressed air.
After stopping the engine, measure the HC concentration inside the surge tank for 15 minutes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| 4000 ppm or more | A |
| Less than 4000 ppm | B |
- If the concentration is 4000 ppm or more, a fuel injector may have a sealing problem.
| 21.CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
Inspect the fuel injector assemblies ().
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Abnormal | A |
| Normal | B |
| A | |
| |
| REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
| 22.CHECK THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY |
Check if carbon is in the airflow passage.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Carbon in passage | A |
| No carbon present | B |
| A | |
| |
| REMOVE FOREIGN OBJECT AND CLEAN THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
Check the intake system for vacuum leaks ().
- OK:
- No leaks in intake system.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE INTAKE SYSTEM |
|
|
| 24.PERFORM SIMULATION TEST |
Check if the engine can be started.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Engine can be started | A |
| Engine cannot be started | B |
| 25.CONFIRM PROBLEM SYMPTOM |
Confirm the problem symptoms.
- The problem symptoms below can be determined by reading the freeze frame data.
Result| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| The engine does not crank | Battery fully depleted
Starter assembly (includes pinion gear wear or tooth damage)
Starter system
Engine assembly (excess friction)
Drive plate wear or tooth damage
| A |
| Abnormal cranking speed | Battery fully depleted
Starter assembly
Engine assembly (excess friction, compression loss)
| B |
| There is no initial combustion (combustion does not occur even once)*1 | Fuel pressure regulator fuel pressure maintenance
Fuel injector leak
Fuel leak from fuel line
Fuel pump control system
Fuel pump
Spark plug
Crankshaft position sensor system
Ignition coil system
| C |
| The engine stalls after starter turnoff (engine stalls immediately after the first time the engine speed increases)*2 | Intake system connections
Throttle body assembly
Camshaft timing oil control valve assembly
Mass air flow meter system
| D |
| The initial combustion and starter turnoff occur late*3 | Engine coolant temperature sensor
Mass air flow meter assembly
Air fuel ratio sensor
Heated oxygen sensor
Fuel injector assembly
Spark plug
Fuel pressure regulator assembly
Fuel pump
Fuel pump control system
| E |
If there is hesitation (cranking speed is slow and combustion occurs before passing TDC) during the initial cranking period, the battery charge may be insufficient or the starter may be malfunctioning.
*1: If there is no initial combustion, a wire harness may be malfunctioning, or the ignition or fuel system may be malfunctioning.
*2: If the engine stalls after starter turnoff, the air-fuel ratio may be incorrect or the camshaft timing oil control valve may have a problem returning.
*3: If the initial combustion and starter turnoff occur late, the fuel injection volume may be incorrect (too low or too high).
| 26.PERFORM SIMULATION TEST |
When cranking the engine, check for a noise indicating that the starter pinion gear is extending, and check that the starter pinion gear is not spinning freely.
Result| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| A noise indicating that the starter pinion gear is extending is heard and the starter pinion gear is not spinning freely*1 | Battery
Excess engine friction
Starter assembly
| A |
| A noise indicating that the starter pinion gear is extending is heard but the starter pinion gear is spinning freely | Drive plate
Starter assembly
| B |
| A noise indicating that the starter pinion gear is extending is not heard | Battery
Starter assembly
Starter system
| C |
- *1: The battery may be fully depleted or there may be excess engine friction.
Check the electrolyte quantity.
- Standard:
- Electrolyte quantity is within the specified range.
Inspect the specific gravity.
Inspect the specific gravity of each cell.
- Standard specific gravity:
- 1.25 to 1.29 (electrolyte is at 20°C (68°F))
If the result is not as specified, recharge or replace the battery.
It is not necessary to inspect a maintenance-free battery.
Inspect the battery voltage.
Turn the engine switch off and turn on the headlights for 20 to 30 seconds. This will remove the surface charge from the battery.
Measure the battery voltage.
- Standard voltage:
- 12.5 to 12.9 V (electrolyte is at 20°C (68°F))
- If the result is not as specified, recharge or replace the battery.
Measure the battery voltage when cranking the engine.
- Standard:
- Approximately 6 V or higher (0°C (32°F) or higher)
- When the battery is depleted, the horn becomes quieter.
| | CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY |
|
|
Check that the crankshaft rotates smoothly when rotating it by hand.
- OK:
- Crankshaft rotates smoothly.
- Excess engine friction may have occurred temporarily. Remove the cylinder head cover and oil pan, and check for foreign matter such as iron fragments. If there is a malfunction or signs of a malfunction present, perform a detailed inspection by disassembling all the parts.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE ENGINE ASSEMBLY |
|
|
| OK | |
| |
| INSPECT STARTER ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
| 29.CHECK STARTER ASSEMBLY |
Remove the starter assembly ().
Check for starter pinion gear wear and damage.
- OK:
- There is no wear or damage.
| | REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| OK | |
| |
| REPLACE DRIVE PLATE AND RING GEAR SUB-ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
Check the electrolyte quantity.
- Standard:
- Electrolyte quantity is within the specified range.
Inspect the specific gravity.
Inspect the specific gravity of each cell.
- Standard specific gravity:
- 1.25 to 1.29 (electrolyte is at 20°C (68°F))
If the result is not as specified, recharge or replace the battery.
It is not necessary to inspect a maintenance-free battery.
Inspect the battery voltage.
Turn the engine switch off and turn on the headlights for 20 to 30 seconds. This will remove the surface charge from the battery.
Measure the battery voltage.
- Standard voltage:
- 12.5 to 12.9 V (electrolyte is at 20°C (68°F))
- If the result is not as specified, recharge or replace the battery.
Measure the battery voltage when cranking the engine.
- Standard:
- Approximately 6 V or higher (0°C (32°F) or higher)
- When the battery is depleted, the horn becomes quieter.
| | CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY |
|
|
| 31.INSPECT STARTER ASSEMBLY |
Inspect the starter assembly ().
| | REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| OK | |
| |
| CHECK STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT ()
|
|
| 32.PERFORM SIMULATION TEST |
Check the cranking speed.
Result| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Cranking speed is slow (100 rpm or less) | Battery
Starter assembly
Excess engine friction
| A |
| Cranking speed is fast (300 rpm or more)*1 | Engine compression loss | B |
- *1: If the cranking speed is fast, there may be compression loss.
Check the electrolyte quantity.
- Standard:
- Electrolyte quantity is within the specified range.
Inspect the specific gravity.
Inspect the specific gravity of each cell.
- Standard specific gravity:
- 1.25 to 1.29 (electrolyte is at 20°C (68°F))
If the result is not as specified, recharge or replace the battery.
It is not necessary to inspect a maintenance-free battery.
Inspect the battery voltage.
Turn the engine switch off and turn on the headlights for 20 to 30 seconds. This will remove the surface charge from the battery.
Measure the battery voltage.
- Standard voltage:
- 12.5 to 12.9 V (electrolyte is at 20°C (68°F))
- If the result is not as specified, recharge or replace the battery.
Measure the battery voltage when cranking the engine.
- Standard:
- Approximately 6 V or higher (0°C (32°F) or higher)
- When the battery is depleted, the horn becomes quieter.
| | CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY |
|
|
Check that the crankshaft rotates smoothly when rotating it by hand.
- OK:
- Crankshaft rotates smoothly.
- Excess engine friction may have occurred temporarily. Remove the cylinder head cover and oil pan, and check for foreign matter such as iron fragments. If there is a malfunction or signs of a malfunction present, perform a detailed inspection by disassembling all the parts.
| OK | |
| |
| INSPECT STARTER ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
| 35.CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
Using a sound scope or screwdriver, check for a fuel injector operating noise while cranking the engine.
- OK:
- Fuel injector operating noise is heard.
Inspect the fuel pressure ().
| 37.CHECK SPARK PLUG AND SPARK |
| 38.CONFIRM VEHICLE CONDITION |
Confirm the conditions present when the malfunction occurred based on the customer problem analysis.
Result| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| When the engine is stopped and a long time has passed, engine starting trouble occurs*1 | Fuel pressure regulator is stuck open | A |
| When the engine is stopped and approximately 15 to 120 minutes have passed, engine starting trouble occurs*2 | Fuel injector leak | B |
| When the engine is stopped and approximately 2 to 3 minutes have passed, engine starting trouble occurs*3 | Failure to maintain fuel pressure by fuel pressure regulator | A |
| Condition other than above, or there is an inconsistency in the conditions present when engine starting trouble occurs | - | C*4 |
- *1: The fuel pressure regulator may be stuck open. Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the ability of the system to maintain fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
- *2: Fuel may be leaking from a fuel injector.
- *3: The fuel pressure regulator may not be able to maintain the fuel pressure. Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the ability of the fuel pressure regulator to maintain fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
- *4: From step 72, perform fuel system troubleshooting C (steps 73 to 77).
- For the fuel pressure inspection, refer to the following procedures ().
Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) or higher (5 minutes after stopping the engine) | A*1 |
| Below 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) (5 minutes after stopping the engine) | B |
If the engine cannot be started, check the fuel pressure after cranking the engine.
*1: From step 72, perform fuel system troubleshooting C (steps 73 to 77).
| |
|
| | REPLACE FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| 40.CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
After stopping the engine, measure the HC concentration inside the surge tank for 15 minutes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| 4000 ppm or more | A |
| Less than 4000 ppm | B*1 |
If the concentration is 4000 ppm or more, a fuel injector may have a sealing problem.
*1: From step 72, perform fuel system troubleshooting C (steps 73 to 77).
| A | |
| |
| REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
Inspect the spark plugs ().
- Even if the spark plug of only one cylinder is malfunctioning, replace the spark plugs of all cylinders.
| 42.READ VALUE USING GTS (ENGINE SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Engine Speed.
While running the engine, read the value of Engine Speed.
- Standard:
- A value that matches the actual engine speed is constantly output.
Check the engine speed using a line graph.
If the engine cannot be started, check the engine speed while cranking the engine.
If the engine speed is 0 rpm, the crankshaft position sensor may have an open or short circuit.
| | CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CIRCUIT ()
|
|
|
| 43.CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (IGNITION COIL POWER SOURCE) |
Disconnect the ignition coil connector.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
| Tester Connection | Switch Condition | Specified Condition |
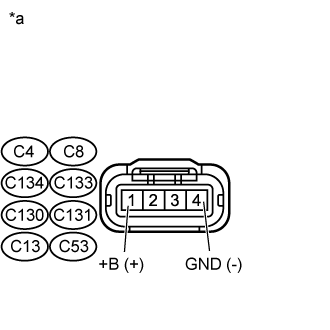
| C4-1 (+B) - C4-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| C134-1 (+B) - C134-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| C130-1 (+B) - C130-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| C13-1 (+B) - C13-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| C8-1 (+B) - C8-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| C133-1 (+B) - C133-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| C131-1 (+B) - C131-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| C53-1 (+B) - C53-4 (GND) | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
Text in Illustration| *a | Front view of wire harness connector
(to Ignition Coil Assembly) |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | CHECK POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT ()
|
|
|
| 44.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL - ECM) |
Disconnect the ignition coil connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C4-2 (IGF1) - C46-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C134-2 (IGF2) - C46-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C130-2 (IGF2) - C46-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C13-2 (IGF1) - C46-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C8-2 (IGF2) - C46-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C133-2 (IGF1) - C46-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C131-2 (IGF1) - C46-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C53-2 (IGF2) - C46-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C4-2 (IGF1) or C46-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C134-2 (IGF2) or C46-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C130-2 (IGF2) or C46-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C13-2 (IGF1) or C46-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C8-2 (IGF2) or C46-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C133-2 (IGF1) or C46-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C131-2 (IGF1) or C46-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C53-2 (IGF2) or C46-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C4-2 (IGF1) - C45-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C134-2 (IGF2) - C45-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C130-2 (IGF2) - C45-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C13-2 (IGF1) - C45-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C8-2 (IGF2) - C45-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C133-2 (IGF1) - C45-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C131-2 (IGF1) - C45-104 (IGF1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C53-2 (IGF2) - C45-105 (IGF2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C4-2 (IGF1) or C45-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C134-2 (IGF2) or C45-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C130-2 (IGF2) or C45-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C13-2 (IGF1) or C45-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C8-2 (IGF2) or C45-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C133-2 (IGF1) or C45-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C131-2 (IGF1) or C45-104 (IGF1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C53-2 (IGF2) or C45-105 (IGF2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 45.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL - ECM) |
Disconnect the ignition coil connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C4-3 (IGT1) - C46-40 (IGT1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C134-3 (IGT2) - C46-33 (IGT2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C130-3 (IGT3) - C46-37 (IGT3) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C13-3 (IGT4) - C46-34 (IGT4) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C8-3 (IGT5) - C46-35 (IGT5) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C133-3 (IGT6) - C46-36 (IGT6) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C131-3 (IGT7) - C46-38 (IGT7) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C53-3 (IGT8) - C46-39 (IGT8) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C4-3 (IGT1) or C46-40 (IGT1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C134-3 (IGT2) or C46-33 (IGT2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C130-3 (IGT3) or C46-37 (IGT3) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C13-3 (IGT4) or C46-34 (IGT4) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C8-3 (IGT5) or C46-35 (IGT5) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C133-3 (IGT6) or C46-36 (IGT6) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C131-3 (IGT7) or C46-38 (IGT7) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C53-3 (IGT8) or C46-39 (IGT8) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C4-3 (IGT1) - C45-40 (IGT1) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C134-3 (IGT2) - C45-33 (IGT2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C130-3 (IGT3) - C45-37 (IGT3) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C13-3 (IGT4) - C45-34 (IGT4) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C8-3 (IGT5) - C45-35 (IGT5) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C133-3 (IGT6) - C45-36 (IGT6) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C131-3 (IGT7) - C45-38 (IGT7) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C53-3 (IGT8) - C45-39 (IGT8) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C4-3 (IGT1) or C45-40 (IGT1) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C134-3 (IGT2) or C45-33 (IGT2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C130-3 (IGT3) or C45-37 (IGT3) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C13-3 (IGT4) or C45-34 (IGT4) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C8-3 (IGT5) or C45-35 (IGT5) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C133-3 (IGT6) or C45-36 (IGT6) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C131-3 (IGT7) or C45-38 (IGT7) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C53-3 (IGT8) or C45-39 (IGT8) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
If the wire harness is normal, after replacing the ignition coil assembly, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs again, proceed to step 72 and perform troubleshooting for the ignition system (steps 78 to 83).
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| OK | |
| |
| REPLACE IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
| 46.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Fuel Pump / Speed.
When performing the Active Test, check for an operating sound from the fuel pump.
- Standard:
| Control the Fuel Pump / Speed | Specified Condition |
| ON | Operating sound heard |
| OFF | Operating sound not heard |
- Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
| | CHECK FUEL PUMP CONTROL SYSTEM ()
|
|
|
| 47.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Fuel Pump / Speed.
When performing the Active Test, check for fuel leakage from the fuel pipes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage are present | A |
| No fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage | B |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Check if the vehicle ran out of fuel, as engine starting trouble due to running out of fuel is also detected.
If there are no fuel leaks, after inspecting the fuel pump control system, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs again, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting C (steps 73 to 77).
| | CHECK FUEL PUMP CONTROL SYSTEM ()
|
|
|
| A | |
| |
| REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL LINE |
|
| 48.READ VALUE USING GTS (ENGINE SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Engine Speed.
While running the engine, read the value of Engine Speed.
- Standard:
- A value that matches the actual engine speed is constantly output.
Check the engine speed using a line graph.
If the engine cannot be started, check the engine speed while cranking the engine.
If the engine speed is 0 rpm, the crankshaft position sensor may have an open or short circuit.
| | REPLACE CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 49.CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (FUEL INJECTOR POWER SOURCE) |
Disconnect the fuel injector connector.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
| Cylinder | Tester Connection | Switch Condition | Specified Condition |
| No. 1 | a5-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 2 | a1-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 3 | a6-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 4 | a2-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 5 | a7-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 6 | a3-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 7 | a8-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 8 | a4-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
Text in Illustration| *a | Front view of wire harness connector
(to Fuel Injector Assembly) |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT ()
|
|
|
| 50.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (FUEL INJECTOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the fuel injector connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Cylinder | Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| No. 1 | a5-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a5-1 - C46-86 (#10) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 2 | a1-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a1-1 - C46-109 (#20) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 3 | a6-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a6-1 - C46-85 (#30) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 4 | a2-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a2-1 - C46-108 (#40) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 5 | a7-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a7-1 - C46-84 (#50) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 6 | a3-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a3-1 - C46-107 (#60) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 7 | a8-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a8-1 - C46-83 (#70) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 8 | a4-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a4-1 - C46-106 (#80) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
for LHD| Cylinder | Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| No. 1 | a5-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a5-1 - C45-86 (#10) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 2 | a1-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a1-1 - C45-109 (#20) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 3 | a6-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a6-1 - C45-85 (#30) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 4 | a2-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a2-1 - C45-108 (#40) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 5 | a7-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a7-1 - C45-84 (#50) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 6 | a3-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a3-1 - C45-107 (#60) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 7 | a8-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a8-1 - C45-83 (#70) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 8 | a4-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a4-1 - C45-106 (#80) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 51.CHECK MASS AIR FLOW METER ASSEMBLY |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
- The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off, and the shift lever should be in N or P.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / MAF.
Check MAF in the Data List during idling.
- Standard:
- 3.4 to 6.2 gm/sec.
Check for air leakage in the intake system [due to vacuum hose disconnection, cracks, damaged gaskets, etc.] ().
If the accelerator pedal is released after racing the engine, the inspection is easier to perform because the vacuum inside the intake manifold increases and the air suction noise becomes louder.
If Short FT and Long FT are largely different from the normal values (differ by more than 15%) when idling (intake air volume is small) and almost the same as the normal values when racing the engine (for example, when maintaining a speed of 3000 rpm) (intake air volume is high), air leakage may be present.
- OK:
- There is no air leakage.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE INTAKE SYSTEM |
|
|
| 53.CHECK THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY |
Disconnect the throttle body connector.
- When the connector is disconnected, the vehicle enters fail-safe mode and the throttle valve opening angle is 4 to 7°.
Crank the engine and check that it starts.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Engine starts | A |
| Engine does not start | B |
Connect the throttle body connector.
- When this inspection is performed, the MIL may illuminate. After finishing the inspection, check and clear DTCs ().
| 54.CHECK THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY |
Check if carbon is in the airflow passage.
| | REMOVE FOREIGN OBJECT AND CLEAN THROTTLE BODY |
|
|
| 55.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE VVT SYSTEM) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the VVT System (Bank 1) or Control the VVT System (Bank 2).
- When performing the Active Test, make sure the A/C is on and the shift lever is in N.
Check the engine speed while operating the camshaft timing oil control valve using the GTS.
- OK:
| GTS Operation | Specified Condition |
| OFF | Normal engine speed |
| ON | Soon after camshaft timing oil control valve switched from OFF to ON, engine idles roughly or stalls |
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| NG | A |
| OK | B |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
When the results of the inspection using the Active Test are normal but the valve operating noise is abnormal, check the valve for any signs of problems.
If the camshaft timing oil control valve is stuck ON, the valve overlap increases and combustion worsens due to the internal EGR which may cause the engine to stall.
| A | |
| |
| REPLACE CAMSHAFT TIMING OIL CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY (FOR INTAKE SIDE) ()
|
|
| 56.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE VVT EXHAUST LINEAR) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the VVT Exhaust Linear (Bank1) or Control the VVT Exhaust Linear (Bank2).
- When performing the Active Test, make sure the A/C is on and the shift lever is in N.
Check the engine speed while operating the camshaft timing oil control valve using the GTS.
- OK*1:
| GTS Operation | Specified Condition |
| 0% | Normal engine speed |
| 100% | Engine idles roughly or stalls |
*1: From step 72, perform intake system troubleshooting (steps 84 to 86). If engine starting trouble still occurs, perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 87 to 94).
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
When the results of the inspection using the Active Test are normal but the valve operating noise is abnormal, check the valve for any signs of problems.
If the camshaft timing oil control valve is stuck ON, the valve overlap increases and combustion worsens due to the internal EGR which may cause the engine to stall.
| |
|
| | REPLACE CAMSHAFT TIMING OIL CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY (FOR EXHAUST SIDE) ()
|
|
|
| 57.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (MASS AIR FLOW METER - ECM) |
Disconnect the mass air flow meter connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C50-3 (VG) - C46-74 (VG) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-2 (E2G) - C46-75 (E2G) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-3 (VG) or C46-74 (VG) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C50-3 (VG) - C45-74 (VG) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-2 (E2G) - C45-75 (E2G) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-3 (VG) or C45-74 (VG) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
If the wire harness is normal, after replacing the mass air flow meter, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs again, proceed to step 72 and perform intake system troubleshooting (steps 84 to 86). If engine starting trouble still occurs, perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 87 to 94).
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| OK | |
| |
| REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
| 58.INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR |
Inspect the engine coolant temperature sensor ().
- If the engine coolant temperature sensor is malfunctioning, after replacing it, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs, replace the ECM. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| | REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 59.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the engine coolant temperature sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C18-2 - C46-76 (THW) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C18-1 - C46-98 (E2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C18-2 or C46-76 (THW) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C18-1 or C46-98 (E2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C18-2 - C45-76 (THW) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C18-1 - C45-98 (E2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C18-2 or C45-76 (THW) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C18-1 or C45-98 (E2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
If the wire harness or connector is malfunctioning, after replacing or repairing it, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs, replace the ECM. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 60.CHECK MASS AIR FLOW METER ASSEMBLY |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
- The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off, and the shift lever should be in N or P.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / MAF.
Check MAF in the Data List during idling.
- Standard:
- 3.4 to 6.2 rm/sec.
- If the mass air flow meter is malfunctioning, after replacing it, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs, replace the ECM. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| | REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| 61.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (MASS AIR FLOW METER - ECM) |
Disconnect the mass air flow meter connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C50-3 (VG) - C46-74 (VG) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-2 (E2G) - C46-75 (E2G) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-3 (VG) or C46-74 (VG) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C50-3 (VG) - C45-74 (VG) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-2 (E2G) - C45-75 (E2G) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C50-3 (VG) or C45-74 (VG) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
If the wire harness or connector is malfunctioning, after replacing or repairing it, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs, replace the ECM. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Long FT and Atmosphere Pressure.
Result| Data List Item | Result | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Long FT | +25% or more or less than -25% | Air fuel ratio sensor
Heated oxygen sensor
Mass air flow meter assembly
Fuel injector assembly
ECM
| A |
| Atmosphere Pressure | 80 kPa or less (when elevation is 0 m) |
| Both Data List items listed above | Values are other than above | - | B |
| 63.PERFORM SIMULATION TEST |
Remove the EFI and ETCS fuses from the engine room relay block.
After 60 seconds or more elapse, install the EFI and ETCS fuses.
Check if the engine can be started.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Engine can be started | A |
| Engine cannot be started | B |
| 64.INSPECT AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Fuel System Status #1 and Fuel System Status #2.
Confirm that Fuel System Status #1 and Fuel System Status #2 are both CL.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / AF Lambda B1S1 and AF Lambda B2S1.
Confirm that AF Lambda B1S1 and AF Lambda B2S1 are both within the range of 0.95 to 1.05 when idling.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F sensor.
Read the output voltage from the air fuel ratio sensor when increasing and decreasing the fuel injection volume.
- Standard:
| GTS Display | Injection Volume | Specified Condition |
AFS Voltage B1S1
AFS Voltage B2S1 | +12.5% | Air fuel ratio sensor output voltage is below 3.1 V |
| -12.5% | Air fuel ratio sensor output voltage is higher than 3.4 V |
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Normal | A |
| Abnormal | B |
The air fuel ratio sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the heated oxygen sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
If the air fuel ratio sensor is malfunctioning, after replacing it, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs, replace the ECM. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| | REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 65.PERFORM SIMULATION TEST |
Check if the idling speed is stable after starting the engine.
- After replacing the fuel injector or mass air flow meter, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble occurs, replace the ECM. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| | REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| OK | |
| |
| REPLACE MASS AIR FLOW METER ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
Inspect the fuel pressure ().
Inspect the spark plugs ().
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| All cylinders are normal | A |
| One cylinder is abnormal*1 | B |
| All cylinders are abnormal*2, *3 | C |
*1: If one cylinder is abnormal, replace the spark plug of that cylinder and inspect the ignition and fuel system for that cylinder. After performing repairs, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
*2: If all cylinders are abnormal, replace the spark plugs of all cylinders and check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
*3: Engine starting trouble may occur if the vehicle is driven extremely short distances repeatedly.
| | REPLACE SPARK PLUG (ABNORMAL CYLINDER) ()
|
|
|
| | REPLACE SPARK PLUG (ALL) ()
|
|
|
| 68.CONFIRM VEHICLE CONDITION |
Confirm the conditions present when the malfunction occurred based on the customer problem analysis.
Result| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| When the engine is stopped and a long time has passed, engine starting trouble occurs*1 | Fuel pressure regulator is stuck open | A |
| When the engine is stopped and approximately 15 to 120 minutes have passed, engine starting trouble occurs*2 | Fuel injector leak | B |
| When the engine is stopped and approximately 2 to 3 minutes have passed, engine starting trouble occurs*3 | Failure to maintain fuel pressure by fuel pressure regulator | A |
| Condition other than above, or there is an inconsistency in the conditions present when engine starting trouble occurs | - | C*4 |
- *1: The fuel pressure regulator may be stuck open. Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the ability of the system to maintain fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
- *2: Fuel may be leaking from a fuel injector.
- *3: The fuel pressure regulator may not be able to maintain the fuel pressure. Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the ability of the fuel pressure regulator to maintain fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
- *4: From step 72, perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
- For the fuel pressure inspection, refer to the following procedures ().
Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) or higher (5 minutes after stopping the engine) | A*1 |
| Below 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) (5 minutes after stopping the engine) | B |
If the engine cannot be started, check the fuel pressure after cranking the engine.
*1: From step 72, perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| |
|
| | REPLACE FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| 70.CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
Clean the inside of the surge tank with compressed air.
After stopping the engine, measure the HC concentration inside the surge tank for 15 minutes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| 4000 ppm or more | A |
| Less than 4000 ppm | B*1 |
If the concentration is 4000 ppm or more, a fuel injector may have a sealing problem.
*1: From step 72, perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| A | |
| |
| REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
| 71.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Fuel Pump / Speed.
When performing the Active Test, check for fuel leakage from the fuel pipes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage are present | A |
| No fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage | B |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Check if the vehicle ran out of fuel, as engine starting trouble due to running out of fuel is also detected.
If there are no fuel leaks, after inspecting the fuel pump control system, check if engine starting trouble occurs again. If engine starting trouble still occurs, proceed to step 72 and perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
| | CHECK FUEL PUMP CONTROL SYSTEM ()
|
|
|
| A | |
| |
| REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL LINE |
|
| 72.CHECK MALFUNCTION CONDITION |
If the malfunction could not be identified during the inspections in steps 38, 39, 40 and 47, perform fuel system troubleshooting C (steps 73 to 77).
Result| Performed Step | Troubleshooting by System | Procedure | Proceed to |
| Steps 38, 39, 40 and 47 | Fuel system troubleshooting C | 73 to 77 | A |
If the malfunction could not be identified during the inspection in step 45, perform ignition system troubleshooting (steps 78 to 83).
Result| Performed Step | Troubleshooting by System | Procedure | Proceed to |
| Step 45 | Ignition system troubleshooting | 78 to 83 | B |
If the malfunction could not be identified during the inspections in steps 55, 56 and 57, perform intake air system troubleshooting (steps 84 to 86). If engine starting trouble still occurs, perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 87 to 94).
Result| Performed Step | Troubleshooting by System | Procedure | Proceed to |
| Step 55, 56 and 57 | Intake air system troubleshooting | 84 to 86 | C |
| Fuel system troubleshooting A | 87 to 94 |
If the malfunction could not be identified during the inspections in steps 58, 59, 60, 61, 64, 65, 67, 68, 69, 70 and 71, perform fuel system troubleshooting A (steps 95 to 102), fuel system troubleshooting B (steps 103 to 105), intake air system troubleshooting (steps 106 to 108), and ignition system troubleshooting (steps 109 to 114), in that order.
Result| Performed Step | Troubleshooting by System | Procedure | Proceed to |
| Steps 58, 59, 60, 61, 64, 65, 67, 68, 69, 70 and 71 | Fuel system troubleshooting A | 95 to 102 | D |
| Fuel system troubleshooting B | 103 to 105 |
| Intake air system troubleshooting | 106 to 108 |
| Ignition system troubleshooting | 109 to 114 |
| 73.INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
Inspect the fuel injector assemblies ().
| | REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| 74.CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (FUEL INJECTOR POWER SOURCE) |
Disconnect the fuel injector connector.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
| Cylinder | Tester Connection | Switch Condition | Specified Condition |
| No. 1 | a5-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 2 | a1-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 3 | a6-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 4 | a2-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 5 | a7-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 6 | a3-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 7 | a8-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
| No. 8 | a4-2 - Body ground | Engine switch on (IG) | 11 to 14 V |
Text in Illustration| *a | Front view of wire harness connector
(to Fuel Injector Assembly) |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT ()
|
|
|
| 75.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (FUEL INJECTOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the fuel injector connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Cylinder | Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| No. 1 | a5-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a5-1 - C46-86 (#10) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 2 | a1-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a1-1 - C46-109 (#20) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 3 | a6-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a6-1 - C46-85 (#30) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 4 | a2-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a2-1 - C46-108 (#40) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 5 | a7-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a7-1 - C46-84 (#50) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 6 | a3-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a3-1 - C46-107 (#60) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 7 | a8-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a8-1 - C46-83 (#70) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 8 | a4-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a4-1 - C46-106 (#80) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
for LHD| Cylinder | Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| No. 1 | a5-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a5-1 - C45-86 (#10) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 2 | a1-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a1-1 - C45-109 (#20) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 3 | a6-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a6-1 - C45-85 (#30) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 4 | a2-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a2-1 - C45-108 (#40) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 5 | a7-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a7-1 - C45-84 (#50) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 6 | a3-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a3-1 - C45-107 (#60) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 7 | a8-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a8-1 - C45-83 (#70) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| No. 8 | a4-1 - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| a4-1 - C45-106 (#80) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 76.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the crankshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 77.CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the camshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 78.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Check the tightening and installation condition of the crankshaft position sensor bolt.
Check the connection of the crankshaft position sensor connector.
- OK:
- Sensor is installed correctly.
| | SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 79.CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Check the tightening and installation condition of the camshaft position sensor bolt.
Check the connection of the camshaft position sensor connector.
- OK:
- Sensor is installed correctly.
| | SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 80.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C46-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C46-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C46-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C46-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C46-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C46-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C45-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C45-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C45-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C45-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C45-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C45-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 81.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the camshaft position sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C99-1 (G2) - C46-90 (G2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-2 (G-) - C46-89 (G2-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-3 (VC) - C46-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-1 (G2) or C46-90 (G2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-2 (G-) or C46-89 (G2-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-3 (VC) or C46-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C99-1 (G2) - C45-90 (G2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-2 (G-) - C45-89 (G2-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-3 (VC) - C45-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-1 (G2) or C45-90 (G2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-2 (G-) or C45-89 (G2-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-3 (VC) or C45-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 82.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the crankshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 83.CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the camshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 84.READ VALUE USING GTS (ISC LEARNING VALUE) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature stabilizes with the A/C switch and all the accessory switches off.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / ISC Learning Value.
Result| Data List Item | Result | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| ISC Learning Value | (engine displacement (liters) x 0.9) or more | | A |
| Less than (engine displacement (liters) x 0.9) | - | B |
| 85.CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE |
Inspect the compression ().
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE ENGINE ASSEMBLY |
|
|
| OK | |
| |
| CHECK ENGINE MECHANICAL SYSTEM |
|
| 86.INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR |
Inspect the engine coolant temperature sensor ().
| | REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR ()
|
|
|
- For the fuel pressure inspection, refer to the following procedures ().
Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the fuel pressure when cranking the engine and after stopping the engine.
Result| Vehicle State | Specified Condition |
| Cranking engine | 304 to 343 kPa (3.1 to 3.5 kgf/cm2) |
| 5 minutes after stopping engine | 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) or higher |
| 88.READ VALUE USING GTS (LONG FT) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Long FT.
Result| Data List Item | Result | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Long FT | -15 to +15% | Wire harness or connector
Fuel
| A |
| +15% or more, or less than -15% | Fuel injector assembly | B |
| | REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| 89.PERFORM SIMULATION TEST |
Check if the idling speed is stable after starting the engine and if an unstable idling speed has ever occurred in the past.
Result| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Current unstable idling speed or history of unstable idling speed | Crankshaft position sensor system | A |
| All current and past idling speeds are stable | Fuel | B |
- Through the customer problem analysis, confirm the fuel being used and the location at which the fuel was added to check if the malfunction is caused by the fuel in the vehicle.
| 90.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Check the tightening and installation condition of the crankshaft position sensor bolt.
Check the connection of the crankshaft position sensor connector.
- OK:
- Sensor is installed correctly.
| | SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 91.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C46-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C46-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C46-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C46-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C46-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C46-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C45-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C45-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C45-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C45-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C45-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C45-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 92.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the crankshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 93.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Fuel Pump / Speed.
When performing the Active Test, check for fuel leakage from the fuel pipes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage are present | A |
| No fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage | B |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
When performing the Active Test, if there is no operating noise from the fuel pump, the fuel pump system may be malfunctioning.
Check if the vehicle ran out of fuel, as engine starting trouble due to running out of fuel is also detected.
| A | |
| |
| REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL LINE |
|
Inspect the fuel pump ().
Make sure there is no foreign matter such as iron particles on the fuel pump and no signs that the fuel pump was stuck.
Make sure the internal connector is securely connected.
Make sure the fuel pump filter is not clogged.
| OK | |
| |
| REPLACE FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
- For the fuel pressure inspection, refer to the following procedures ().
Attach a fuel pressure gauge and check the fuel pressure after stopping the engine.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) or higher (5 minutes after stopping the engine) | A |
| Below 147 kPa (1.5 kgf/cm2) (5 minutes after stopping the engine) | B |
| 96.READ VALUE USING GTS (LONG FT) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Long FT.
Result| Data List Item | Result | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Long FT | -15 to +15% | Wire harness or connector
Fuel
| A |
| +15% or more, or less than -15% | Fuel injector assembly | B |
| | REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
|
| 97.PERFORM SIMULATION TEST |
Check if the idling speed is stable after starting the engine and if an unstable idling speed has ever occurred in the past.
Result| Problem Symptom | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| Current unstable idling speed or history of unstable idling speed | Crankshaft position sensor system | A |
| All current and past idling speeds are stable | Fuel | B |
- Through the customer problem analysis, confirm the fuel being used and the location at which the fuel was added to check if the malfunction is caused by the fuel in the vehicle.
| 98.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Check the tightening and installation condition of the crankshaft position sensor bolt.
Check the connection of the crankshaft position sensor connector.
- OK:
- Sensor is installed correctly.
| | SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 99.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C46-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C46-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C46-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C46-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C46-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C46-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C45-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C45-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C45-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C45-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C45-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C45-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 100.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the crankshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 101.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE FUEL PUMP / SPEED) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Fuel Pump / Speed.
When performing the Active Test, check for fuel leakage from the fuel pipes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage are present | A |
| No fuel leakage or signs of fuel leakage | B |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
When performing the Active Test, if there is no operating noise from the fuel pump, the fuel pump system may be malfunctioning.
Check if the vehicle ran out of fuel, as engine starting trouble due to running out of fuel is also detected.
| A | |
| |
| REPAIR OR REPLACE FUEL LINE |
|
Inspect the fuel pump ().
Make sure there is no foreign matter such as iron particles on the fuel pump and no signs that the fuel pump was stuck.
Make sure the internal connector is securely connected.
Make sure the fuel pump filter is not clogged.
Disconnect the vacuum hose (on the canister side) of the purge VSV.
Disconnect the connector of the purge VSV.
Check if air flows through the purge VSV.
- Standard:
- Air does not flow
Connect the connector of the purge VSV.
Connect the vacuum hose of the purge VSV.
- When this inspection is performed, the MIL may illuminate. After finishing the inspection, check and clear DTCs ().
| 104.CHECK FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY |
Clean the inside of the surge tank with compressed air.
After stopping the engine, measure the HC concentration inside the surge tank for 15 minutes.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| 4000 ppm or more | A |
| Less than 4000 ppm | B |
- If the concentration is 4000 ppm or more, a fuel injector may have a sealing problem.
| A | |
| |
| REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY ()
|
|
Check if carbon is on the intake valves.
Result| Result | Proceed to |
| Carbon present | A |
| No carbon present | B |
| 106.READ VALUE USING GTS (ISC LEARNING VALUE) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the engine switch on (IG).
Start the engine, turn off all accessory switches and warm up the engine until the engine coolant temperature stabilizes.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / ISC Learning Value.
Result| Data List Item | Result | Suspected Area | Proceed to |
| ISC Learning Value | (engine displacement (liters) x 0.9) or more | | A |
| Less than (engine displacement (liters) x 0.9) | - | B |
| 107.CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE |
Inspect the compression ().
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE ENGINE ASSEMBLY |
|
|
| 108.INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR |
Inspect the engine coolant temperature sensor ().
| | REPLACE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 109.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Check the tightening and installation condition of the crankshaft position sensor bolt.
Check the connection of the crankshaft position sensor connector.
- OK:
- Sensor is installed correctly.
| | SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 110.CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Check the tightening and installation condition of the camshaft position sensor bolt.
Check the connection of the camshaft position sensor connector.
- OK:
- Sensor is installed correctly.
| | SECURELY REINSTALL SENSOR ()
|
|
|
| 111.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C46-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C46-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C46-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C46-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C46-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C46-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C114-1 (NE+) - C45-110 (NE+) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-2 (NE-) - C45-111 (NE-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-3 (VC) - C45-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C114-1 (NE+) or C45-110 (NE+) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-2 (NE-) or C45-111 (NE-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C114-3 (VC) or C45-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 112.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the camshaft position sensor connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for RHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C99-1 (G2) - C46-90 (G2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-2 (G-) - C46-89 (G2-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-3 (VC) - C46-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-1 (G2) or C46-90 (G2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-2 (G-) or C46-89 (G2-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-3 (VC) or C46-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
for LHD| Tester Connection | Condition | Specified Condition |
| C99-1 (G2) - C45-90 (G2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-2 (G-) - C45-89 (G2-) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-3 (VC) - C45-66 (VCV2) | Always | Below 1 Ω |
| C99-1 (G2) or C45-90 (G2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-2 (G-) or C45-89 (G2-) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| C99-3 (VC) or C45-66 (VCV2) - Body ground | Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
Jiggle the wire harness and connector to increase the likelihood of detecting malfunctions that do not always occur.
Make sure there is not an excessive amount of force applied to the wire harness.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 113.CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the crankshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|
| 114.CHECK CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR |
Replace the camshaft position sensor ().
Check the engine start operation.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
| OK | |
| |
| END (CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR IS DEFECTIVE) |
|