Ecd System (For Dpf) -- Data List / Active Test |
| DATA LIST |
- HINT:
- Using the intelligent tester to read the Data List allows the values or states of switches, sensors, actuators and other items to be read without removing any parts. This non-intrusive inspection can be very useful because intermittent conditions or signals may be discovered before parts or wiring is disturbed. Reading the Data List information early in troubleshooting is one way to save diagnostic time.
- NOTICE:
- In the table below, the values listed under "Normal Condition" are reference values. Do not depend solely on these reference values when deciding whether a part is faulty or not.
Warm up the engine.
Turn the ignition switch off.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Start the engine.
Turn the intelligent tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List.
- HINT:
- To display the list box, press the pull down menu button next to "Primary". Then select a measurement group.
- When you select a measurement group, the ECU data belonging to that group is displayed.
- Measurement Group List / Description
- All Data / All data
- Primary / -
- Engine Control / Engine control system related data
- Vehicle Information / Vehicle information
- Monitor Status / Monitor status related data
- AF Control System / Not Applicable
- Catalytic Converter / Not Applicable
- Evaporative / Not Applicable
- A/T / Automatic transaxle system related data
- ETCS / Not Applicable
- Misfire / Not Applicable
- Compression / Data used during "Check the Cylinder Compression" Active Test
- HC Adsorber System / Not Applicable
- Diesel Driving / Driving condition data
- Diesel Injection / Fuel system related data
- Diesel EGR / EGR system related data
- Diesel Throttle / Diesel throttle system related data
- Diesel VN Turbo / VN turbo related data
- Diesel Exhaust / Exhaust system related data
- Diesel Starting / "Difficult to start" related data
- Diesel Rough / "Rough idle" related data
- Diesel Power / "Lack of power" related data
Check the values by referring to the table below.
- NOTICE:
- Normal Condition: If no idling conditions are specified, the shift lever is in the neutral position, and the A/C switch and all accessory switches are OFF.
- "Result of real-vehicle check" is the assessment of one vehicle. Use it only for reference.
 |
| Engine Control |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Calculate Load | Load calculated by ECM/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% |
| Calculated by ECM | Malfunction in which turbo pressure or Mass Air Flow decreases |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Calculated load = (Final injection volume / max. injection volume at current engine speed) x 100. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| MAF | Air flow rate from mass air flow meter/ Min.: 0 gm/s, Max.: 400 gm/s |
| Sensor output (mass air flow meter) |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Rough idling | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Speed | Engine speed/ Min.: 0 rpm, Max.: 6000 rpm |
| Sensor output (crankshaft position sensor) |
|
| Diagnostic Note: When the crankshaft position sensor is malfunctioning, "Engine Speed" is approximately 0 or varies greatly from the actual engine speed. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Target Idle Engine Speed | Target Idling Engine Speed/ Min.: 0 rpm, Max.: 10000 rpm | - | Target idling speed (ECM calculated value) | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| MAP | Absolute pressure inside intake manifold/ Min.: 0 kPa, Max.: 320 kPa |
| Sensor output (manifold absolute pressure sensor) |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Lack of power | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Vehicle Speed | Vehicle speed/ Min.: 0 km/h, Max.: 255 km/h | Actual vehicle speed | Sensor output (speed sensor) |
|
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Coolant Temp | Engine coolant temperature/ Min.: -40°C, Max.: 140°C | After warming up engine: 70 to 90°C (158 to 194°F) | Sensor output (engine coolant temperature sensor) |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Difficulty starting when engine is cold, rough idle, black smoke, lack of power | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Intake Air | Intake air temperature/ Min.: -40°C, Max.: 140°C | Equivalent to temperature at location of mass air flow meter | Sensor output (intake air temperature sensor (built into mass air flow meter)) | Intake air temperature sensor |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Initial Engine Coolant Temp | Initial engine coolant temperature/ Min.: -40°C, Max.: 120°C | Engine coolant temperature when engine started | Sensor output when engine started | - |
| Diagnostic Note: For freeze frame data, this tells whether the malfunction happened at a cold start or with a warm engine. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Initial Intake Air Temp | Initial intake air temperature/ Min.: -40°C, Max.: 120°C | Intake air temperature when engine started | Sensor output when engine started | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Intake Air Temp (Turbo) | Intake air temperature after intercooler/ Min.: -40°C, Max.: 190°C | 70°C (158°F) or less | Sensor output (intake air temperature sensor after intercooler) | Decreased cooling efficiency of intercooler (contamination, clogging) |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Glow Control Unit Duty | Glow Control Unit Duty/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 127.5% | - | Result of ECU calculations | - |
| Diagnostic Note: This is the ECM command. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Alternate Duty Ratio | Alternator generation duty ratio/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% |
| Duty value from ALT terminal |
|
| Results of real-vehicle check: Idling (no electrical load) (warm up the engine): 40% (2 minutes after starting the vehicle) | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Starter Signal | Starter signal/ ON or OFF | ON: Cranking | - |
|
Symptoms when out of range:
| ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Ignition switch (STA) output:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| A/C Signal | A/C (Air Conditioner) signal/ ON or OFF | ON: A/C on | A/C operation signal output from A/C amplifier
|
|
| Symptoms when out of range: OFF malfunction (OFF even when A/C switch is turned on):
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Stop Light Switch | Stop light switch/ ON or OFF |
| Switch output (stop light switch) |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Stop light switch malfunction DTC P0504 is stored | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Stop light switch (STP) operation condition:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Immobiliser Communication | Immobiliser communication/ ON or OFF |
| - |
|
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Clutch Switch | Clutch switch/ ON or OFF | ON: Clutch pedal depressed | Switch output (Clutch switch assembly for cruise control system) | - |
| Symptoms when out of range: The cruise control, pilot quantity learning, etc. may not function properly or may not function at all. | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: When this item displays "OFF" with the clutch pedal depressed, the shock when accelerating and decelerating the vehicle becomes larger and pilot quality learning cannot be performed. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Battery Voltage | Battery voltage/ Min.: 0 V, Max.: 15 V | 11 to 14 V | - | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: If 5 V or less, starting becomes difficult | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: If 11 V or less, characteristics of some electrical components change. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Atmosphere Pressure | Atmospheric pressure value/ Min.: 50 kPa, Max.: 120 kPa | Actual atmospheric pressure | Sensor output (atmospheric pressure sensor (built into ECM)) | Atmospheric pressure sensor itself has failed (atmospheric pressure sensor is inside the ECM) |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| ACT VSV | A/C cut status for Active Test/ ON or OFF | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: "Control the A/C Cut Signal" Active Test support data. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| TC and TE1 | TC and TE1 connection status for Active Test/ ON or OFF | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: When the "Connect the TC and TE1" Active Test is performed, the system behaves as if TC and CG were connected. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| # Codes (Include History) | Number of codes/ Min.: 0, Max.: 255 | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Number of DTCs appearing at least once during the last 40 times the vehicle was warmed up. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Check Mode | Check mode/ ON or OFF | ON: Check mode on | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Check Mode: The mode in which certain DTCs can be detected more easily and with higher sensitivity. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| MIL | MIL status/ ON or OFF | OFF: MIL off | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| MIL ON Run Distance | Distance traveled with MIL on/ Min.: 0 km, Max.: 65535 km | Distance traveled after DTC stored | Result of ECU calculations (using the vehicle speed) | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Running Time from MIL ON | Running time after MIL turns on/ Min.: 0 min., Max.: 65535 min. | Running time after MIL turns on | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Run Time | Engine run time/ Min.: 0 sec., Max.: 65535 sec. | Time after the ignition switch turned to ON | Result of ECU calculations (using the engine speed) | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Time passed since the ignition switch was turned to ON. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Time after DTC Cleared | Time after DTC cleared/ Min.: 0 min., Max.: 65535 min. | Time after DTCs cleared | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Time elapsed since the DTCs were cleared (or shipment from the factory). | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Distance from DTC Cleared | Distance driven after DTC cleared/ Min.: 0 km, Max.: 65535 km | Distance driven after DTCs cleared | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Warmup Cycle Cleared DTC | Warmup cycles after DTC cleared/ Min.: 0, Max.: 255 | - | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| OBD Requirements | Identifying OBD requirement | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Euro-OBD | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Number of Emission DTC | Number of emissions-related DTCs | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Complete Parts Monitor | Complete parts monitor/ Not Avl or Avail | - | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Start Time | Engine start time/ Min.: 0 ms, Max.: 267000 ms | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Time necessary for the engine to start. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Accel Position | Accelerator position status/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% |
|
| - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
- HINT:
- Accel Sens. No.1 Volt % and Accel Sens. No.2 Volt % express the value obtained by dividing the output voltage from the accelerator pedal position sensor by 5. This is used only for diagnosing malfunctions in the accelerator pedal position sensor. Under normal conditions, it is sufficient to only check the final accelerator opening angle value "Accel Position".
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Accel Sens. No.1 Volt % | Accelerator position No. 1/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% |
| Sensor output (Accelerator pedal position sensor) | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Read value with ignition switch ON (do not start engine). | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Accel Sens. No.2 Volt % | Accelerator position No. 2/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% |
| Sensor output (Accelerator pedal position sensor) | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Read value with ignition switch ON (do not start engine). | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Swirl Control Valve VSV | Status of VSV for swirl control valve/ ON or OFF | ON: Idling | - | - |
| Compression |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Speed of Cyl #1 | Engine speed for No. 1 cylinder/ Min.: 0 rpm, Max.: 51199 rpm | Engine speeds of all cylinders almost same | - | Cyl #1 compression goes down |
| Symptoms when out of range: When the engine speeds of all cylinders are not equal, idling will be rough. | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Speed of Cyl #2 to #4 | Engine speed for No. 2 to No. 4 cylinder/ Min.: 0 rpm, Max.: 51199 rpm | - | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Av Engine Speed of All Cyl | Engine speed for all cylinders/ Min.: 0 rpm, Max.: 51199 rpm | - | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Vehicle Information |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Model Code | Model code | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Identifying model code | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Type | Engine type | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Identifying engine type: 1KDFTV | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Cylinder Number | Cylinder number/ Min.: 0, Max.: 255 | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Identifying cylinder number: 4 | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Transmission Type | Transaxle type/ MT or ECT 5th | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Identifying transaxle type:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Destination | Destination | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Identifying destination | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Model Year | Model year/ Min.: 1900, Max.: 2155 | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Identifying model year: 20## | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Turbo Type | VN turbo type/ Not Avl, Commo, Vacuum, CAN com, DC | DC*
| - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Indicates the VN turbo vane actuation method.
| ||||
| Diesel Injection |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Target Common Rail Pressure | Target common rail pressure/ Min.: 0 kPa, Max.: 250000 kPa | 30000 to 200000 kPa when engine running | Target common rail pressure (ECU calculated value) | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Fuel Press | Fuel pressure/ Min.: 0 kPa, Max.: 250000 kPa | Idling: 30000 to 50000 kPa | Sensor output (fuel pressure sensor) |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Difficult to start, poor driveability, lack of power, abnormal combustion noise | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Common Rail Pres Sens 2 | Fuel pressure/ Min.: 0 kPa, Max.: 250000 kPa | Idling: 30000 to 50000 kPa | Sensor output (fuel pressure sensor) |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Poor driveability, lack of power, abnormal combustion noise. | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: This is a backup output value from the fuel pressure sensor. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Target Pump SCV Current | Final pump current target value/ Min.: 0 mA, Max.: 4000 mA | Idling: 923 to 1123 mA | Target value control (pump current) |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Difficulty starting, lack of power or rough idling | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Pump SCV Learning Value | Pump SCV learning value/ Min.: -4096 mA, Max.: 4095.8 mA |
| Learned value |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Difficulty starting, lack of power or rough idling | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: If the value is stuck at 200 mA or higher or -200 mA or less, it indicates that the operation is poor (poor movement due to deposits, etc.). | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Inj. FB Vol. for Idle | Idle stability status integral control volume/ Min.: -80 mm3/st, Max.: 79 mm3/st | -10 to 10 mm3/st | - | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Idling (warm up the engine): 0.88 mm3/st | ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Engine friction problem, compression problem or injector breakdown | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Idle Signal Output Value | Idle Signal Output Value/ Min.: 0, Max.: 255 |
| - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Injection Volume | Injection volume/ Min.: 0 mm3/st, Max.: 1279.98 mm3/st | Idling: 2 to 11 mm3/st | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Inj Vol Feedback Learning | Injection volume feedback learning value/ Min.: -10 mm3/st, Max.: 9.92 mm3/st | - | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Injector Memory Error | Injector Memory Error/ No Error or Error | No Error | Calculated value | - |
| Symptoms when out of range: Rough idling, poor driveability, black smoke, white smoke, combustion noise | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: If the injector compensation codes are not input into the new ECM, or if an injector compensation code of a different injector model or a compensation code representing a value which exceeds the compensation setting range is input into the new ECM, DTC P062F is stored and "Injector Memory Error" displays "Error". | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Reju Pilot Quantity Learning | Pilot quantity learning prohibition state/ READY or NG | - | Calculated value | - |
| Diagnostic Note: The status is only displayed while performing "Pilot Quantity Learning". | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Pilot Quantity Learning | State of "Pilot Quantity Learning"/ Standby, Wait, Learn, Stop, Comple | - | Calculated value | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Fuel Return Temp | Fuel return temperature/ Min.: -40°C, Max.: 140°C | Idling after engine warmed-up: 35 to 85°C (95 to 185°F) | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: If the "Fuel Return Temp" value is not between 35°C (95°F) and 110°C (230°F), "Pilot Quantity Learning" is prohibited. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Injection Pressure Correction | Injection pressure feedback compensation volume/ Min.: -500 mm3/st, Max.: 780 mm3/st | -400 to 400 mm3/st at standard temperature | Calculated value |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Injection Feedback Val #1 Injection Feedback Val #2 Injection Feedback Val #3 Injection Feedback Val #4 | Injection volume correction for each cylinder/ Min.: -10 mm3/st, Max.: 10 mm3/st | Idling: -3.0 to 3.0 mm3/st | Learned value |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Rough idling, black smoke, white smoke, poor driveability, lack of power, abnormal combustion noise, difficult to start | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Pilot 1 Injection Period | Pilot 1 injection period/ Min.: 0 μs, Max.: 65535 μs | Idling: 100 to 400 μs | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Combustion noise, poor driveability, white smoke | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Check to see if "Pilot 1 Injection Period" is not zero when symptoms occur. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Pilot 2 Injection Period | Pilot 2 injection period/ Min.: 0 μs, Max.: 65535 μs | Idling: 100 to 400 μs | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Symptoms when out of range: Combustion noise, poor driveability, white smoke | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Check to see if "Pilot 2 Injection Period" is not zero when symptoms occur. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Main Injection Period | Main injection period/ Min.: 0 μs, Max.: 65535 μs | Idling: 200 to 500 μs | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| After Injection Period | After injection period/ Min.: 0 μs, Max.: 65535 μs | - | Calculated value | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Check to see if "After Injection Period" is not zero when the following symptoms occur: Black smoke, poor driveability. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Pilot 1 Injection Timing | Pilot 1 injection timing/ Min.: -70°CA, Max.: 20°CA | Idling after engine warmed up and vehicle under normal atmospheric pressure: -13.3 to -9.3°CA | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Pilot 2 Injection Timing | Pilot 2 injection timing/ Min.: -50°CA, Max.: 20°CA | Idling after engine warmed up and vehicle under normal atmospheric pressure: -8.8 to -4.8°CA | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Main Injection Timing | Main injection timing/ Min.: -90°CA, Max.: 90°CA | Idling after engine warmed up and vehicle under normal atmospheric pressure: -2.8 to 1.2°CA | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Use "Main Injection Timing" to check poor drivability when the following symptoms are present: Bad injection timing, black smoke, and white smoke. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| After Injection Timing | After injection timing/ Min.: -10°CA, Max.: 50°CA | - | Calculated Value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Fuel Temperature | Fuel temperature/ Min.: -40°C, Max.: 140°C | Actual fuel temperature | Sensor output (fuel temperature sensor) | - |
| Diagnostic Note: After fully cold soaking the engine, the fuel temperature is the same as the outside air temperature. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Pressure Discharge Valve | Pressure discharge valve operation/ ON or OFF | ON: Pressure discharge valve open | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: This is the ECM command. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Idle Injection Volume (Min) | Idle minimum injection volume/ Min.: 0 mm3/st, Max.: 39.8 mm3/st | - | - | - |
| EGR System |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Target EGR Position | EGR valve target opening amount/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% | Idling after engine warmed up: 0 to 90% | ECU-calculated value based on sensors (mass air flow meter, manifold absolute pressure sensor, intake air temperature (built into mass air flow meter), etc.) | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Symptoms when out of range:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Actual EGR Valve Pos. | EGR valve position/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% | Idling after engine warmed up: 0 to 92% | Calculated from EGR valve position sensor | |
Symptoms when out of range:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| EGR Operation Prohibit | EGR operation prohibition/ OK or NG | OK: Possible to perform "Control the EGR Step Position" and "Activate the EGR Valve Close" Active Tests | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| EGR Close Lrn. Val. | EGR fully closed position learned value/ Min.: 0 V, Max.: 5 V | 0 to 1 V | EGR valve position sensor value when EGR valve fully closed | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 0.65 V | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| EGR Close Lrn. Status | EGR valve fully closed position learning status/ OK or NG | OK | - | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: OK | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| EGR Cooler Bypass VSV | Status of the EGR Cooler Bypass VSV/ ON or OFF |
| - |
|
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| EGR Cooler Bypass Position | Status of the EGR Cooler Bypass Position/ Cooler or Bypass |
| - |
|
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Diesel Throttle System |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Throttle Sensor Volt % | Absolute throttle position sensor/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% |
| Sensor output (throttle position sensor) | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Symptoms when out of range:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Target Throttle Position | Target throttle position/ Min.: -128%, Max.: 127% |
| Value calculated by ECM | - |
| Diagnostic Note: If there is a malfunction of the throttle actuator, compare the target and actual throttle position values for troubleshooting. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Actual Throttle Position | Actual diesel throttle position/ Min.: -20%, Max.: 120% | Idling after engine warmed-up: 0 to 92% | - | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Symptoms when out of range:
| ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Closing percentage of the throttle valve.
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Throttle Motor Duty | Diesel throttle motor duty/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% | - | - | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Diagnostic Note: When the moving force to open and close the diesel throttle valve increases, the value of the Throttle Motor Duty increases. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Throttle Close Learning Val. | Throttle fully closed position learned value/ Min.: 0 deg, Max.: 84 deg | 14.25 to 21.25 deg | - | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 17.9 deg | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Diesel Throttle Learn Status | Diesel throttle learning history/ OK or NG | OK | - | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: OK | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| VN Turbo System |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Target Booster Pressure | Target booster pressure/ Min.: 0 kPa, Max.: 320 kPa | Driving vehicle on level surface at 3000 rpm with full load: 200 to 225 kPa | Value calculated by ECM | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Boost Pressure Deviation | Boost pressure deviation/ Min.: -320 kPa, Max.: 320 kPa | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Difference between target and actual boost pressure. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Turbo Error Level | VN turbo driver opening angle level when abnormality detected/ 0, 1, 2 or 3 | 0: Normal | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Turbo Command | VN turbo command value/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% | 0 to 98% | Controls the VN turbo vane opening position | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Actual VN Position | Actual VN turbo position/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 127.5% | 0 to 100% | - | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
| Diagnostic Note: If the vanes do not move smoothly or become stuck, the difference between the actual value and the target value ("VN Turbo Command") becomes larger, and as a result, the motor duty also becomes larger. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Position Sensor Out | VN position sensor output voltage/ Min.: 0 V, Max.: 5 V | Idling after engine warmed-up: 1 to 3 V | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Motor Duty | VN turbo motor duty/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 127.5% | 2 to 88% | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: If the vanes do not move smoothly, the duty will increase towards 100%. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Close Learn Value | VN turbo fully closed position learned value/ Min.: 0 V, Max.: 5 V | 1.5 to 2 V | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Close Learn Status | VN turbo fully closed position learning status/ OK or NG | OK | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: If learning is not complete, the vehicle performance may decrease (power output is low). | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Turbo Max Angle | VN turbo maximum opening amount/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% | - | - | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 99.6% | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Turbo Min Angle | VN turbo minimum opening amount/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 100% | - | - | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 39.8% | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| VN Turbo Operation prohibit | VN turbo operation prohibition/ OK or NG | OK: The "Test the Turbo Charger Step Motor" and "Activate the VN Turbo Open" Active Tests can be performed. | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: When NG is displayed, the ECM does not permit "Test the Turbo Charger Step Motor" and "Activate the VN Turbo Open" Active Tests to be performed. | ||||
| Exhaust control system |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| AF Lambda B1S1 | Lambda equivalent ratio/ Min.: 0, Max.: 255 |
| - |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
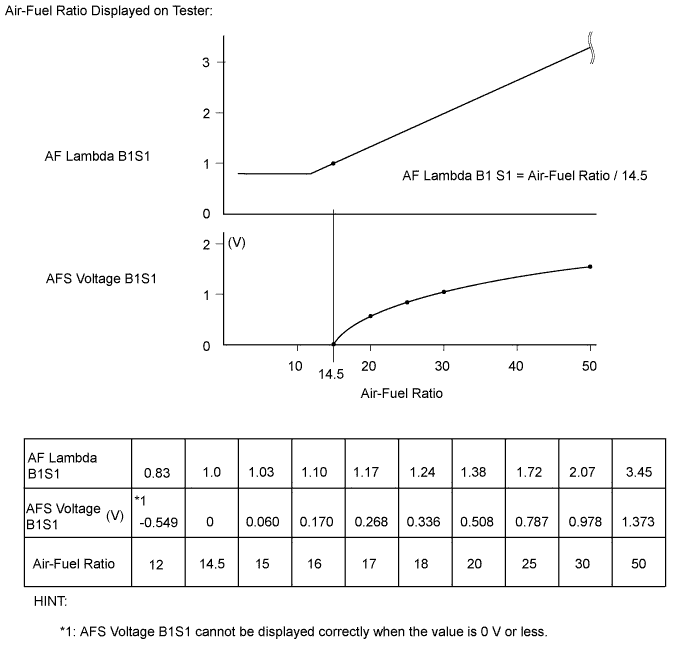
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| AFS Voltage B1S1 | Air fuel ratio sensor output voltage/ Min.: 0 V, Max.: 7.999 V | - | - |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| AFS Current B1S1 | Air fuel ratio sensor current/ Min.: -128 mA, Max.: 128 mA | - | - |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| AF Sensor Learning Value | Air fuel ratio sensor learning value/ Min.: 0 V, Max.: 5 V | - | Value calculated by ECM | - |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 1.92 V | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: Inspect the air fuel ratio sensor performance. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Exhaust Temperature B1S1 Supported Exhaust Temperature B1S2 Supported Exhaust Temperature B1S3 Supported | Status of exhaust gas temperature Supported/ Supp or Unsupp | Supp | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: If this item displays "Unsupp", a fixed value is displayed for "Exhaust Temperature", as exhaust gas temperature sensors are not equipped on the vehicle. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Exhaust Temperature B1S1 | Exhaust gas temperature of CCo catalyst/ Min.: 0°C, Max.: 1000°C |
| Sensor output (Exhaust gas temperature sensor B1S1) |
|
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Exhaust Temperature B1S2 | Exhaust gas temperature of DPF catalyst/ Min.: 0°C, Max.: 1000°C |
| Sensor output (No. 2 exhaust gas temperature sensor B1S2) |
|
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Exhaust Temperature B1S3 | Exhaust gas temperature of DPF catalyst/ Min.: 0°C, Max.: 1000°C |
| Sensor output (No. 3 exhaust gas temperature sensor B1S3) |
|
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| DPF Differential Pressure | DPF differential pressure/ Min.: -5 kPa, Max.: 100 kPa | Ignition switch ON: Approximately 0 kPa | Sensor output (DPF differential pressure sensor) |
|
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Catalyst Differential Press | Amount of clogging in catalyst/ Min.: -4, Max.: 3.9998 | 0.45 or less | Calculated value | - |
Results of real-vehicle check:
| ||||
Symptoms when out of range:
| ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Diff. Press. Sensor Corr. | Differential pressure sensor 0 point learned value/ Min.: -10 kPa, Max.: 245.9 kPa | Ignition switch ON (engine stopped): - 1.5 to 1.5 kPa | - | Differential pressure sensor |
Diagnostic Note
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Exhaust Fuel Addition FB | Exhaust fuel addition correction value/ Min.: 0.8, Max.: 1.99 | 0.86 to 1.41 | Value calculated by ECM |
|
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 1.03 | ||||
Diagnostic Note
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| DPF Thermal Deteriorate | DPF catalyst thermal deteriorate/ Normal or Deteriorated | Normal | Value calculated by ECM |
|
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| DPF No Activate | DPF operation/ Activate or No Activate | During PM forced regeneration: Activate | Value calculated by ECM |
|
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: Activate | ||||
| Diagnostic Note If the exhaust gas temperature does not rise enough when the PM forced regeneration is performed, "No Activate" appears on the intelligent tester display. In this case, DPF catalyst deterioration and clogging of the exhaust fuel addition injector are possible causes of the malfunction. Other possible causes include EGR valve malfunction, exhaust temperature sensor malfunction, and injector malfunction. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Catalyst Memory Error | Catalyst memory error/ No Error or Error | No Error | Calculated value | - |
| Symptoms when out of range: Rough idling, poor driveability, black smoke, white smoke, combustion noise. | ||||
| Diagnostic Note: If the catalyst deterioration learning value from the old ECM is not input into the new ECM, or if a catalyst deterioration learning value that exceeds the setting range is input into the new ECM, DTC P062F is stored and "Catalyst Memory Error" displays "Error". | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Add. INJ Flow Excessive | Exhaust fuel addition injector injection volume excessive/ Normal or Error | Normal | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: This item indicates whether there is an abnormal decrease in the actual air-fuel ratio. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| DPF Overtemperature | DPF catalyst overheat/ Normal or Error | Normal | - | - |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| DPF PM Block | DPF PM Block/ No block or Blocked | No Block | Calculated value |
|
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: No Block | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| DPNR/DPF Status Reju (PM) | PM forced regeneration status/ Standby, Ready, Operate, Compl | During PM forced regeneration: Operate | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: The status is only displayed while performing "Activate the DPF Rejuvenate (PM)".
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| PM Accumulation Ratio | PM accumulation ratio/ Min.: 0%, Max.: 510% | - | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Diesel Starting |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Speed (Starter Off) | Engine speed when starter off/ Min.: 0 rpm, Max.: 1594 rpm | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Engine speed immediately after starting the engine. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Starter Count | Starter on count/ Min.: 0, Max.: 255 | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Number of times the starter turned on from the time the ignition switch was turned to ON. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Run Dist of Previous Trip | Distance driven during previous trip/ Min.: 0 km, Max.: 261 km | - | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Before 5 seconds elapse after starting the engine, which is the DTC P1604 (Startability Malfunction) detection duration, this parameter indicates the distance driven during the previous trip. After 5 seconds elapse after starting the engine, this parameter indicates the distance driven during the current trip calculated from the vehicle speed signal.
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Glow Request Lighting Time | Glow Request Lighting Time/ Min.: 0 ms, Max.: 33423 ms | - | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| IG-ON Time | IG-ON Time/ Min.: 0 ms, Max.: 33423 ms | - | - | - |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Immobiliser Fuel Cut History | Immobiliser fuel cut history/ ON or OFF | OFF | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: If Immobiliser Fuel Cut History was "ON" when DTC P1604 (Startability Malfunction) was stored, the engine could not be started due to the immobiliser. | ||||
| Diesel Rough |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Rough Idle #1 Rough Idle #2 Rough Idle #3 Rough Idle #4 | Status of the Rough Idle #1 to #4/ ON or OFF | OFF | - | Injector assembly |
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Electric Duty Feedback Value | Electric load feedback value/ Min.: 0 mm3/st, Max.: 39.8 mm3/st | 0 to 3.3 mm3/st | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Expected injection volume increase after the electrical load turns from off to on. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| A/C Duty Feedback Value | A/C load feedback value/ Min.: 0 mm3/st, Max.: 39.8 mm3/st | 0 to 3.4 mm3/st | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Expected injection volume increase after the A/C turns from off to on. | ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| PS Duty Feedback Value | Power steering load feedback value/ Min.: 0 mm3/st, Max.: 39.8 mm3/st | 0 mm3/st | - | - |
| Diagnostic Note: Expected injection volume increase after the power steering turns from off to on. | ||||
| Diesel Power |
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| MAF Low | Mass air flow Low/ ON or OFF | OFF | - |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Lack of power | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Boost Pressure Low | Status of the Boost Pressure Low/ ON or OFF | OFF | - |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Lack of power | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Common Rail Pressure Low | Status of the Common Rail Pressure Low/ ON or OFF | OFF | - |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Lack of power | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| Engine Coolant Temp High | Status of the Engine Coolant Temp High/ ON or OFF | OFF | - |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Lack of power | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| Tester Display | Measurement Item/Range | Normal Condition | Type | Cause of Out of Range |
| MAF/Estimate MAF Ratio | Ratio of intake air amount to estimated intake air amount/ Min.: 0, Max.: 2.55 | Engine speed 4000 rpm, EGR system off: 0.6 to 1.4 | - |
|
| Symptoms when out of range: Lack of power | ||||
Diagnostic Note:
| ||||
| ACTIVE TEST |
- HINT:
- Using the intelligent tester to perform Active Tests allows relays, VSVs, actuators and other items to be operated without removing any parts. This non-intrusive functional inspection can be very useful because intermittent operation may be discovered before parts or wiring is disturbed. Performing Active Tests early in troubleshooting is one way to save diagnostic time. Data List information can be displayed while performing Active Tests.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Turn the intelligent tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test.
Perform the Active Test.
Tester Display Test Part Control Range Diagnostic Note Activate the VSV for Swirl Control Valve Activate the VSV for swirl control valve ON/OFF - Control the A/C Cut Signal Control the A/C signal ON/OFF Confirm that the vehicle is stopped and the engine is idling Connect the TC and TE1 Turn on the TC and TE1 connection ON/OFF - Control the EGR Step Position Control the electric EGR control valve assembly 0 to 100% Test is possible when the following conditions are met: - Ignition switch ON.
- Engine is stopped.
Activate the DPF Rejuvenate (PM) PM forced regeneration Raise temperature of DPF to more than 600°C (1112°F) by adding fuel intermittently using the exhaust fuel addition injector ON/OFF - Diesel Throttle Target Angle Control the diesel throttle valve (bank 1) 0 to 90% Test is possible when the following conditions are met: - Ignition switch ON.
- Engine is stopped.
Test the Turbo Charger Step Motor Activate the turbocharger 40 to 100% Test is possible when the following conditions are met: - Ignition switch ON.
- Engine is stopped.
Test the Fuel Leak Pressurize the common rail interior and check for fuel leaks Stop/Start - Fuel pressure inside common rail pressurized to specified value and engine speed increased to 2000 rpm when ON is selected
- Above conditions preserved while test is ON
- HINT:
- If this Active Test is performed when the engine is cold, combustion may become unstable. However, this is not a malfunction. It is only necessary to confirm that the pressure rises to the target pressure and that there are no fuel leaks.
Activate the VN Turbo Open Activate the turbocharger ON/OFF Confirm that the engine is running. Activate the EGR Valve Close Activate the electric EGR control valve assembly ON/OFF Confirm that the vehicle is stopped and the engine is idling Activate the VSV for EGR Cooler Bypass Activate the vacuum switching valve assembly (for EGR cooler) Bypass/Half Pos/Cooler Test is possible when the following conditions are met: - Engine warmed up
- Engine is idling
- Shift lever in neutral
Control the Cylinder#1 Fuel Cut Stop fuel injection from the No. 1 injector assembly ON/OFF Fuel injection is stopped while the test is ON. - Confirm that the vehicle is stopped and the engine is idling.
- If the running condition of the engine does not worsen even though injection of the designated cylinder is stopped, the cylinder can be determined to be malfunctioning.
Control the Cylinder#2 Fuel Cut Stop fuel injection from the No. 2 injector assembly ON/OFF Fuel injection is stopped while the test is ON. - Confirm that the vehicle is stopped and the engine is idling.
- If the running condition of the engine does not worsen even though injection of the designated cylinder is stopped, the cylinder can be determined to be malfunctioning.
Control the Cylinder#3 Fuel Cut Stop fuel injection from the No. 3 injector assembly ON/OFF Fuel injection is stopped while the test is ON. - Confirm that the vehicle is stopped and the engine is idling.
- If the running condition of the engine does not worsen even though injection of the designated cylinder is stopped, the cylinder can be determined to be malfunctioning.
Control the Cylinder#4 Fuel Cut Stop fuel injection from the No. 4 injector assembly ON/OFF Fuel injection is stopped while the test is ON. - Confirm that the vehicle is stopped and the engine is idling.
- If the running condition of the engine does not worsen even though injection of the designated cylinder is stopped, the cylinder can be determined to be malfunctioning.
Check the Cylinder Compression* Check the cylinder compression pressure ON/OFF Fuel injection stops in all cylinders. - Ignition switch ON.
- HINT:
- *: When cranking the engine, the Active Test measures the speed of each cylinder. In this Active Test, the fuel of all cylinders is cut when the engine is cranked for approximately 10 seconds.
- Warm up the engine.
- Turn the ignition switch off.
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Check the Cylinder Compression.
- HINT:
- If the results are not displayed normally, select the display items from the Data List before performing the Active Test. Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Compression / Engine Speed of Cyl #1, Engine Speed of Cyl #2, Engine Speed of Cyl #3, Engine Speed of Cyl #4 and Av Engine Speed of All Cyl.
- While the engine is not running, press the RIGHT or LEFT button to change Check the Cylinder Compression to ON.
- HINT:
- After performing the above procedure, the "Check the Cylinder Compression" Active Test will start. Fuel injection for all cylinders is prohibited and the engine speed measurement of each cylinder enters standby mode.
- Crank the engine for about 10 seconds.
- Monitor the engine speed (Engine Speed of Cyl #1 to #4, Av Engine Speed of All Cyl) displayed on the tester.
- HINT:
- At first, the tester display will show the engine speed measurement of each cylinder to be extremely high. After approximately 10 seconds of engine cranking, the engine speed measurement of each cylinder will change to the actual engine speed.
- NOTICE:
- After the "Check the Cylinder Compression" Active Test is turned on, it will automatically turn off after 255 seconds.
- When the "Check the Cylinder Compression" test is off and the engine is cranked, the engine will start.
- If the "Check the Cylinder Compression" test needs to be performed after it is turned on and performed once, press "EXIT" to return to the Active Test menu screen. Then perform the "Check the Cylinder Compression" test again.
- Use a fully-charged battery.
| SYSTEM CHECK |
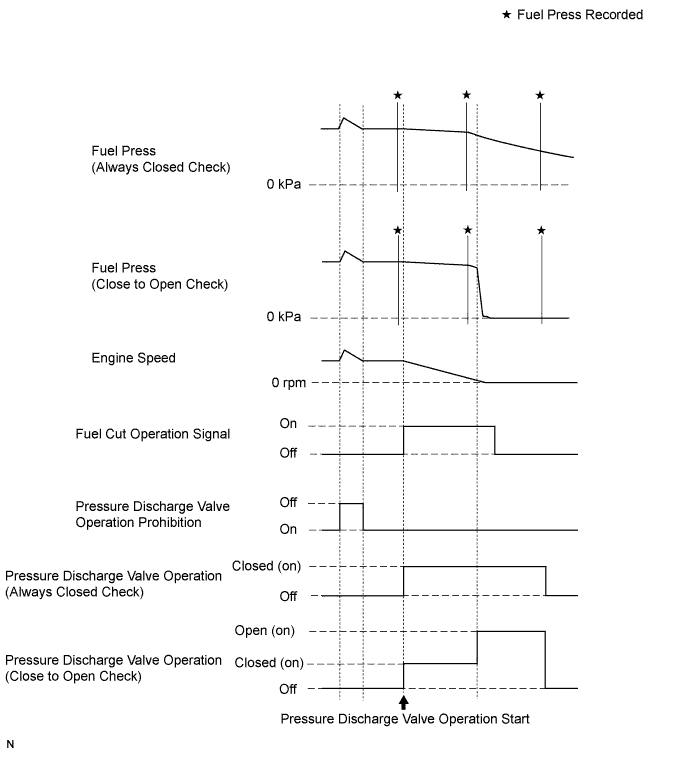
Activate the Pressure Discharge Valve Check
- HINT:
- This is the procedure for troubleshooting fuel pressure control malfunctions and combustion problems.
- Malfunctions can be determined by checking the fuel pressure when performing a fuel cut and operating the pressure discharge valve with the intelligent tester.
- During "Pressure Discharge Valve Check", the intelligent tester measures the fuel pressure while the engine is running, after the engine is stopped, and after the pressure discharge valve operates.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Turn the tester on.
- NOTICE:
- Confirm the following conditions:
- Engine is idling.
- Vehicle is stopped.
- Fuel pressure is not extremely high (below 100000 kPa).
- Fuel pressure is not extremely low (higher than 26000 kPa).
- Fuel pressure sensor is normal.
- Battery voltage is higher than 8 V.
- HINT:
- When the common rail pressure is unstable, the fuel pressure may decrease to a level where the test cannot be performed. In this situation, wait until the common rail pressure meets the test condition, and then perform the test.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / Pressure Discharge Valve Check.
Press "Next".
Press "Next" again to proceed.
Select the "Pressure Discharge Valve Check" type.
- HINT:
- "Close to Open Check" opens the pressure discharge valve after the engine stops.
- "Always Closed Check" holds the pressure discharge valve closed during the check.
Press "Next".
Perform troubleshooting based on the measurement results.

- HINT:
- During "Close to Open Check", if there is no large change in fuel pressure when the pressure discharge valve is closed while the engine is running and after the engine is stopped, and if the value is 0 kPa when the pressure discharge valve is open, the system is normal.
- Perform "Always Closed Check" if the value is not 0 kPa when the pressure discharge valve is open during "Close to Open Check". If the results are the same as during "Close to Open Check", there is a pressure discharge valve operation malfunction.
- If the fuel temperature is high, perform "Pressure Discharge Valve Check" after the fuel has cooled to the outside air temperature.
- If a large amount of fuel is leaking, the fuel pressure decreases when the engine is stopped. However, the condition of the pressure discharge valve can still be determined by comparing the measurement results of "Close to Open Check" and "Always Closed Check".