Ecd System (W/O Dpf) -- System Description |
| SYSTEM DIAGRAM |

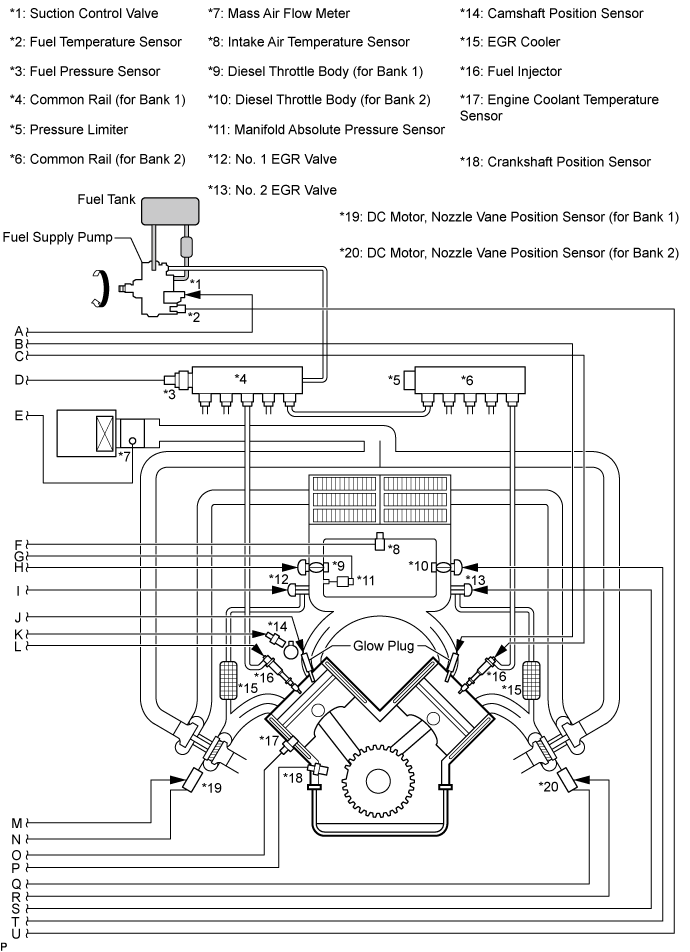
| COMMON RAIL INJECTION SYSTEM |
- The common rail injection system uses high-pressure fuel to improve fuel economy and to provide robust engine power, while suppressing engine vibration and noise.
This system stores fuel, which has been pressurized and supplied by the fuel supply pump, in the common rail. By storing fuel at high-pressure, the common rail system can provide fuel at stable fuel injection pressures, regardless of engine speed or engine load.
The ECM regulates the fuel injection timing and volume by using the EDU to provide an electric current to the solenoid valve in the fuel injector. The ECM also monitors the internal fuel pressure of the common rail using the fuel pressure sensor. The ECM causes the fuel supply pump to supply the fuel necessary to obtain the target fuel pressure.
In addition, this system has a 2-Way Valve (TWV) inside the fuel injector to open and close the fuel passage. As a result, both fuel injection timing and fuel injection volume can be precisely regulated by the ECM.
The common rail system provides two split fuel injections. In order to soften combustion shock, this system performs "pilot-injection" as the subsidiary fuel injection prior to the main fuel injection. This helps to reduce engine vibration and noise.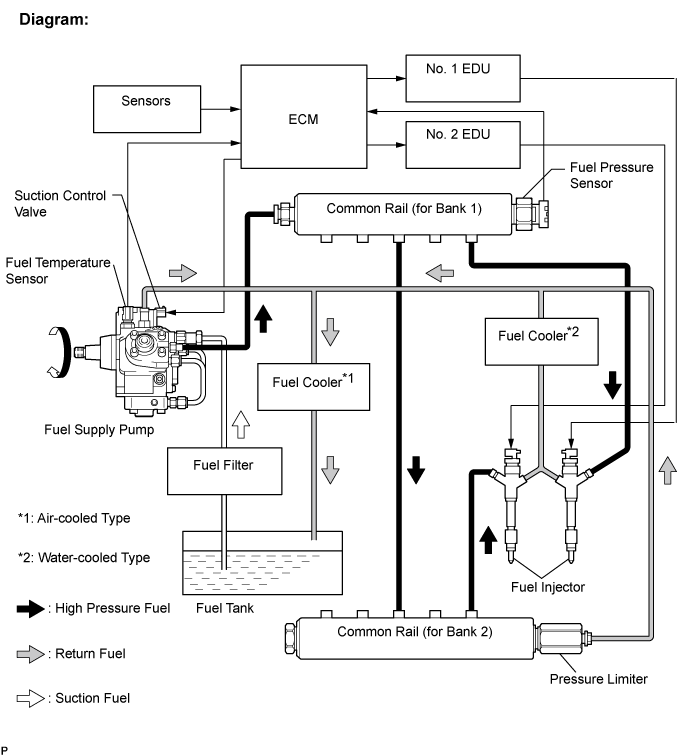
Components: Component Description Common rail Stores high-pressure fuel produced by fuel supply pump Fuel supply pump Operated by crankshaft. Supplies high-pressure fuel to common rail. Fuel injector Injects fuel to combustion chamber based on signals from ECM Fuel pressure sensor Monitors internal fuel pressure of common rail and sends signals to ECM Pressure limiter Opens pressure limiter valve to reduce internal pressure in common rail when common rail pressure exceeds specified level Suction control valve Based on signals from ECM, adjusts fuel volume supplied to common rail and regulates internal fuel pressure
- HINT:
- This table indicates typical DTCs for each malfunction.
Component Trouble Area DTC No. Fuel injector Open or short in fuel injector circuit P062D, P062E, P1238, P0093* Stuck open P0093, P1238 Stuck closed P1238 Fuel pressure sensor Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit or pressure sensor output fixed P0087, P0190, P0192, P0193 Pressure limiter Stuck open P0093 Stuck closed P0088* Suction control valve Open or short in suction control valve circuit P0627, P1229, P0088* Stuck open P1229, P0088* Stuck closed - Injector driver (EDU) Faulty EDU P0093*, P062D*, P062E*, P1238* Common rail system (Fuel system) Fuel leaks in high-pressure areas P0093 - HINT:
- *: There may be no DTC output depending on the condition of the malfunction.
| DTC No. | Description |
| P0087 | Fuel pressure sensor output does not change |
| P0088 | Internal fuel pressure too high (230 MPa [2345 kgf/cm2, 33350 psi] or more) |
| P0093 | Fuel leaks in high-pressure areas |
| P0190 | Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit (Low or high output) |
| P0192 | Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit (Low output) |
| P0193 | Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit (High output) |
| P062D | Open or short in No. 1 injector driver or fuel injector circuit |
| P062E | Open or short in No. 2 injector driver or fuel injector circuit |
| P0627 | Open or short in suction control valve circuit |
| P1229 | Fuel over-feed |
| P1238 | Injection malfunction; excludes open or short in fuel injector circuit |
| P1601 | Fuel injector compensation code malfunction |
| INJECTION CONTROL |
The feed pump is used to pump fuel from the fuel tank to the fuel supply pump.

| FUEL SUPPLY PUMP |
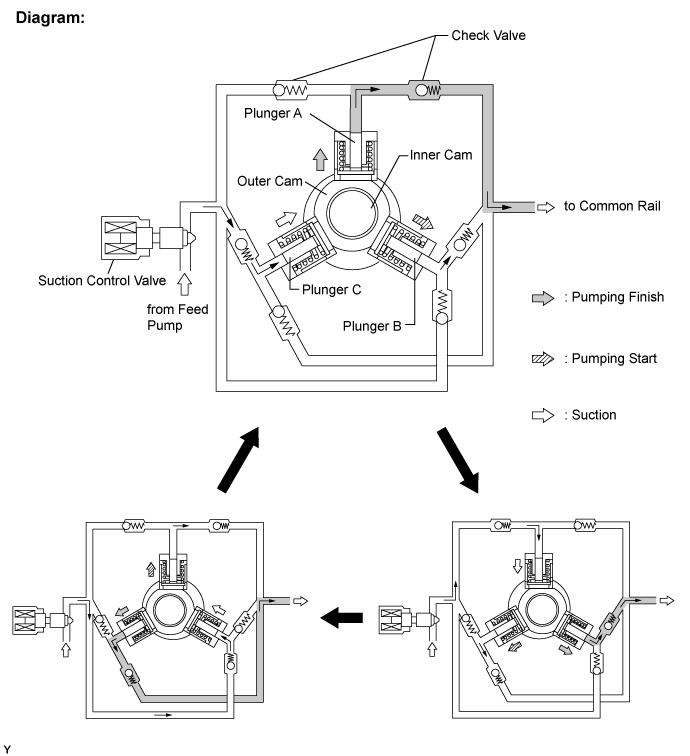
| SUCTION CONTROL VALVE |
- HINT:
- The ECM controls the suction control valve operation to regulate the fuel volume that is pumped by the fuel supply pump to the common rail. This control is performed to adjust the internal fuel pressure of the common rail to the targeted injection pressure.
Small opening of the suction control valve:
When the opening of the suction control valve is small, the fuel suction path is kept narrow. Therefore the transferable fuel volume is reduced*A.
The suction volume becomes small due to the narrow path despite the plunger stroke being full. The difference between the geometrical volume and suction volume creates a vacuum*B.
Pumping will start when the fuel pressure becomes higher than the common rail pressure*C.
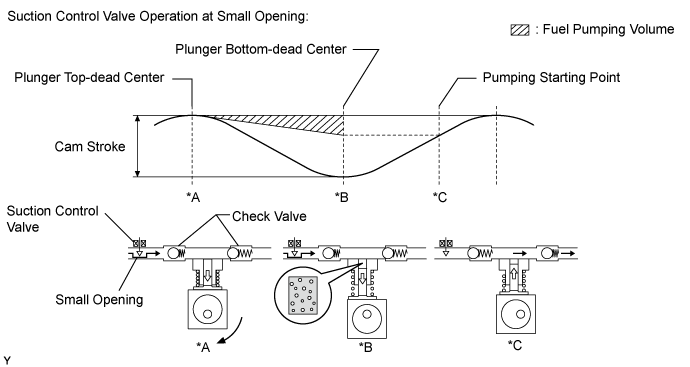
Large opening of the suction control valve:
When the opening of the suction control valve is large, the fuel suction path is kept wide. Therefore the transferable fuel volume is increased*D.
If the plunger stroke is full, the suction volume becomes large because of the wide path*E.
Pumping will start when the fuel pressure becomes higher than the common rail pressure*F.
