DESCRIPTION
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
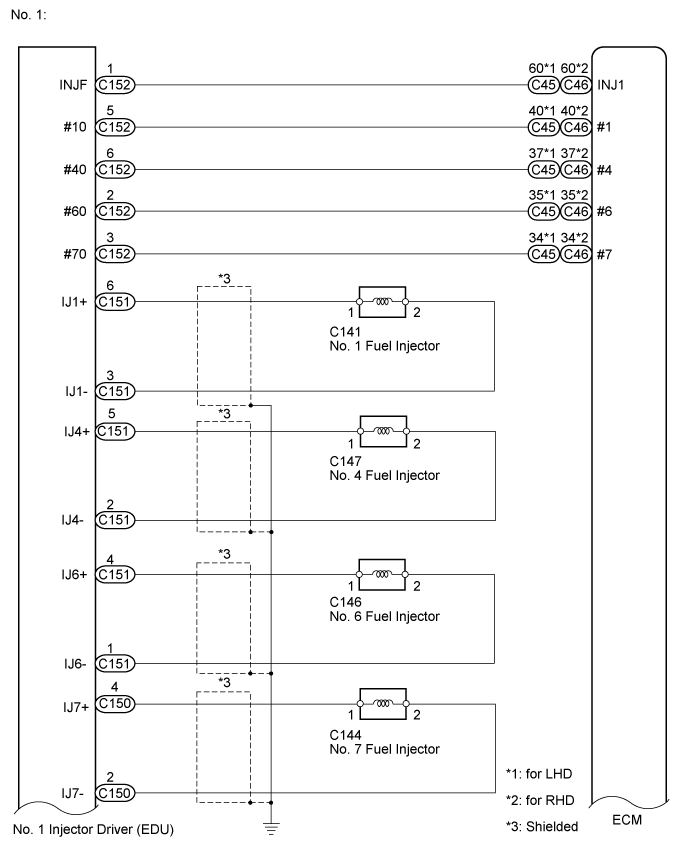
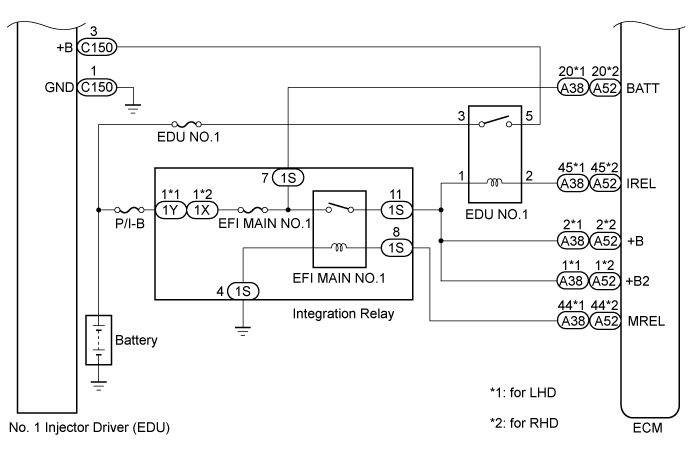
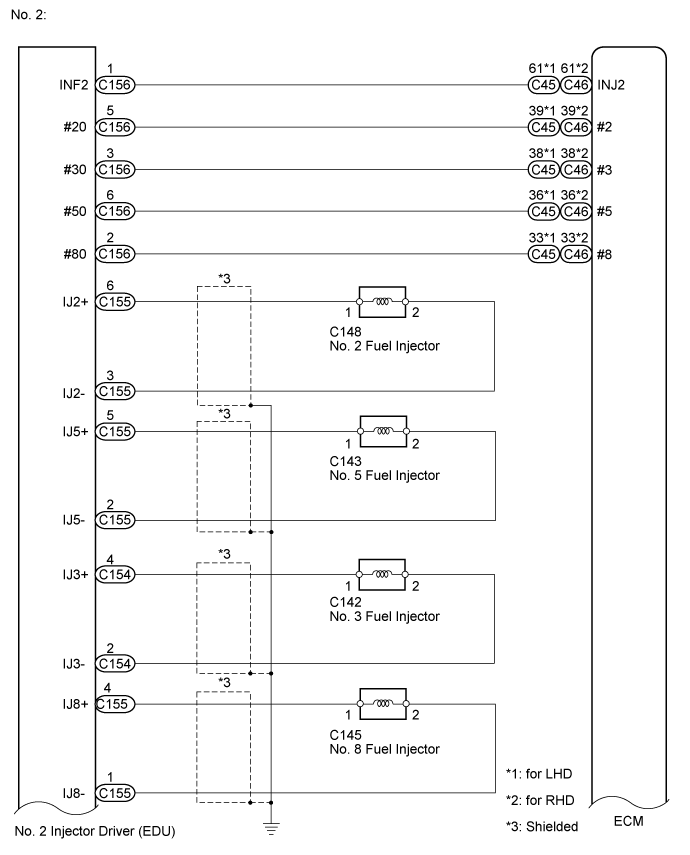
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
CHECK ENGINE CRANKING CONDITION AND DTC OUTPUT
INSPECT ECM
CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (POWER SOURCE)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU) - ECM)
REPLACE INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU)
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS
INSPECT INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU)
REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (RELEVANT CYLINDER)
BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM
REGISTER INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE AND PERFORM PILOT QUANTITY LEARNING
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU) - ECM)
REPLACE ECM
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (INJECTOR ASSEMBLY - INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU))
REPLACE INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU)
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR
GO TO INJECTOR CIRCUIT
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
DTC P0201 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 1) |
DTC P0202 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 2) |
DTC P0203 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 3) |
DTC P0204 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 4) |
DTC P0205 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 5) |
DTC P0206 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 6) |
DTC P0207 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 7) |
DTC P0208 Injector Circuit / Open - (Cylinder 8) |
DTC P062D No. 1 Fuel Injector Driver Circuit Performance |
DTC P062E No. 2 Fuel Injector Driver Circuit Performance |
DESCRIPTION
The injector driver (EDU) delivers drive signals to fuel injectors using the DC/DC converter, which provides a high-voltage and quick-charging system.Soon after the injector driver (EDU) receives a fuel injection command (# 1 to # 8) signal from the ECM, the injector driver (EDU) responds to the command with an injector injection confirmation (INJF, INF2) signal when the current is applied to the injector assembly.P0201 to P0208:DTC Detection Drive Pattern
| DTC Detection Condition
| Trouble Area
|
Idling for 5 seconds
| Open or short in injector circuit occurs a certain number of times (a maximum of approx. 0.5 seconds).
(1 trip detection logic)
| - Open or short in injector assembly circuit
- Injector assembly
- No. 1 Injector driver (EDU)
- No. 2 Injector driver (EDU)
- ECM
|
P062D (No. 1), P062E (No. 2)DTC Detection Drive Pattern
| DTC Detection Condition
| Trouble Area
|
Idling for 5 seconds
| Inconsistency in the injection waveforms between the injector driver (EDU) and ECM while the engine is running a certain number of times (a maximum of approx. 0.5 seconds).
(1 trip detection logic)
| - Open or short in injector driver (EDU) circuit
- Injector assembly
- No. 1 injector driver (EDU)
- No. 2 injector driver (EDU)
- ECM
|
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
- P0201 to P0208:
The ECM compares injection command (# 1 to # 8) signals and injection confirmation (INJF, INF2) signals for each cylinder. If the ECM determines that a cylinder has a malfunction, DTC P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205, P0206, P0207 or P0208 will be stored.
- P062D, P062E:
The ECM continuously monitors both injection command (#1 to #8) signals and injection confirmation (INJF, INF2) signals. These DTCs DTC will be stored if the ECM determines that the number of #1 to #8 signals and INJF, INF2 signals are inconsistent.
The injector assemblies are grounded over a Field Effect Transistor (FET) and a serial resistor. This resistor creates a voltage drop, which is monitored by the injector driver (EDU) (injector drive circuit) in relation to the current drawn by the injector assembly. When the injector assembly current becomes too high, the voltage drop over the resistor exceeds a specified level and no INJF or INF2 signal for that cylinder is sent to the ECM.
After the engine is started, when there is no injection confirmation (INJF, INF2) signal from the injector driver (EDU) to the ECM even though the ECM sends injection command (#1 to #8) signals to the injector driver (EDU), DTC P062D or P062E is stored.
If either of these DTCs is stored, the ECM enters fail-safe mode and limits engine power or stops the engine. The fail-safe mode continues until the ignition switch is turned off.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- CAUTION:
- Make sure to perform work on high voltage circuits with the ignition switch off.
- NOTICE:
- After replacing the ECM, the new ECM needs registration (Click here) and initialization (Click here).
- After replacing an injector assembly, the ECM needs registration (Click here).
- HINT:
- Read freeze frame data using the GTS. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
| 1.CHECK ENGINE CRANKING CONDITION AND DTC OUTPUT |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes.
Read the DTCs.
Check the engine cranking condition.
ResultResult
| Proceed to
|
Engine starts, but idling is rough (P062D or P062E is output)*1
| A
|
Engine starts, but idling is rough*2
| B
|
Engine does not start (P062D and P062E are output)*3
| C
|
Except above
| D
|
- HINT:
- *1: Only one of either DTC P062D or P062E is output and one of the injector drivers (EDU) has stopped.
- *2: DTC P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205, P0206, P0207, P0208, P062D and P062E are stored at this time.
- *3: When the engine cannot be started due to a malfunction in the No. 1 and No. 2 injector driver (EDU), DTCs are not stored again if they are cleared. Also, the value for "Common Rail Pressure" is higher than the value for "Target Common Rail Pressure"
Disconnect the No. 1 and No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connectors.
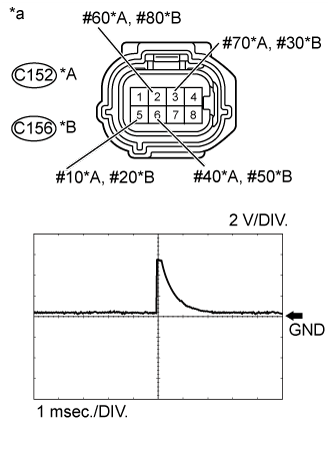
Check the waveform of the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector using an oscilloscope.
- OK:
Tester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C152-5 (#10) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
C156-5 (#20) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
C156-3 (#30) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
C152-6 (#40) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
C156-6 (#50) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
C152-2 (#60) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
C152-3 (#70) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
C156-2 (#80) - Body ground
| Cranking
| Correct waveform is as shown
|
Text in Illustration*A
| for Bank 1 (No. 1 injector Driver (EDU))
|
*B
| for Bank 2 (No. 2 injector Driver (EDU))
|
*a
| Front view of wire harness connector
(to Injector Driver (EDU))
|
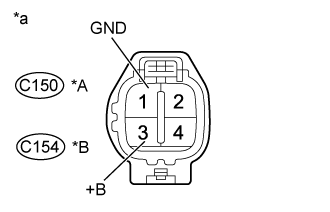
| 3.CHECK TERMINAL VOLTAGE (POWER SOURCE) |
Turn the ignition switch off.
- HINT:
- Powering of the EDU relay may be prohibited by the fail-safe function. Therefore, turn the ignition switch off to disable the failsafe function before performing this inspection.
Disconnect the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
Tester Connection
| Switch Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C150-3 (+B) - C150-1 (GND)
| Ignition switch ON
| 11 to 14 V
|
C154-3 (+B) - C154-1 (GND)
| Ignition switch ON
| 11 to 14 V
|
Text in Illustration*A
| for Bank 1 (No. 1 injector Driver (EDU))
|
*B
| for Bank 2 (No. 2 injector Driver (EDU))
|
*a
| Front view of wire harness connector
(to Injector Driver (EDU))
|
Reconnect the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector.
| 4.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU) - ECM) |
Disconnect the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for LHDTester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C152-5 (#10) - C45-40 (#1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-5 (#20) - C45-39 (#2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-3 (#30) - C45-38 (#3)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-6 (#40) - C45-37 (#4)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-6 (#50) - C45-36 (#5)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-2 (#60) - C45-35 (#6)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-3 (#70) - C45-34 (#7)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-2 (#80) - C45-33 (#8)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-1 (INJF) - C45-60 (INJ1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-1 (INF2) - C45-61 (INJ2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-5 (#10) or C45-40 (#1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-5 (#20) or C45-39 (#2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-3 (#30) or C45-38 (#3) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-6 (#40) or C45-37 (#4) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-6 (#50) or C45-36 (#5) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-2 (#60) or C45-35 (#6) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-3 (#70) or C45-34 (#7) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-2 (#80) or C45-33 (#8) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-1 (INJF) or C45-60 (INJ1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-1 (INF2) or C45-61 (INJ2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
for RHDTester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C152-5 (#10) - C46-40 (#1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-5 (#20) - C46-39 (#2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-3 (#30) - C46-38 (#3)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-6 (#40) - C46-37 (#4)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-6 (#50) - C46-36 (#5)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-2 (#60) - C46-35 (#6)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-3 (#70) - C46-34 (#7)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-2 (#80) - C46-33 (#8)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-1 (INJF) - C46-60 (INJ1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-1 (INF2) - C46-61 (INJ2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-5 (#10) or C46-40 (#1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-5 (#20) or C46-39 (#2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-3 (#30) or C46-38 (#3) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-6 (#40) or C46-37 (#4) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-6 (#50) or C46-36 (#5) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-2 (#60) or C46-35 (#6) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-3 (#70) or C46-34 (#7) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-2 (#80) or C46-33 (#8) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-1 (INJF) or C46-60 (INJ1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-1 (INF2) or C46-61 (INJ2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
Reconnect the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector.
Reconnect the ECM connector.
| 5.REPLACE INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU) |
Replace the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) (Click here).
| 6.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the GTS on.
Clear the DTCs (Click here).
Turn the ignition switch off for 30 seconds.
Start the engine and idle it for 30 seconds.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes.
Check the DTCs output on the GTS.
- HINT:
- The cylinder with the malfunctioning injector assembly can be determined based on the output DTCs.
- If DTC P0201 is output, check the No. 1 injector assembly circuit.
- If DTC P0202 is output, check the No. 2 injector assembly circuit.
- If DTC P0203 is output, check the No. 3 injector assembly circuit.
- If DTC P0204 is output, check the No. 4 injector assembly circuit.
- If DTC P0205 is output, check the No. 5 injector assembly circuit.
- If DTC P0206 is output, check the No. 6 injector assembly circuit.
- If DTC P0207 is output, check the No. 7 injector assembly circuit.
- If DTC P0208 is output, check the No. 8 injector assembly circuit.
| 7.INSPECT INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU) |
Disconnect the injector assembly connectors for all cylinders.
- NOTICE:
- If only the injector assembly connector of the malfunctioning cylinder is disconnected, the engine will start and there will be rough idling. Therefore, disconnect all injector assembly connectors before inspecting the waveform.
Check the waveform of the injector assembly connectors using an oscilloscope.
- OK:
Tester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C141-1 - C141-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
C148-1 - C148-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
C142-1 - C142-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
C147-1 - C147-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
C143-1 - C143-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
C146-1 - C146-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
C144-1 - C144-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
C145-1 - C145-2
| Cranking
| Voltage increases by 50 V or more
|
Text in Illustration*a
| Front view of wire harness connector
(to Injector Assembly)
|
| 8.REPLACE INJECTOR ASSEMBLY (RELEVANT CYLINDER) |
Replace the injector assembly of the cylinder relevant to the DTC (Click here).
- NOTICE:
- When replacing the injector assembly for a cylinder, always be sure to use a new injection pipe.
- Follow the procedure in the repair manual and temporarily install the injection pipes and nozzle leakage pipe, and then correctly position the injector assemblies. After that, tighten parts according to the torque specifications.
- If the installation procedure is not performed correctly, injector assemblies may become out of position, which may cause the injector assemblies to deteriorate, resulting in malfunctions.
- If an injector assembly deteriorates and malfunctions, other problems such as knocking, rough idle, etc. may occur.
- If an injector assembly becomes out of position, it is possible that the seal between the injector assembly and injection pipe may become incomplete, resulting in a fuel leak.
| 9.BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |
Bleed the air from the fuel system (Click here).
Perform PM forced regeneration (Click here).
- HINT:
- When fuel lines are disconnected, air may enter the fuel lines, leading to engine starting trouble. Therefore, perform forced regeneration and bleed the air from the fuel lines.
| 10.REGISTER INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE AND PERFORM PILOT QUANTITY LEARNING |
Register the injector compensation code (Click here).
Perform the injector pilot quantity learning (Click here).
| 11.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU) - ECM) |
Disconnect the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector.
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
for LHDTester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C152-5 (#10) - C45-40 (#1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-5 (#20) - C45-39 (#2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-3 (#30) - C45-38 (#3)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-6 (#40) - C45-37 (#4)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-6 (#50) - C45-36 (#5)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-2 (#60) - C45-35 (#6)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-3 (#70) - C45-34 (#7)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-2 (#80) - C45-33 (#8)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-1 (INJF) - C45-60 (INJ1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-1 (INF2) - C45-61 (INJ2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-5 (#10) or C45-40 (#1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-5 (#20) or C45-39 (#2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-3 (#30) or C45-38 (#3) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-6 (#40) or C45-37 (#4) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-6 (#50) or C45-36 (#5) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-2 (#60) or C45-35 (#6) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-3 (#70) or C45-34 (#7) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-2 (#80) or C45-33 (#8) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-1 (INJF) or C45-60 (INJ1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-1 (INF2) or C45-61 (INJ2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
for RHDTester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C152-5 (#10) - C46-40 (#1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-5 (#20) - C46-39 (#2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-3 (#30) - C46-38 (#3)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-6 (#40) - C46-37 (#4)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-6 (#50) - C46-36 (#5)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-2 (#60) - C46-35 (#6)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-3 (#70) - C46-34 (#7)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-2 (#80) - C46-33 (#8)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-1 (INJF) - C46-60 (INJ1)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C156-1 (INF2) - C46-61 (INJ2)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C152-5 (#10) or C46-40 (#1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-5 (#20) or C46-39 (#2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-3 (#30) or C46-38 (#3) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-6 (#40) or C46-37 (#4) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-6 (#50) or C46-36 (#5) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-2 (#60) or C46-35 (#6) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-3 (#70) or C46-34 (#7) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-2 (#80) or C46-33 (#8) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C152-1 (INJF) or C46-60 (INJ1) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C156-1 (INF2) or C46-61 (INJ2) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
Reconnect the injector driver (EDU) connector.
Reconnect the ECM connector.
Replace the ECM (Click here).
| 13.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (INJECTOR ASSEMBLY - INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU)) |
Disconnect the injector assembly connectors.
Disconnect the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
Tester Connection
| Condition
| Specified Condition
|
C141-1 - C151-6 (IJ1+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C141-2 - C151-3 (IJ1-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C148-1 - C155-6 (IJ2+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C148-2 - C155-3 (IJ2-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C142-1 - C154-4 (IJ3+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C142-2 - C154-2 (IJ3-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C147-1 - C151-5 (IJ4+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C147-2 - C151-2 (IJ4-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C143-1 - C155-5 (IJ5+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C143-2 - C155-2 (IJ5-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C146-1 - C151-4 (IJ6+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C146-2 - C151-1 (IJ6-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C144-1 - C150-4 (IJ7+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C144-2 - C150-2 (IJ7-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C145-1 - C155-4 (IJ8+)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C145-2 - C155-1 (IJ8-)
| Always
| Below 1 Ω
|
C141-1 or C151-6 (IJ1+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C141-2 or C151-3 (IJ1-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C148-1 or C155-6 (IJ2+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C148-2 or C155-3 (IJ2-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C142-1 or C154-4 (IJ3+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C142-2 or C154-2 (IJ3-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C147-1 or C151-5 (IJ4+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C147-2 or C151-2 (IJ4-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C143-1 or C155-5 (IJ5+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C143-2 or C155-2 (IJ5-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C146-1 or C151-4 (IJ6+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C146-2 or C151-1 (IJ6-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C144-1 or C150-4 (IJ7+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C144-2 or C150-2 (IJ7-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C145-1 or C155-4 (IJ8+) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
C145-2 or C155-1 (IJ8-) - Body ground
| Always
| 10 kΩ or higher
|
Reconnect the injector assembly connectors.
Reconnect the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connector.
| 14.REPLACE INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU) |
Replace the No. 1 or No. 2 injector driver (EDU) (Click here).
| 15.REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
Repair or replace the harness or connector.
| 16.GO TO INJECTOR CIRCUIT |
Go to injector circuit (Click here).
| 17.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Turn the GTS on.
Clear the DTCs (Click here).
Turn the ignition switch off and wait for 30 seconds or more.
Start the engine and idle it for 5 seconds or more.
Turn the GTS on.
Enter the following menus: Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes.
Confirm that the DTC is not output again.