Engine -- On-Vehicle Inspection |
| 1. INSPECT IGNITION TIMING |
- NOTICE:
- Turn all electrical systems off.
- Perform the inspection when the cooling fan motor is turned off.
Warm up the engine.
When using the GTS:
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / IGN Advance.
- Standard ignition timing:
- 7 to 24° BTDC @ idle (transmission in neutral and A/C switch off)
- HINT:
- Refer to the GTS operator's manual for further details.
Check that the ignition timing advances immediately when the engine speed is increased.
Disconnect the GTS from the DLC3.
When not using the GTS:
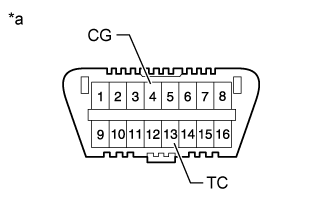
Using SST, connect terminals 13 (TC) and 4 (CG) of the DLC3.
- SST
- 09843-18040
Text in Illustration *a Front view of DLC3 - NOTICE:
- Be sure not to improperly connect the terminals. This may damage the engine.
Connect the tester probe of a timing light to the wire of the ignition coil connector for the No. 1 cylinder.
- NOTICE:
- Use a timing light that detects primary signals.
Inspect the ignition timing during idling.
- Standard ignition timing:
- 8 to 12° BTDC @ idle (transmission in neutral and A/C switch off)
Remove SST from the DLC3.
Inspect the ignition timing during idling.
- Standard ignition timing:
- 7 to 24° BTDC @ idle (transmission in neutral and A/C switch off)
Disconnect the timing light from the engine.
| 2. INSPECT ENGINE IDLE SPEED |
- NOTICE:
- Turn all the electrical systems off.
- Perform the inspection when the cooling fan motor is turned off.
Warm up the engine.
When using the GTS:
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Engine Speed.
- Standard idle speed:
- 650 to 750 rpm (transmission in neutral and A/C switch off)
- HINT:
- Refer to the GTS operator's manual for further details.
Disconnect the GTS from the DLC3.
When not using the GTS:
Connect SST to terminal 9 (TAC) of the DLC3.
- SST
- 09843-18030
Text in Illustration *a Front view of DLC3 - NOTICE:
- Be sure not to improperly connect SST. This may damage the engine.
Race the engine at 2500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
Inspect the engine idle speed.
- Standard idle speed:
- 650 to 750 rpm (transmission in neutral and A/C switch off)

| 3. INSPECT COMPRESSION |
Warm up and stop the engine.
Check for DTCs (Click here).
Remove the 8 spark plugs (Click here).
Disconnect the 8 fuel injector connectors.
Inspect the cylinder compression pressure.
Insert a compression gauge into the spark plug hole. (Procedure A)
While cranking the engine, measure the compression pressure. (Procedure B)
- Standard compression pressure:
- 1300 kPa (13.3 kgf/cm2, 189 psi) or higher
- Minimum pressure:
- 1000 kPa (10.2 kgf/cm2, 145 psi)
- Difference between each cylinder:
- 100 kPa (1.0 kgf/cm2, 15 psi) or less
- HINT:
- Use a fully-charged battery so that the engine speed can be increased to 250 rpm or more.
- Measure the compression in as short a time as possible.
If the cylinder compression is low, pour a small amount of engine oil into the cylinder through the spark plug hole and repeat procedures A and B for cylinders with low compression.
- HINT:
- If adding oil increases the compression, the piston rings and/or cylinder bore may be worn or damaged.
- If pressure stays low, a valve may be stuck or seated improperly, or there may be leakage from the gasket.
Repeat procedures A and B for each cylinder.
Connect the 8 injector connectors.
Install the 8 spark plugs (Click here).
Clear the DTCs (Click here).
| 4. INSPECT CO/HC |
- HINT:
- This check is to determine whether or not the idle CO/HC concentration complies with regulations.
Start the engine.
Run the engine at 2500 rpm for approximately 180 seconds.
Insert the CO/HC meter testing probe at least 40 cm (1.31 ft) into the tailpipe during idling.
Immediately check the CO/HC concentration during idling and/or at 2500 rpm.
- HINT:
- When carrying out the 2 tests (idling and 2500 rpm), the measurement procedures are prescribed by applicable local regulations.
If the CO/HC concentration does not comply with regulations, perform troubleshooting in the order given below.
Check the air fuel ratio sensor operation (Click here) and heated oxygen sensor operation (Click here).
Refer to the table below for possible causes, and then inspect and correct the corresponding causes if necessary.
CO HC Symptom Causes Normal High Rough idling - Faulty ignition:
- Incorrect timing
- Plugs are contaminated or shorted, or plug gaps are incorrect
- Leaky intake and exhaust valves
- Leaky cylinders
Low High Rough idling
(Fluctuating HC reading)- Vacuum leaks:
- PCV hoses
- Intake manifold
- Throttle body
- Lean mixture causing misfire
High High Rough idle
(Black smoke from exhaust)- Restricted air filter
- Plugged PCV valve
- Faulty SFI system:
- Faulty pressure regulator
- Defective engine coolant temperature sensor
- Faulty mass air flow meter
- Faulty ECM
- Faulty injectors
- Faulty throttle position sensor
- Faulty ignition: