DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
CHECK ENGINE CRANKING CONDITION
READ ALL OUTPUT DTCS
TAKE SNAPSHOT DURING STARTING AND IDLING (PROCEDURE 3)
CHECK SNAPSHOT (COMMON RAIL PRESSURE)
CHECK IF FUEL IS BEING SUPPLIED TO FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE - ECM)
REPLACE FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE)
BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM
PERFORM SUPPLY PUMP INITIALIZATION
READ VALUE USING GTS (COMMON RAIL PRESSURE)
INSPECT INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (INSPECTION FOR VALVE CLOSING PROBLEM)
CHECK AND REPAIR OR REPLACE CLOGGED FUEL PIPE (INCLUDING FROZEN FUEL) (FUEL TANK - FUEL SUPPLY PUMP)
BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM
READ VALUE USING GTS (COMMON RAIL PRESSURE)
REPLACE FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE)
PERFORM SUPPLY PUMP INITIALIZATION
REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES OF ALL CYLINDERS
INSPECT INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (CHECKING FOR PRESENCE OF AIR)
CHECK DATA LIST
REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES OF ALL CYLINDERS
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CHECK THE CYLINDER COMPRESSION)
CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER
REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLY OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER
CLEAN FUEL FILTER CASE AND REPLACE FUEL FILTER
BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM
REGISTER INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE AND PERFORM PILOT QUANTITY LEARNING
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
INSPECT INJECTOR DRIVER
INSPECT INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (CHECKING FOR PRESENCE OF AIR)
CHECK TEMPERATURE WHEN STARTING TROUBLE OCCURS
READ VALUE USING ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (COOLANT TEMP)
INSPECT GLOW PLUG (RESISTANCE)
CHECK FUEL QUALITY
READ OUTPUT DTC (RELATED TO ENGINE)
CHECK COMMUNICATION BETWEEN GTS AND ECM
READ VALUE USING GTS (STARTER SIGNAL AND NEUTRAL POSITION SW SIGNAL)
CHECK STARTING SYSTEM
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
ECD SYSTEM (w/ DPF) - Engine Difficult to Start or Stalling |
DESCRIPTION
| Faults and Symptoms of Common Rail Diesel Components |
Engine Control
Mass Air Flow MeterMain fault
| Decrease in performance (foreign matter is stuck)
|
Symptoms
| Lack of power, black smoke
|
Data List
| MAF
|
- HINT:
- The maximum fuel injection volume is controlled according to the output from the mass air flow meter.
|
Intake SystemSymptom and Corresponding Main Fault
| - Lack of power (no black smoke) due to air filter blockage or crushed or leaking air duct
- Black smoke (no lack of power) due to leakage between the turbo and intake manifold
|
Data List
| MAP
|
Turbocharger SystemMain fault
| - Air leak in the turbocharged air passage
- ECM not operating well
- Turbocharger sub-assembly (turbine, bearing)
|
Symptoms
| Lack of power (when vehicle is starting, under heavy load)
(Black smoke is not emitted when racing while vehicle is stopped)
|
Data List
| MAP
- With the ignition switch ON or during idling, MAP = atmospheric pressure (standard atmospheric pressure = 101 kPa). When the engine speed is about 1500 rpm or more, the turbocharger starts to take effect and MAP becomes higher than atmospheric pressure.
- Atmospheric pressure decreases by 1 kPa each time elevation increases by 100 m, and is also affected by the current weather conditions.
|
Exhaust SystemMain fault
| Blockage
|
Symptoms
| Lack of power (high engine speed, under heavy load)
|
Glow SystemMain fault
| Glow system malfunction
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle, knocking, white smoke (when cold)
|
Data List
| Check the glow plug indicator light
|
Diagnostic Point
| Measure the resistance of the glow plug
|
BatteryMain fault
| Battery is depleted
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start (cannot crank, crank speed is low), horn is quiet
|
Data List
| Battery Voltage
When cranking, battery voltage is below 5 V.
|
Engine - 1Main fault
| Damaged, seized up
|
Symptoms
| Cannot crank, crank speed is low, strange noise
|
Engine - 2Main fault
| Loss of compression
|
Symptoms
| Rough idle (lack of power always)
|
Data List
| Engine Speed of Cyl
- When cranking during the "Check the Cylinder Compression" Active Test, if there is a high speed cylinder, approx. 100 rpm more than the other cylinders, that cylinder may lose compression.
Injection Feedback Val
- When an Injector Feedback Val is more than 3 mm3/st, there may be a malfunction in the corresponding cylinder.
|
Start SystemMain fault
| Starter system malfunction
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start
|
Data List
| Starter Signal
- Ignition switch (STA) output:
Open: Starter is operating
Close: Starter is not operating
|
Diesel Injection
Fuel Supply Pump AssemblyMain fault
| -
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, engine stalling, rough idle, lack of power
|
Data List
| Common Rail Pressure, Target Common Rail Pressure, Target Pump SCV Current
- Common Rail Pressure is within 5000 kPa of Target Common Rail Pressure during idling with the engine warmed up (engine coolant temperature is higher than 75°C (167°F)).
- If the fuel pressure is 20000 kPa below the target pressure, then a lack of power will be felt.
- If the fuel pressure is below 25000 kPa, then idling will be rough.
- HINT:
- The fuel pressure changes at engine start, but is approx. 25000 kPa at engine start after the engine is warmed up.
- When Target Pump SCV Current is 3000 mA or higher, the suction control valve has a tendency to become stuck.
|
Diagnostic Trouble Code
| Even if Common Rail Pressure is below Target Common Rail Pressure, a DTC will not be stored.
|
Fuel FilterMain fault
| Blockage
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, engine stalling, rough idle, lack of power
|
Data List
| Common Rail Pressure, Target Common Rail Pressure
- Common Rail Pressure is within 5000 kPa of Target Common Rail Pressure during idling with the engine warmed up (engine coolant temperature is higher than 75°C (167°F)).
- If the fuel pressure is 20000 kPa below the target pressure, then a lack of power will be felt.
- If the fuel pressure is below 25000 kPa, then idling will be rough.
- HINT:
- The fuel pressure changes at engine start, but is approx. 25000 kPa at engine start after the engine is warmed up.
|
Diagnostic Trouble Code
| Even if Common Rail Pressure is below Target Common Rail Pressure, a DTC will not be stored.
|
Injector AssemblyMain fault
| Blockage
|
Symptoms
| Rough idle, lack of power, black smoke, white smoke, knocking
|
Data List
| Injection Feedback Val
- When an Injector Feedback Val is more than 3 mm3/st, there may be a malfunction in the corresponding cylinder. This value can be read after idling for 1 minute.
|
Pressure Discharge ValveMain fault
| Does not completely close
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, engine stall, rough idle, lack of power
|
Injector DriverMain fault
| Circuit fault: The injector assembly does not open.
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle, lack of power, black smoke, white smoke, knocking
|
Data List
| Same as injector assembly
|
Diagnostic Trouble Code
| When the injector driver has a fault, some DTCs may be stored.
|
Fuel Pressure SensorMain fault
| Open circuit, decrease in performance (foreign matter is stuck)
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle, engine stall, lack of power
|
Data List
| Common Rail Pressure, Target Common Rail Pressure
- Slowly raise the engine speed from idling to 3000 rpm with the vehicle stopped and check that Common Rail Pressure follow Target Common Rail Pressure. If the fuel pressure sensor malfunctions, the actual fuel pressure may deviate from the target fuel pressure (either Common Rail Pressure decreases to a value less than Target Common Rail Pressure).
|
Diagnostic Trouble Code
| When the fuel pressure sensor has a fault, some DTCs may be stored.
|
Irregular FuelMain fault
| -
|
Symptoms
| Difficult to start, rough idle (especially when cold)
|
Diesel EGR
EGR SystemMain fault
| - Does not move smoothly
- Does not close completely
|
Symptoms
| - Rough idle
- EGR valve stuck closed: A loud turbocharger sound.
- EGR valve stuck open: Difficult to start (does not stall), black smoke, lack of power (if there is an excess in the quantity of EGR and there is a heavy load, when the vehicle starts moving, a lack of power will be felt).
|
Data List
| Actual EGR Valve Pos, Actual EGR Valve Pos #2, Target EGR Valve Pos, Target EGR Valve Pos #2
- Generally, Actual EGR Valve Pos = Target EGR Valve Pos +/-5% (fully closed: 0%, fully open: 100%).
- Using the EGR valve Active Test, check whether Actual EGR Valve Pos follows Target EGR Valve Pos (the engine coolant temperature and intake air temperature should be considered when a malfunction occurs).
- EGR valve is fully closed when the ignition switch is turned to ON (engine stopped).
- EGR valve opens to the halfway point at idling after the engine is warmed up.
EGR Close Lrn. Val., EGR Close Lrn. Val. #2
- When leaving the vehicle idling, the normal range of EGR Close Lrn. Val. is 3.5 to 4.5 V.
- In cases when EGR Close Lrn. Val. is out of the normal range (3.5 to 4.5 V), it is possible that the EGR valve cannot completely close.
|
Diesel Throttle
Diesel Throttle SystemMain fault
| Stuck, does not move smoothly
|
Symptoms
| - Stuck closed: Lack of power, difficult to start, rough idle, engine stall, black smoke. These may occur when stuck almost fully closed.
- Stuck open: Turbocharger sound increases. When the engine is stopped, engine vibrations may occur.
|
Data List
| - Actual Throttle Position, Actual Throttle Position #2
100%: Fully open
0%: Fully closed
- When the ignition switch is ON (the engine is stopped), the diesel throttle is fully open. When idling, the diesel throttle is at the halfway point. When the ignition switch is turned from ON to off, the throttle is fully closed temporarily.
|
| Data List Related to Starting Trouble |
- MAP
- MAF
- Intake Air
- Coolant Temp
- Battery Voltage
- Starter Signal
- Engine Speed of Cyl #1 (to #8)
- Target Common Rail Pressure
- Common Rail Pressure
- Target Pump SCV Current
- Injection Feedback Val #1 (to #8)
- Injection Volume
- Actual Throttle Position
- Actual Throttle Position #2
- Target EGR Valve Pos.
- Target EGR Valve Pos #2
- Actual EGR Valve Pos
- Actual EGR Valve Pos #2
- EGR Close Lrn. Val.
- EGR Close Lrn. Val #2
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Starting Trouble
| For good starting it is essential to have:
- Sufficient cranking speed.
- Properly operating engine preheating system.
- Good quality fuel.
The fuel is ignited by the heat which is generated by compression pressure.
With problems such as a depleted battery, the crankshaft speed can become low, or if the engine compression is poor due to leakage, the compression pressure will not rise and there will be difficulty starting.
When the engine is cold, even if there is compression heat, it will escape from the combustion chamber. For this reason, when the engine is started when it is cold, the glow plugs heat the compressed air.
Also, after starting the engine, by charging the glow plugs for a fixed time set according to the engine coolant temperature, diesel knocking and white smoke are prevented. The quantity of fuel injected is determined by the fuel pressure and also the amount of time the injector assembly is open.
|
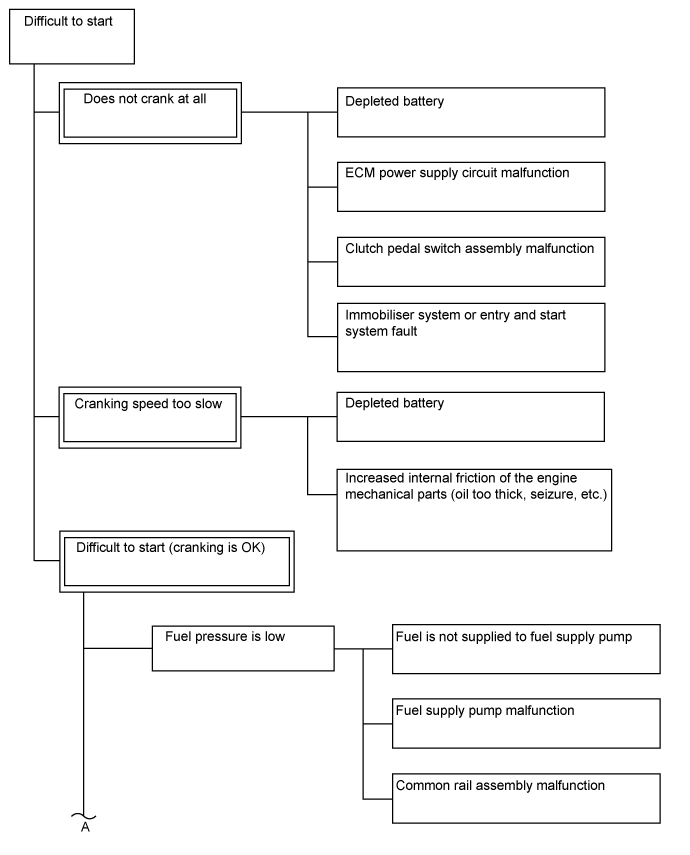
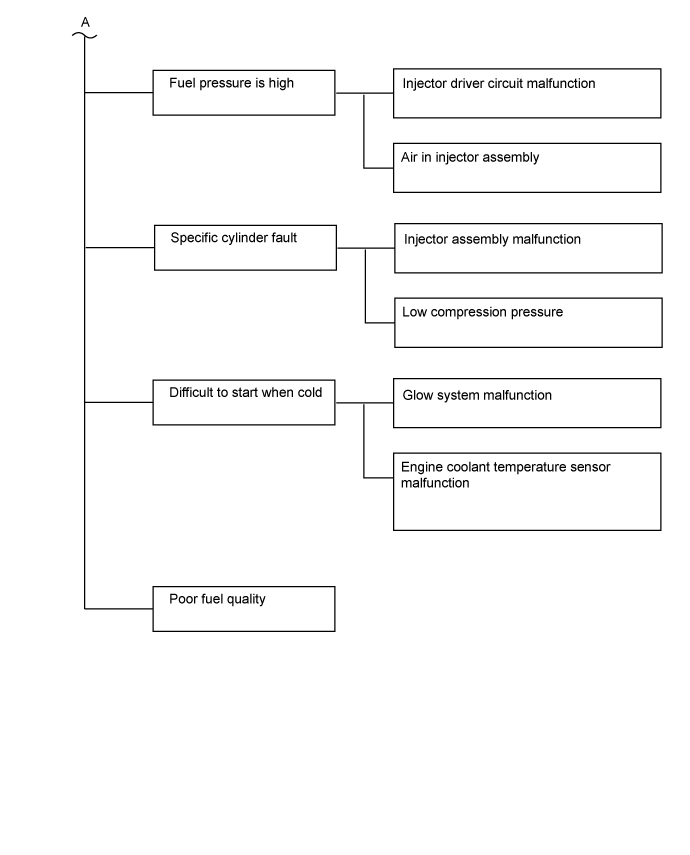
| Trouble Area Chart According to Problem Cause |
- NOTICE:
- After replacing the ECM, the new ECM needs registration (Click here) and initialization (Click here).
- After replacing the fuel supply pump assembly, the ECM needs initialization (Click here).
- After replacing an injector assembly, the ECM needs registration (Click here).
- HINT:
- Specified values in the following troubleshooting flowchart are for reference only. Variations in the Data List values may occur depending on the measuring conditions or the vehicle age. Do not assume the vehicle is normal when the Data List outputs standard values. There may be concealed factors of the malfunction.
| 1.CHECK ENGINE CRANKING CONDITION |
Check the engine cranking condition.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Cranking is OK.
| A
|
Low cranking speed.
- HINT:
- When cranking speed is low, especially when the temperature is low, check if the engine oil grade matches the recommendation.
| B
|
Does not crank at all.
| C
|
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Utility / All Codes.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
No DTC is output
| A
|
Engine related DTCs are output
| B
|
- HINT:
- If only DTC P1604 is output, proceed to step 3.
| 3.TAKE SNAPSHOT DURING STARTING AND IDLING (PROCEDURE 3) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data.
Take a snapshot when idling with no load after the engine is warmed up and when starting trouble is occurring.
- HINT:
- A snapshot can be used to compare vehicle data from the time of the malfunction to normal data and is very useful for troubleshooting. The data in the illustration below is that of a normal vehicle, but as the data varies between individual vehicles, this data should only be used for reference.
- When there is trouble starting with a cold engine, take the snapshot when the engine is cold. Then warm up the engine (engine coolant temperature is 75°C (167°F) or higher) and after idling the vehicle for 1 minute (A/C off, electrical load off), take a snapshot of the data for 15 seconds while idling.
- Take a snapshot when the problem is occurring, such as when the engine is cold. However, if the problem does not reoccur, it is acceptable to only take a snapshot after the engine is warmed up and when the engine is started.
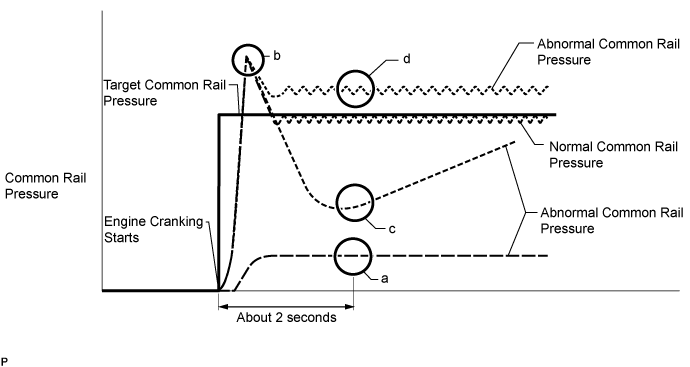
| 4.CHECK SNAPSHOT (COMMON RAIL PRESSURE) |
Check Common Rail Pressure in the snapshot taken in procedure 3 when the engine was started.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
At the point in the illustration labeled "a", Common Rail Pressure is less than 10000 kPa from the value of Common Rail Pressure when cranking starts
| A
|
At the point in the illustration labeled "c", Common Rail Pressure is below Target Common Rail Pressure by 15000 kPa or more
| B
|
Common Rail Pressure increases to a value that is higher than Target Common Rail Pressure immediately after cranking, and, at the point in the illustration labeled "d", Common Rail Pressure is higher than Target Common Rail Pressure
| C
|
Except above
| D
|
- HINT:
- Even if Common Rail Pressure is temporarily higher than Target Common Rail Pressure, as shown at the point in the illustration labeled "b", the fuel supply pump assembly is normal.
- Common Rail Pressure is about 25000 to 35000 kPa when the engine is cranking and the engine coolant temperature is 0°C (32°F) or higher.
- Common Rail Pressure increases rapidly during cranking.
| 5.CHECK IF FUEL IS BEING SUPPLIED TO FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY |
Disconnect the inlet hose from the fuel supply pump assembly.
Operate the priming pump and check that fuel is being supplied to the fuel supply pump assembly.
- OK:
- Fuel is properly supplied to the fuel supply pump assembly when the priming pump is operated.
- HINT:
- When there is a lack of fuel, fuel pressure drops.
- Inspect for fuel filter clogging (check that the fuel filter is not clogged).
Reconnect the inlet hose.
| 6.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE - ECM) |
Disconnect the suction control valve connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for LHDTester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
z64-1 (+B) - C45- 104 (PCV+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
z64-2 (PCV) - C45-105 (PCV-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
z64-1 (+B) or C45- 104 (PCV+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
z64-2 (PCV) or C45-105 (PCV-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
- Standard Resistance:
for RHDTester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
z64-1 (+B) - C46- 104 (PCV+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
z64-2 (PCV) - C46-105 (PCV-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
z64-1 (+B) or C46- 104 (PCV+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
z64-2 (PCV) or C46-105 (PCV-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
Reconnect the suction control valve connector.
Reconnect the ECM connector.
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
|
| 7.REPLACE FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE) |
Replace the supply pump assembly (Click here).
| 8.BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |
Bleed the air from the fuel system (Click here).
Perform PM forced regeneration (Click here).
- HINT:
- When fuel lines are disconnected, air may enter the fuel lines, leading to engine starting trouble. Therefore, perform forced regeneration and bleed the air from the fuel lines.
| 9.PERFORM SUPPLY PUMP INITIALIZATION |
Perform supply pump initialization (Click here).
| 10.READ VALUE USING GTS (COMMON RAIL PRESSURE) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Data List / Common Rail Pressure.
Start the engine.
Read the Fuel Press values while cranking and idling the engine.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
The engine cannot be started or the engine can be started but Common Rail Pressure is below 20000 kPa 2 seconds after the starter signal changes from OFF to ON
| B
|
Except above
| A
|
| 11.INSPECT INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (INSPECTION FOR VALVE CLOSING PROBLEM) |
Remove the glow plug assembly for all the cylinders (Click here).
Visually check if there is fuel on the glow plugs.
- HINT:
- If there is fuel on a glow plug, fuel may be leaking from an injector assembly.
- After replacing an injector assembly, make sure that the common rail pressure is within 5000 kPa of the target fuel pressure while cranking the engine.
- If there is fuel on a glow plug, fuel may have mixed with the engine oil. Check the engine oil amount and whether the engine oil smells of diesel fuel. If the oil level is above the full line or the engine oil smells of diesel fuel, replace the engine oil.
Install the glow plug assembly (Click here).
| 12.CHECK AND REPAIR OR REPLACE CLOGGED FUEL PIPE (INCLUDING FROZEN FUEL) (FUEL TANK - FUEL SUPPLY PUMP) |
Check and repair or replace the clogged fuel pipe.
| 13.BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |
Bleed the air from the fuel system (Click here).
Perform PM forced regeneration (Click here).
- HINT:
- When fuel lines are disconnected, air may enter the fuel lines, leading to engine starting trouble. Therefore, perform forced regeneration and bleed the air from the fuel lines.
| 14.READ VALUE USING GTS (COMMON RAIL PRESSURE) |
Check Common Rail Pressure in the snapshot taken in procedure 3 when the engine was warmed up.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Difference between Common Rail Pressure and Target Common Rail Pressure is 5000 kPa (51.0 kgf/cm2, 725 psi) or more
| A
|
Except above
| B
|
| 15.REPLACE FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY (SUCTION CONTROL VALVE) |
Replace the fuel supply pump assembly (Click here).
| 16.PERFORM SUPPLY PUMP INITIALIZATION |
Perform supply pump initialization (Click here).
| 17.REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES OF ALL CYLINDERS |
Replace the injector assemblies (Click here).
- NOTICE:
- When replacing the injector assembly for a cylinder, always be sure to use a new injection pipe.
- Follow the procedure in the repair manual and temporarily install the injection pipes and nozzle leakage pipe, and then correctly position the injector assemblies. After that, tighten parts according to the torque specifications.
- If the installation procedure is not performed correctly, injector assemblies may become out of position, which may cause the injector assemblies to deteriorate, resulting in malfunctions.
- If an injector assembly deteriorates and malfunctions, other problems such as knocking, rough idle, etc. may occur.
- If an injector assembly becomes out of position, it is possible that the seal between the injector assembly and injection pipe may become incomplete, resulting in a fuel leak.
| 18.INSPECT INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (CHECKING FOR PRESENCE OF AIR) |
When the engine does not start, perform the following procedure.
Stop the engine and leave the vehicle for 4 hours or more.
- HINT:
- It is necessary to leave the vehicle for 4 hours or more to wait for air in the injector assembly to come out.
Check that the engine starts.
- OK:
- The engine starts.
When the engine starts, perform the following procedure.
Bleed the air from the fuel system (Click here).
Check that the engine starts.
- OK:
- The engine starts.
Check Injection Feedback Val # in the snapshot taken in procedure 3 when the engine was idling.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Injection Feedback Val #1 to #8 are 3 mm3/st or less.
Injection Volume is more than 13 mm3/st.
| A*
|
Injection Feedback Val for at least one cylinder is more than +3 mm3/st
- HINT:
- There may be a malfunction in the corresponding cylinder.
| B
|
Except above
| C
|
- HINT:
- *: When this case occurs, usually symptoms may be noticeable, such as difficulty starting or lack of power.
- The shift lever should be in neutral and the A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off.
| 20.REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES OF ALL CYLINDERS |
Replace the injector assemblies (Click here).
- NOTICE:
- When replacing the injector assembly for a cylinder, always be sure to use a new injection pipe.
- Follow the procedure in the repair manual and temporarily install the injection pipes and nozzle leakage pipe, and then correctly position the injector assemblies. After that, tighten parts according to the torque specifications.
- If the installation procedure is not performed correctly, injector assemblies may become out of position, which may cause the injector assemblies to deteriorate, resulting in malfunctions.
- If an injector assembly deteriorates and malfunctions, other problems such as knocking, rough idle, etc. may occur.
- If an injector assembly becomes out of position, it is possible that the seal between the injector assembly and injection pipe may become incomplete, resulting in a fuel leak.
| 21.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CHECK THE CYLINDER COMPRESSION) |
- HINT:
- Use this Active Test to help determine whether a cylinder has compression loss or not.
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Active Test / Check the Cylinder Compression / Data List / Compression / Engine Speed of Cyl #1 to #8.
Check the engine speed during the Active Test.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Except below
| A
|
The values of Engine Speed Cyl #1 to #8 are within +/-10 rpm of each other.
| B
|
- HINT:
- When cranking, if the speed of a cylinder is approximately 100 rpm more than the other cylinders, there is probably a complete loss of compression in that cylinder.
| 22.CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER |
- HINT:
- Measure the compression of the cylinder that had a high speed during the "Check the Cylinder Compression" Active Test.
Check the cylinder compression pressure (Click here).
| | CHECK ENGINE TO DETERMINE CAUSE OF LOW COMPRESSION |
|
|
| 23.REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLY OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER |
- HINT:
- It can be determined that the injector assembly is faulty as the corresponding cylinder is malfunctioning, but has no compression loss.
Replace the injector assembly (Click here).
- NOTICE:
- When replacing the injector assembly for a cylinder, always be sure to use a new injection pipe.
- Follow the procedure in the repair manual and temporarily install the injection pipes and nozzle leakage pipe, and then correctly position the injector assemblies. After that, tighten parts according to the torque specifications.
- If the installation procedure is not performed correctly, injector assemblies may become out of position, which may cause the injector assemblies to deteriorate, resulting in malfunctions.
- If an injector assembly deteriorates and malfunctions, other problems such as knocking, rough idle, etc. may occur.
- If an injector assembly becomes out of position, it is possible that the seal between the injector assembly and injection pipe may become incomplete, resulting in a fuel leak.
| 24.CLEAN FUEL FILTER CASE AND REPLACE FUEL FILTER |
Clean the fuel filter case and replace the fuel filter.
- HINT:
- Be sure to clean the inside of the fuel filter case as the fuel injectors may not operate properly if the fuel filter is installed with foreign matter remaining inside the fuel filter case.
| 25.BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |
Bleed the air from the fuel system (Click here).
Perform PM forced regeneration (Click here).
- HINT:
- When fuel lines are disconnected, air may enter the fuel lines, leading to engine starting trouble. Therefore, perform forced regeneration and bleed the air from the fuel lines.
| 26.REGISTER INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE AND PERFORM PILOT QUANTITY LEARNING |
Register the injector compensation codes (Click here).
Perform the injector pilot quantity learning (Click here).
| 27.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
| 28.INSPECT INJECTOR DRIVER |
Even in cases where DTC P062D and P062E are not stored even though the engine cannot be started, perform the DTC P062D troubleshooting procedure (Click here).
- HINT:
- When the engine cannot be started due to a malfunction in the injector driver system, once the DTCs are cleared, the system cannot store DTC P062D and P062E even if it is confirmed that the engine cannot be started when trying to reproduce the problem symptoms.
As DTC P062D and P062E cannot be stored when starting the engine, fuel injection signals are output by the ECM, but fuel is not actually injected. Therefore, an excessive amount of fuel is supplied to the common rail by the fuel supply pump assembly, and as a result, the fuel pressure is higher than the target common rail pressure in the data recorded at the time the engine was having trouble starting.
- If the problem cannot be determined even after performing the DTC P062D and P062E troubleshooting procedure and the fuel pressure is higher than the target common rail pressure when attempting to start the engine, proceed to the next step.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Injector driver (EDU) circuit is normal
| A
|
Injector driver (EDU) circuit is abnormal
| B
|
| | REPAIR OR REPLACE MALFUNCTIONING PARTS |
|
|
| 29.INSPECT INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (CHECKING FOR PRESENCE OF AIR) |
When the engine does not start, perform the following procedure.
Stop the engine and leave the vehicle for 4 hours or more.
- HINT:
- It is necessary to leave the vehicle for 4 hours or more to wait for air in the injector assembly to come out.
Confirm the engine starts.
When the engine starts, perform the following procedure.
Bleed the air from the fuel system (Click here).
Confirm the engine starts.
| 30.CHECK TEMPERATURE WHEN STARTING TROUBLE OCCURS |
Check the temperature when starting trouble occurs.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Difficult to start only for cold engine.
| A
|
Difficult to start both for cold and warmed up engine.
| B
|
| 31.READ VALUE USING ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (COOLANT TEMP) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Coolant Temp.
Read the value displayed on the GTS.
- OK:
- Coolant Temp is not high when the engine is cold, and not low after the engine is warmed up
| | INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Click here) |
|
|
| 32.INSPECT GLOW PLUG (RESISTANCE) |
Inspect the glow plug (Click here).
Check that only diesel fuel is being used.
Check that the fuel does not contain any impurities.
| 34.READ OUTPUT DTC (RELATED TO ENGINE) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes.
Read the DTCs.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
No DTC is output
| A
|
Engine related DTCs are output
| B
|
| 35.CHECK COMMUNICATION BETWEEN GTS AND ECM |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Check if the normal starting screen appears (check whether communication with the ECM is possible).
- HINT:
- Use a GTS that is able to communicate with other vehicles.
- OK:
- Communication is possible (vehicle can be recognized).
| 36.READ VALUE USING GTS (STARTER SIGNAL AND NEUTRAL POSITION SW SIGNAL) |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Starter Signal and Neutral Position SW Signal.
Read the value displayed on the GTS.
- OK:
GTS Display
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
Starter Signal
| Cranking
| ON
|
Neutral Position SW Signal
| Shift lever in neutral
| ON
|
| | INSPECT PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH ASSEMBLY |
|
|
Inspect the starting system.
- HINT:
- Be sure to inspect the following areas:
- Starter relay
- Starter assembly
- Immobiliser system
| 38.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |