Land Cruiser URJ200 URJ202 GRJ200 VDJ200 - 1VD-FTV ENGINE CONTROL
CHECK ENGINE CRANKING CONDITION
CHECK COMMUNICATION BETWEEN INTELLIGENT TESTER AND ECM
READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (CLUTCH SWITCH)
INSPECT SMART START SYSTEM (IN CASE OF VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH SMART ENTRY AND START SYSTEM)
INSPECT CRANKING HOLDING FUNCTION CIRCUIT
CHECK INITIALIZATION (FUEL SUPPLY PUMP)
READ OUTPUT DTC (RELATED TO ENGINE)
TAKE DATA LIST DURING STARTING AND IDLING
CHECK SNAPSHOT (FUEL PRESS, TARGET COMMON RAIL PRESSURE ETC.)
CHECK IF FUEL IS BEING SUPPLIED TO FUEL SUPPLY PUMP
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
CHECK FUEL LEAK (FUEL SUPPLY PUMP)
CHECK FUEL LEAK (PRESSURE LIMITER (COMMON RAIL (for Bank 2))
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
CHECK SNAPSHOT (TARGET PUMP SCV CURRENT)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER
CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER
REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER
CHECK TEMPERATURE WHEN STARTING TROUBLE OCCURS
INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
INSPECT GLOW PLUG ASSEMBLY (RESISTANCE)
INSPECT INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED
INSPECT INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU POWER SOURCE)
ECD SYSTEM (w/o DPF) - Engine Difficult to Start or Stalling
DESCRIPTION
| Faults and Symptoms of Common Rail Diesel Components |
Engine Control
| Component | Mass air flow meter |
| Main fault | Decrease in performance (foreign matter is stuck) |
| Symptoms | Lack of power, black smoke |
| Data List | MAF |
|
| Component | Intake system |
| Symptom: Main fault | Lack of power (No black smoke): Air filter blockage, Air duct is crushed/leaking Black smoke (No lack of power): Leakage between the turbo and the intake manifold |
| Data List | MAP (inside intake air pressure) Target Booster Pressure When the accelerator is fully depressed, if the MAP is 20 kPa lower than Target Booster Pressure for more than 5 seconds then a lack of power will be felt. |
| Component | Turbocharger system |
| Main fault | Air leak in the turbocharged air passage Turbo motor driver not operating well Turbocharger (turbine, bearing) |
| Symptoms | Lack of power (when vehicle starting, when heavy load) (Black smoke is not emitted when racing while vehicle stopped) |
| Data List | MAP (inside intake air pressure), Target Booster Pressure When the accelerator is fully depressed, if MAP is 20 kPa lower than Target Booster Pressure for more than 5 seconds then a lack of power will be felt. With the ignition switch ON or idling, MAP = Atmospheric Pressure (standard atmospheric pressure = 101 kPa). When the engine speed is about 1500 rpm or more, the turbocharger starts to take effect and the MAP becomes higher than atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure increases 1 kPa each time altitude increases by 100 m, and is also affected by the current weather conditions. 0%: Fully open vanes (drive rod contracts) Over 90%: Fully closed (drive rod expands and turbo operates effectively) |
| Diagnostic Point | Using the Active Test "Test the Turbo Charger Step Motor", check the drive rod movement. Check the drive rod movement when the ignition switch is turned from ON to off. |
| Component | Exhaust system |
| Main fault | Blockage |
| Symptoms | Lack of power (high engine speed, when heavy load) |
| Data List | MAP (inside intake air pressure) When the accelerator is fully depressed, if the MAP is 20 kPa lower than Target Booster Pressure for more than 5 seconds then a lack of power will be felt. |
| Component | Glow system |
| Main fault | Open circuit, glow plug relay fault |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start, rough idle, knocking, white smoke (when cold) |
| Data List | Check the glow plug indicator light |
| Diagnostic Point | Try to measure the resistance of the glow plug |
| Component | Battery |
| Main fault | Battery is depleted |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start (cannot crank, crank speed is low), horn is quiet. |
| Data List | Battery Voltage When cranking, battery voltage is less than 5 V |
| Component | Engine |
| Main fault | Damaged, Seized up |
| Symptoms | Cannot crank, crank speed is low, strange noise |
| Component | Engine |
| Main fault | Loss of compression |
| Symptoms | Rough idle (lack of power always) |
| Data List | Engine Speed of Cyl When cranking during the "Check the Cylinder Compression" Active Test, if there is a high speed cylinder, approx. 100 rpm more than the other cylinders, that cylinder may loose compression. If Injection Feedback Val is more than 3 mm3/st, the cylinder may have a fault. |
| Component | Entry and Start system |
| Main fault | Starter system malfunction |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start |
| Data List | Starter Signal Ignition switch (STA) operation ON: Starter is operating OFF: Starter is not operating |
| Component | Engine immobiliser system |
| Main fault | Engine immobiliser system/Problem Symptoms Table () |
| Symptoms | Engine does not start |
| Data List | Immobiliser Communication ON: Normal OFF: GND short or immobiliser is set |
Diesel Injection
| Component | Fuel supply pump |
| Main fault | - |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start, engine stalling, rough idle, lack of power |
| Data List | Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure, Target Pump SCV Current At a stable condition (e.g. Idling), Fuel Press is within +/-5000 kPa of "Target Common Rail Pressure". If the fuel pressure is 20000 kPa below the target pressure then a lack of power will be felt. If the fuel pressure is below 25000 kPa then idling will be rough.
The fuel pressure changes at engine starting, but is approx. 25000 kPa at engine start after the engine is warmed up. When Target Pump SCV Current is 3000 mA or more, the suction control valve has a tendency to become stuck. |
| Diagnostic Trouble Code | Even if Fuel Press is less than Target Common Rail Pressure, a DTC will not be stored. |
| Component | Fuel filter |
| Main fault | Blockage |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start, engine stalling, rough idle, lack of power |
| Data List | Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure At a stable condition (e.g. Idling), the fuel pressure is within +/-5000 kPa of "Target Common Rail Pressure ". If the fuel pressure is 20000 kPa below the target pressure then a lack of power will be felt. If the fuel pressure is below 25000 kPa then idling will be rough.
|
| Diagnostic Trouble Code | Even if Fuel Press is less than Target Common Rail Pressure, a DTC will not be stored. |
| Component | Fuel injector |
| Main fault | Blockage |
| Symptoms | Rough idle, lack of power, black smoke, white smoke, knocking |
| Data List | Injection Feedback Val When an Injection Feedback Val is more than 3 mm3/st, the cylinder is not normal. This can be read after idling for 1 minute with the engine warmed up (engine coolant temperature is more than 70°C (158°F)). |
| Component | Pressure limiter |
| Main fault | Does not completely close |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start, engine stall, rough idle, lack of power |
| Component | Injector Driver (EDU) |
| Main fault | Circuit fault: The fuel injector does not open. |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start, rough idle, lack of power, black smoke, white smoke, knocking |
| Data List | Same as fuel injector |
| Diagnostic Trouble Code | When the EDU has a fault, some DTCs may be stored. |
| Component | Fuel pressure sensor |
| Main fault | Open circuit, Decrease in performance (foreign matters is stuck) |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start, rough idle, engine stall, lack of power |
| Data List | Fuel Press, Target Common Rail Pressure Slowly raise the engine speed from idling to 3000 rpm with the vehicle stopped, and check that Fuel Press follows Target Common Rail Pressure. If the fuel pressure sensor malfunctions, the actual fuel pressure may deviate from the target fuel pressure. (However, the value may not deviate even when a malfunction is present). |
| Diagnostic Trouble Code | When the fuel pressure sensor has a fault, some DTCs may be stored. |
| Component | Irregular fuel |
| Main fault | - |
| Symptoms | Difficult to start, rough idle (especially when cold) |
Diesel EGR
| Component | EGR system |
| Main fault | Does not move smoothly Does not close completely |
| Symptoms | Rough idle EGR valve stuck closed: A loud turbocharger sound. EGR valve stuck open: Difficult to start (does not stall), black smoke, lack of power (if there is an excess in the quantity of EGR and there is a heavy load, when the vehicle starts moving, a lack of power will be felt). |
| Data List | Actual EGR Valve Pos., Target EGR Pos. Generally, Actual EGR Valve Pos. = Target EGR Pos. +/-5% (fully closed 0%, fully open 100%) Using EGR valve Active Test, check whether Actual EGR Valve Pos. follows Target EGR Pos. (The engine coolant temperature and intake air temperature should be considered when a malfunction occurs). EGR valve is fully closed when the ignition switch is ON (engine stopped). EGR valve opens to halfway point at idling after engine warmed up. Leaving the vehicle idling, when EGR Close Lrn. Status is OK, the normal range of EGR Close Lrn. Val. is 3.5 to 4.5 V. In cases when EGR Close Lrn. Status. is NG or EGR Close Lrn. Val. is out of the normal range (3.5 to 4.5 V), it is possible that the EGR valve cannot completely close. |
Diesel Throttle
| Component | Diesel throttle system |
| Main fault | Stuck, does not move smoothly |
| Symptoms | Stuck closed: Lack of power, difficult to start, rough idle, engine stall, black smoke. It may occur when stuck almost fully closed. Stuck open: Turbocharger sound increases. When the engine is stopped, engine vibrations may occur. |
| Data List | Actual Throttle Position, Actual Throttle Position #2 0%: Fully open 100%: Fully closed Throttle Motor Duty Normally operates at 50 +/-20%. If outside the range of 50 +/-40% for a few seconds, the throttle may not be sliding properly. 0%: Open diesel throttle 100%: Close diesel throttle When ignition switch is ON (engine stopped), diesel throttle is fully open. When idling, diesel throttle is at halfway point. When ignition switch is turned from ON to off, temporarily closed fully. |
| Data List Related to Starting Trouble |
- NOTICE:
- The Data List values in the table are the results of checking one vehicle under a specific condition (engine coolant temperature, intake air temperature, atmosphere pressure etc.). That is why use these values for reference only.
Engine Control
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| MAP | When MAP is low, there will be difficulty starting. With ignition switch ON or idling, MAP is nearly equal to Atmosphere Pressure (standard atmospheric pressure = 101 kPa). | When MAP is low, the following conditions are possible: The diesel throttle is nearly fully closed. Intake system blocked (turbocharger system also). Exhaust system blocked. | When the ignition switch is ON or the vehicle is idling, MAP (intake manifold absolute pressure) and Atmosphere Pressure are mostly the same (standard atmospheric pressure = 101 kPa). Above approx. 1500 rpm, the turbo becomes effective, and the pressure becomes higher than atmospheric pressure. Inspect while comparing with "Target Booster Pressure". With the accelerator fully open, if the actual Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) is low compared to the target booster pressure by at least 20 kPa for 5 seconds or more, a feeling of insufficient power will occur. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 99 kPa Cranking: 99 kPa Idling (warm up the engine): 99 kPa (2 minutes after starting the vehicle) Running without load (2500 rpm): 113 kPa Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 143 kPa Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 209 kPa |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| MAF | - | MAF meter MAF meter circuit Intake system clogging, leaking Exhaust system clogging Turbocharger sub-assembly Leaking or clogging of turbocharger passages EGR valve does not close | Based on the MAF, the ECM controls the fuel injection volume, injection timing, EGR, etc. If the value is always approximately 0 g/sec.: Mass air flow meter power source circuit is open. VG circuit is open or shorted. If the value is always 200 g/sec. or more: EVG circuit is open. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: w/ EGR Ignition switch ON: 1.54 g/sec. Cranking: 15 g/sec. Idling (warm up the engine): 9 g/sec. (2 minutes after starting the vehicle) Running without load (2500 rpm): 80 g/sec. Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 110 g/sec. Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 230 g/sec. | |||
|
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Intake Air | - | Intake air temperature sensor. | After a long soak, the engine coolant temperature, intake air temperature, and ambient air temperature are approximately equal. If the value is -40°C (-40°F) or 140°C (284°F), the sensor circuit is open or shorted. |
| - |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Coolant Temp | Engine coolant temperature is approximately equal to intake air temperature after leaving overnight. After warm-up: Engine coolant temperature is 70°C (158°F) or more. In cases when the engine coolant temperature output is obviously higher than the actual engine coolant temperature, when it is cold, there will be difficulty starting due to problems with glow plugs or insufficient fuel injection. In cases when the engine coolant temperature sensor output is obviously lower than the actual engine coolant temperature, when it is warm, there will be difficulty starting (black smoke will also occur) due to an excess of injected fuel. | Engine coolant temperature sensor | If the value is -40°C (-40°F) or 140°C (284°F), the sensor circuit is open or shorted. After a long soak, the coolant temperature, intake air temperature, and ambient air temperature are approximately equal. |
| - |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Battery Voltage | When cranking, in cases when Battery Voltage becomes less than 5 V, the battery is depleted. | Battery | If 11 V or less, characteristics of some electrical components change. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 12.5 V Cranking (with engine warmed up): 9.0 V Idling (warm up the engine): 13.4 V Running without load (2500 rpm): 13.5 V Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 13 V Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 13.2 V |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Starter Signal | Operation of ignition switch (STA) ON: Starter is operating OFF: Starter is not operating | Entry and Start system | Ignition switch (STA) output: ON: Starter is operating OFF: Starter is not operating |
| - |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Engine Speed of Cyl #1 (to #8) | When cranking, the engine speed of each cylinder is the same under normal conditions. When a cylinder is approximately 100 rpm higher than the other cylinders, it is conceivable that the compression of that cylinder is being lost.
| - | Output only when the Active Test "Check the Cylinder Compression" is performed. With this Active Test, the fuel injection is stopped. Indicates the speed of each cylinder when cranking. Example - Normal: "Engine speed" of all cylinders is approximately equal. No. 1 cylinder compression low: "Engine speed of Cyl#1" = approximately 300 rpm, "Engine speed of Cyl #2 to #8 cylinder" = approximately 200 rpm. |
| - |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Immobiliser Communication | Engine immobiliser system/Data List () | Engine immobiliser system/Problem Symptoms Table () | When there is a malfunction in the immobiliser system, a DTC is stored () |
| - |
Diesel Injection
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Target Common Rail Pressure | - | - | Inspect the (actual) fuel pressure, comparing it against the common rail target value. Considered normal when the actual fuel pressure is within +/-5000 kPa of the target fuel pressure under stable conditions. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 32000 kPa Cranking: 29000 kPa Idling (warm up the engine): 32000 kPa (2 minutes after starting the vehicle) Running without load (2500 rpm): 62000 kPa Running without load (3500 rpm): 80200 kPa Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 95000 kPa Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 155000 kPa |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Fuel Press | In a stable operating condition (e.g. idling), Fuel Press is Target Common Rail Pressure +/-5000 kPa. During cranking, if Fuel Press is lower than 25000 kPa, there may be difficulty starting. (Take care as there is a response lag when the pressure rises). When Fuel Press is lower than 25000 kPa, rough idling will occur. | If there is a fault with the fuel supply pump (lack of discharge quantity) or pressure limiter (will not fully close), the fuel pressure will drop. Also, a blocked fuel filter, leakage from fuel pipes, and lack of fuel will also make the fuel pressure drop. If air mixes with the fuel, the fuel pressure will shift away from the target fuel pressure. When there is a fault with the fuel supply pump, there is a possibility of lack of power, engine stall, rough idle and difficulty starting. | Fuel press is the actual common rail fuel pressure. Inspect by comparing Fuel Press with Target Common Rail Pressure. The ECM uses Fuel Press for feedback control of Target Fuel Pressure via the supply pump. The injection amount is determined based on the injection timing and fuel pressure. Also, the spray pattern is selected based on the fuel pressure. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 0 kPa Cranking: 29000 kPa Idling (warm up the engine): 32000 kPa (2 minutes after starting the vehicle) Running without load (2500 rpm): 62000 kPa Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 92000 kPa Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 155000 kPa |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Target Pump SCV Current | Idling after warming up, roughly 923 to 1123 mA. When this value is large, the pump is trying to increase the fuel discharge rate. | With this data, component fault not specified, use this data as a reference. If the current is 3000 mA or more, there is a possibility the suction control valve is stuck. | ECU-calculated value for the suction control valve actuation target current. Value is large when a high fuel pressure is desired. When this deviates from the standard value, it indicates that for some reason, even though the pump is running hard, the actual fuel pressure is inconsistent with the target fuel pressure. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 0 mA Cranking: 1200 mA Running without load (2500 rpm): 1300 mA Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 1440 mA Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 1560 mA |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Injection Feedback Val #1 (to #8) | When idling after the engine is warmed up, the fuel quantity of each fuel injector is corrected to make each cylinder engine speed equal. Cylinders more than 3 mm3/st may have a fault.
| Fault with a fuel injector or lack of compression of a cylinder with a large Injection Feedback Val. Do a compression Active Test. If there is a cylinder that is around 100 rpm more than the other cylinder, there is a possibility that the compression of that cylinder is being lost. If all the cylinder speeds are even according to the compression Active Test result, then the fuel injector of the cylinder may have a fault. With fuel injector faults, other than difficulty starting, there is a possibility of rough idling, lack of power, black smoke, white smoke and knocking. | When idling after warm up, the injection amount for each cylinder is corrected to optimize the difference of each cylinder engine speed. Example: For cylinders that are slowing the engine speed compared to other cylinders, the injection volume is increased. "Injection Feedback Val" more than 3.0 mm3/st: Injector breakdown or insufficient compression is causing poor combustion. |
| - |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Injection Volume | - | - | After warming up the engine, when Injection Volume during idling is 10 mm3/st or more, there is tendency for the injector to clog. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Cranking: 21 mm3/st (Note: Varies depending on coolant temperature) Idling (warm up the engine): 6 mm3/st Running without load (2500 rpm): 9 mm3/st Running without load (4700 rpm): 16 mm3/st Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 50 mm3/st Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 70 mm3/st |
Diesel Throttle
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Actual Throttle Position Actual Throttle Position #2 | When the ignition switch is turned to ON (engine stopped), the diesel throttle is fully open. When the ignition switch is turned from ON to off, the diesel throttle will be fully closed temporarily. With the diesel throttle stuck almost fully closed, there is a possibility of rough idling, engine stall, black smoke, difficulty starting and lack of power. | Diesel throttle body | Actual Throttle Position is the closing percentage of the throttle valve. Fully closed: 100% Fully open: 0%
|
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 0% Cranking: 0% Idling (warm up the engine): 84% Running without load (2500 rpm): 32% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 0% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 0% |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Throttle Motor Duty #1 Throttle Motor Duty #2 | Normally operates at 50 +/-20%. If 50 +/-40% continues for a few seconds, it is conceivable that the throttle valve is not sliding properly. 0%: Drive throttle to open side 100%: Drive throttle to closed side | - | When this value is large but the actual opening angle does not move smoothly, there is an unable to close malfunction. If this value is small but the actual opening angle does not move smoothly, there is an unable to open malfunction. Usually this value is at approx. 50 +/-20%, but momentary jumps outside this range do occur. If a duty is outside 50 +/-40% for several seconds, it will be judged that the diesel throttle does not move properly and the MIL will be illuminated. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 61.5% Cranking: 63% Idling (warm up the engine): 37% Running without load (2500 rpm): 53% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 62.5% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 64% |
Diesel EGR
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Target EGR Valve Pos. Target EGR Valve Pos. #2 | - | - | Fully open: 100% Fully closed: 0% Used for comparison to "Actual EGR Valve Pos". |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 0% Cranking: 0% Idling (warm up the engine): 43% Running without load (2500 rpm): 22% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 0% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 0% |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| Actual EGR Valve Pos. Actual EGR Valve Pos. #2 | Generally Actual EGR Valve Pos. = Target EGR Pos. (Fully closed = 0%, Fully open = 100%) The EGR valve Active Test can be used to check whether the Actual EGR Valve Pos. = Target EGR Pos. | EGR valve assembly | Inspect while comparing to "Target EGR Valve Pos.". Sometimes the malfunction only occurs around a certain temperature, so refer to the engine coolant temperature and outside temperature at the time the malfunction occurred. |
| Results of real-vehicle check: Ignition switch ON: 0% Cranking: 0% Idling (warm up the engine): 84% Running without load (2500 rpm): 34% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 2000 rpm: 0% Driving with the accelerator fully open at 3000 rpm: 0% |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| EGR Close Lrn. Status | "OK" means the fully closed position learning has completed normally. When NG, the learned fully closed position may be outside of the normal range. | - | After disconnecting and reconnecting the battery cable, if the ignition switch has not been turned off once, learning may not be completed. |
| - |
| Data List | Judgment of Data List Values | Faulty Component | Diagnosis Note |
| EGR Close Lrn. Val. | Leave the vehicle idling, with the EGR Close Lrn. Status OK, the normal range of EGR Close Lrn. Val. is within 3.5 to 4.5 V. In cases when EGR Close Lrn. Status is NG or EGR Close Lrn. Val. is at the maximum or minimum (3.5 to 4.5 V) of normal range, it is possible that the EGR valve is not completely closed or a foreign object is lodged in the EGR valve seat area. | - | This value is the EGR position sensor output voltage. As the maximum and minimum settings are 3.5 V and 4.5 V, if the value becomes stuck at either of these, there is a malfunction in the lift sensor or the valve position is shifted (due to foreign matter, etc.). |
| - |
| Actual Examples of Malfunction |
- HINT:
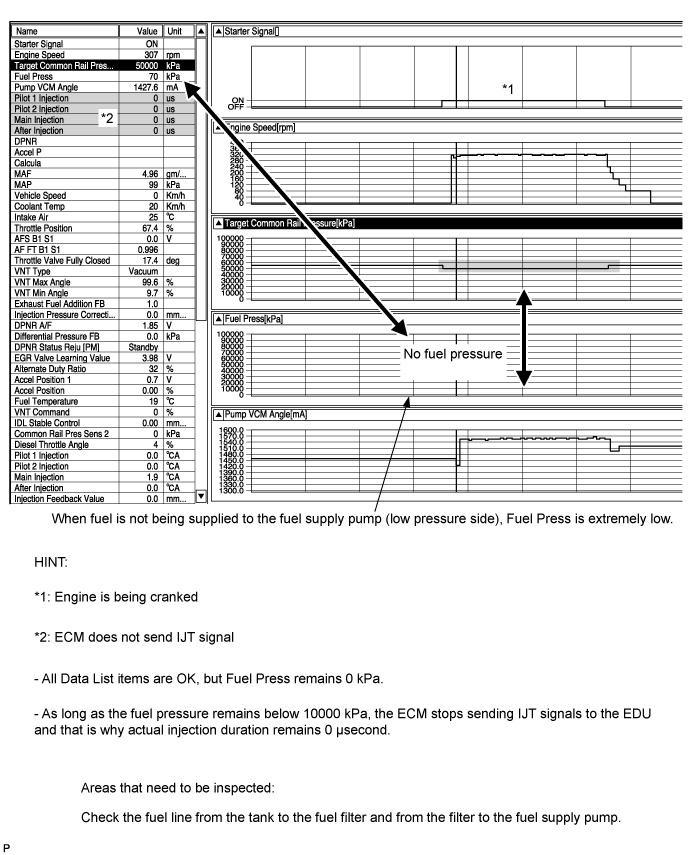
Fuel is not being supplied to supply pump (Low pressure fuel line clogged)
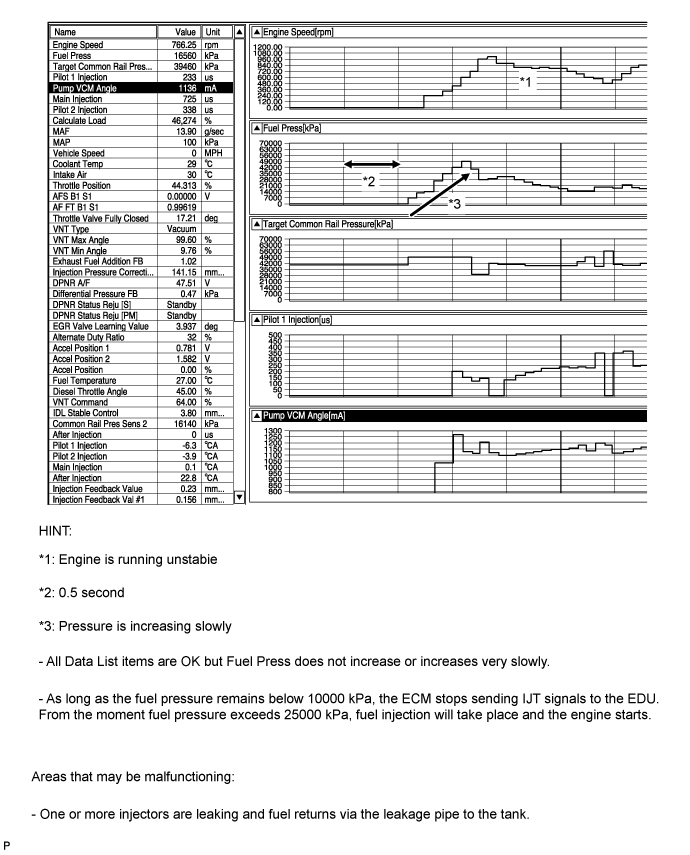
Fuel is not being injected (Injectors are leaking)
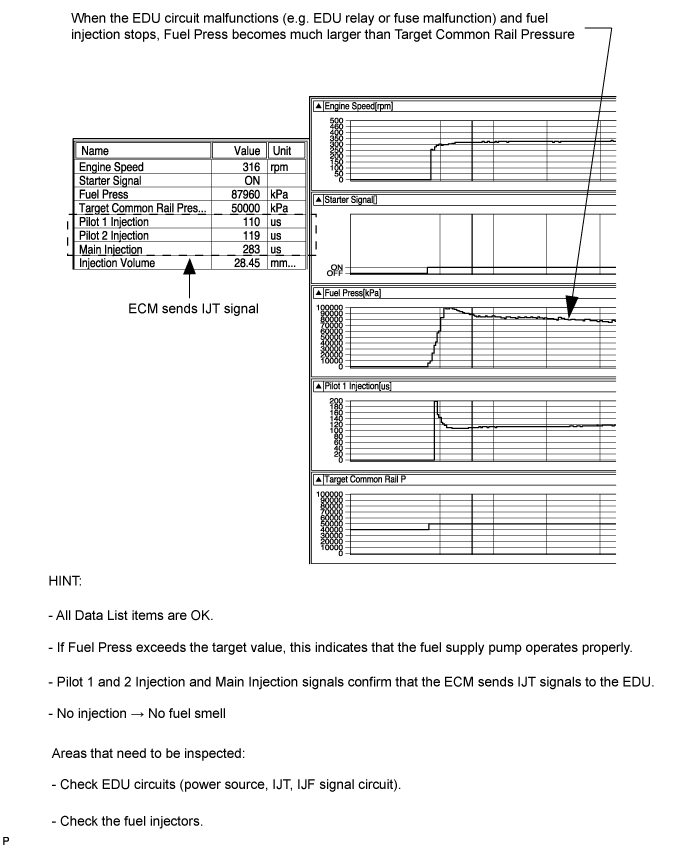
Fuel is not being injected (EDU circuit malfunction)
Fuel supply pump malfunction (Suction control valve momentary sticking)

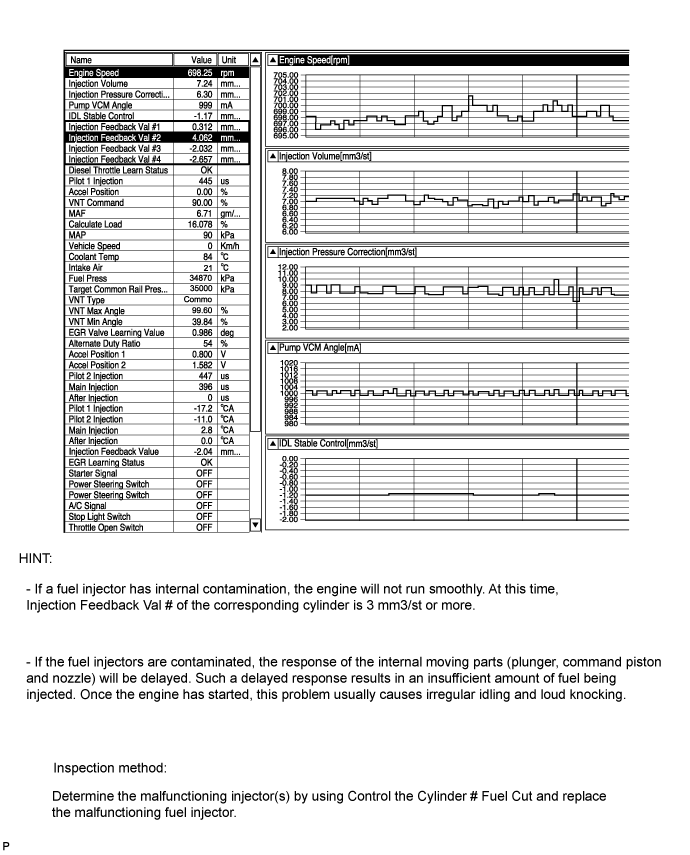
Increased opening delay of injectors (Internal contamination)
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
| Explanation of Symptom |
| Starting Trouble | For good starting it is essential to have: Sufficient cranking speed. Properly operating engine preheating system. Good quality fuel. With problems such as a depleted battery, the crankshaft speed can become low, or if the engine compression is leaking, the compression pressure will not rise and there will be difficulty starting. When the engine is cold, even if there is compression heat, it will escape from the combustion chamber. For this reason, when the engine is started when it is cold, the glow plugs heat the compressed air. Also after starting the engine, by charging the glow plugs for a fixed time set according to the engine coolant temperature, diesel knocking and white smoke are prevented. The quantity of fuel injected is determined by the fuel pressure and also the amount of time the fuel injector is open. |
| Trouble Area Chart According to Problem Cause |
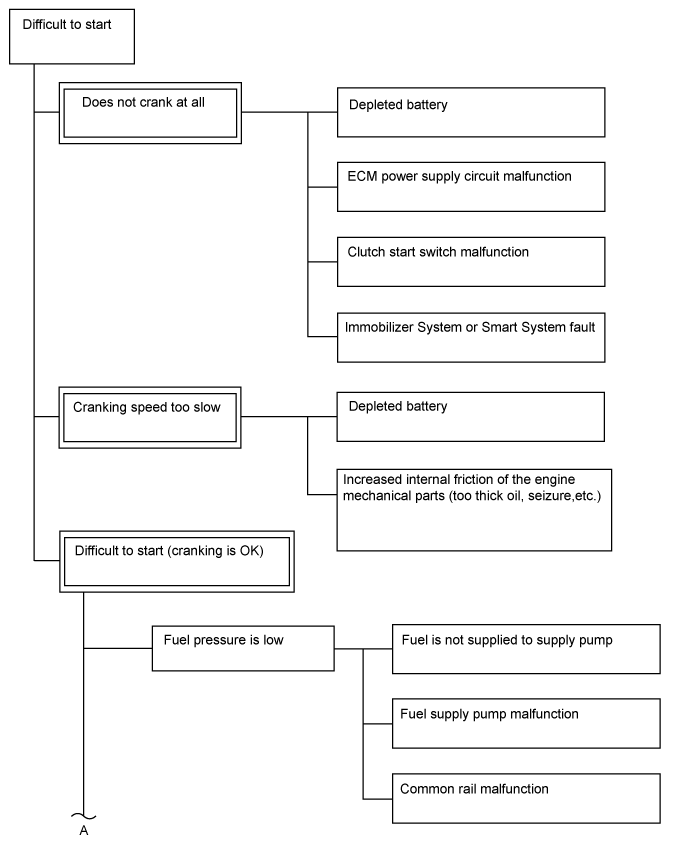

- NOTICE:
- HINT:
| 1.CHECK ENGINE CRANKING CONDITION |
Check the engine cranking condition.
| Result | Proceed to |
| Does not crank at all. | A |
Low cranking speed.
| B |
| Cranking is OK. | C |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.CHECK BATTERY CONDITION |
Check battery condition ().
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 3.CHECK COMMUNICATION BETWEEN INTELLIGENT TESTER AND ECM |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Check if the normal starting screen appears (check whether communication with the ECM is possible).
- HINT:
- Use a tester that is able to communicate with other vehicles.
- OK:
- Communication is possible (Vehicle can be recognized).
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (CLUTCH SWITCH) |
- HINT:
- This inspection is not necessary for A/T vehicles.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Data List / All Data / Clutch Switch.
Read the value displayed on the tester.
- Standard Value:
Tester Display Condition Specified Condition Clutch Switch Clutch pedal depressed ON
- Result:
Result Proceed to OK A NG (for LHD) B NG (for RHD) C
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 5.READ ALL OUTPUT DTCS |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Utility / All Codes.
| Result | Proceed to |
| No DTC is output | A |
| DTCs related to engine are output | B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 6.INSPECT SMART START SYSTEM (IN CASE OF VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH SMART ENTRY AND START SYSTEM) |
Check if the "Door Control Transmitter" functions of each key functions properly.
- HINT:
Near broadcasting stations, large screens, airports, transformer stations, gasoline stations, etc., the door control transmitter may not operate due to electric wave interference.
| NEXT | |
| 7.INSPECT CRANKING HOLDING FUNCTION CIRCUIT |
- HINT:
- Check that "Starter Signal" in the Data List changes to ON when the engine is started.
Inspect the cranking holding function circuit ().
| NEXT | ||
| ||
| 8.CHECK INITIALIZATION (FUEL SUPPLY PUMP) |
When the engine does not start or another problem such as rough idling is present, perform initialization and check to see if the problem symptoms disappear. If the problem symptoms do not disappear, perform the next procedure.
- HINT:
- When replacing the ECM, the supply pump initialization must be performed ().
| NEXT | |
| 9.READ OUTPUT DTC (RELATED TO ENGINE) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
| Result | Proceed to |
| No DTC is output | A |
| DTCs related to engine are output | B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 10.TAKE DATA LIST DURING STARTING AND IDLING |
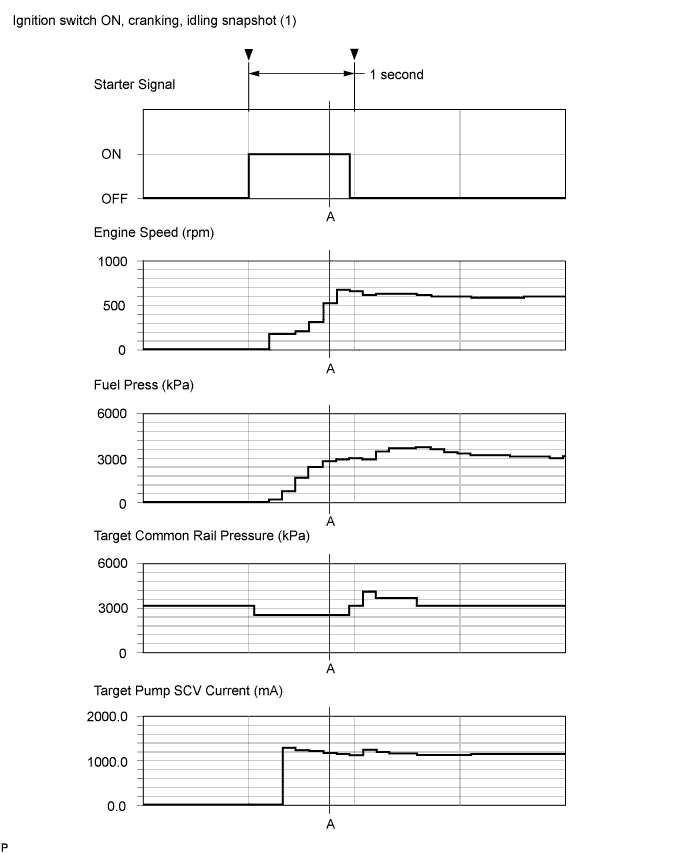


Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Data List / All Data.
Take a snapshot of the following Data Lists with the intelligent tester during "Ignition switch ON (5 seconds) → Starting → Idling (10 seconds)".
- HINT:
| Data List |
| Starter Signal |
| Engine Speed |
| Fuel Press |
| Target Common Rail Pressure |
| Target Pump SCV Current |
| Injection Volume |
| Main Injection Period |
| Inj. FB Vol. for Idle |
| Injection Feedback Val #1 |
| Injection Feedback Val #2 |
| Injection Feedback Val #3 |
| Injection Feedback Val #4 |
| Injection Feedback Val #5 |
| Injection Feedback Val #6 |
| Injection Feedback Val #7 |
| Injection Feedback Val #8 |
| Battery Voltage |
| Actual EGR Valve Pos. Actual EGR Valve Pos. #2 |
| Target EGR Pos Target EGR Pos. #2 |
| Actual Throttle Position Actual Throttle Position #2 |
| MAF |
| Target Booster Pressure |
| MAP |
| Data List | Value | Unit |
| Starter Signal | ON | - |
| Engine Speed | 524 | rpm |
| Fuel Press | 27820 | kPa |
| Target Common Rail Pressure | 25000 | kPa |
| Injection Volume | 22.71 | μs |
| Main Injection Period | 1142 | μs |
| Inj. FB Vol. for Idle | -1.33 | mm3/st |
| Battery Voltage | 11.0 | V |
| Target EGR Pos. Target EGR Pos. #2 | 0 | % |
| Actual EGR Valve Pos. Actual EGR Valve Pos. #2 | 0.0 | % |
| Actual Throttle Position Actual Throttle Position #2 | -1 | % |
| MAF | 16.45 | g/sec |
| MAP | 99 | kPa |
| Target Boost Pressure | 100.91 | kPa |
| Coolant Temp | 40 | °C |
| Data List | Value | Unit |
| Engine Speed | 599 | rpm |
| Target Booster Pressure | 99.23 | kPa |
| MAP | 97 | kPa |
| MAF | 8.39 | g/sec |
| Target Common Rail Pressure | 32000 | kPa |
| Fuel Press | 32100 | kPa |
| Injection Volume | 6.13 | mm3/st |
| Actual EGR Valve Pos. Actual EGR Valve Pos. #2 | 43.5 | % |
| Actual Throttle Position Actual Throttle Position #2 | 84 | % |
| Injection Feedback Val #1 | 0.0 | mm3/st |
| Injection Feedback Val #2 | 0.3 | mm3/st |
| Injection Feedback Val #3 | 0.0 | mm3/st |
| Injection Feedback Val #4 | -0.4 | mm3/st |
| Injection Feedback Val #5 | -0.4 | mm3/st |
| Injection Feedback Val #6 | 0.3 | mm3/st |
| Injection Feedback Val #7 | 0.0 | mm3/st |
| Injection Feedback Val #8 | -0.5 | mm3/st |
| Target EGR Pos. Target EGR Pos. #2 | 43.5 | % |
| Coolant Temp | 78 | °C |
- HINT:
- Actual Examples of Malfunction (See "Diagnostic Help" menu)
Fuel Press: Approximately 1000 kPa or less during cranking.
Fuel Press: 80000 to 90000 kPa during cranking.
Fuel Press: 60000 to 70000 kPa during cranking.
Target Pump SCV Current intermittently reaches 3000 mA or more. The suction control valve plunger intermittently becomes stuck. If there is difficult to start when the engine is cold, cool the engine and inspect it.
Injector clogging or internal contamination:
Injection Feedback Val # of one or more of the cylinders is 3 mm3/st or more.
Injection Feedback Val # can be read when the engine is idling after being warmed up.
| NEXT | |
| 11.CHECK SNAPSHOT (FUEL PRESS, TARGET COMMON RAIL PRESSURE ETC.) |
Check Fuel Press and Target Common Rail Pressure in the snapshot taken when the engine was starting.
| Result | Proceed to |
2 seconds after Starter Signal turns from OFF to ON, Fuel Press is less than "Target Common Rail Pressure -5000 kPa"
| A |
| 2 seconds after Starter Signal turns from OFF to ON, Fuel Press is 5000 kPa or more higher than Target Common Rail Pressure | B |
| 2 seconds after Starter Signal turns from OFF to ON, Fuel Press is within +/-5000 kPa of Target Common Rail Pressure | C |
- HINT:
- Fuel pressure is about 20000 to 35000 kPa when engine cranking and engine coolant temperature 0°C (32°F) or more.
- Fuel pressure increases rapidly during cranking.
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 12.BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |

Using the hand pump as indicated by the arrow in the illustration, bleed air from the fuel system. Continue pumping until pumping becomes difficult.
- HINT:
- When the fuel pressure during cranking is extremely low (1000 kPa or less), it is possible that fuel is not being supplied to the supply pump.
| NEXT | |
| 13.CHECK IF FUEL IS BEING SUPPLIED TO FUEL SUPPLY PUMP |
Disconnect the inlet hose from the fuel supply pump.
Operate the priming pump and check that fuel is being supplied to the fuel supply pump.
- OK:
- Fuel is properly supplied to the fuel supply pump when the priming pump is operated.
- HINT:
(Check that the fuel filter is not clogged)
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 14.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
Check whether the difficulty starting has been successfully repaired by starting the engine.
- HINT:
- Fuel pressure during cranking is within +/-5000 kPa of target fuel pressure.
- OK:
- Malfunction has been repaired successfully.
|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||
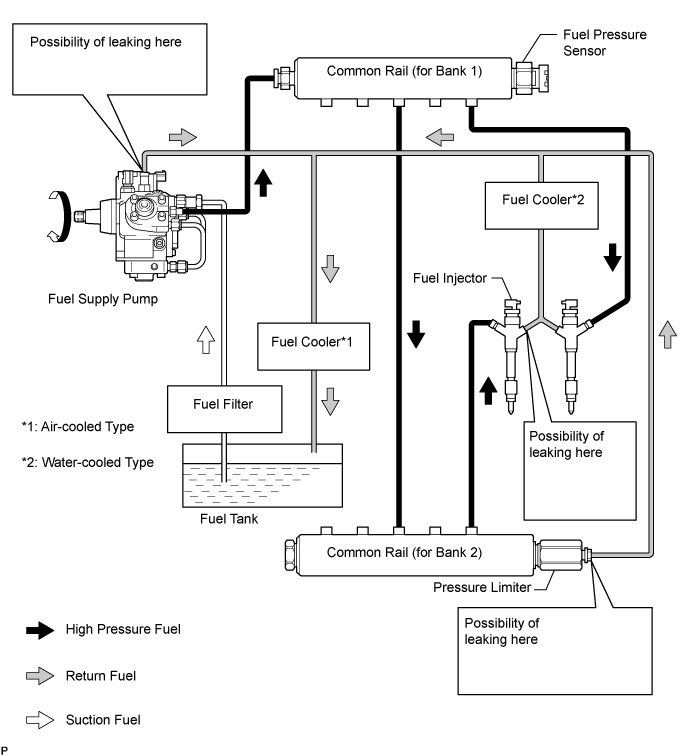
| 15.CHECK FUEL LEAK (FUEL SUPPLY PUMP) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester ON.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Data List / Fuel Press.
Pinch the supply pump return hose and check that Fuel Press during cranking increases.
| Result | Proceed to |
| Fuel Press increases | A |
| No change | B |
|
| ||||
| B | |
| 16.CHECK FUEL LEAK (PRESSURE LIMITER (COMMON RAIL (for Bank 2)) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester ON.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Data List / Fuel Press.
Pinch the pressure limiter return hose and check that Fuel Press during cranking increases.
| Result | Proceed to |
| Fuel Press increases | A |
| No change | B |
|
| ||||
| B | |
| 17.REPLACE FUEL SUPPLY PUMP |
Replace fuel supply pump ().
| NEXT | |
| 18.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
Check whether the difficulty starting has been successfully repaired by starting the engine.
- HINT:
- Fuel pressure during cranking is within +/-5000 kPa of target fuel pressure.
| NEXT | ||
| ||
| 19.CHECK SNAPSHOT (TARGET PUMP SCV CURRENT) |
Check Target Pump SCV Current in the snapshot taken when the engine was starting.
- Result:
Result Proceed to Target Pump SCV Current is 3000 mA or more A Target Pump SCV Current is less than 3000 mA B
|
| ||||
| B | |
| 20.CHECK DATA LIST |
Check Injection Feedback Val # and Injection Volume in the snapshot taken when the engine was idling.
- Result:
Result Proceed to Injection Feedback Val #1 to #8 is outside the range of +/-3 mm3/st - HINT:
- There may be malfunction in the corresponding cylinder.
A Injection Feedback Val #1 to #8 is within the range of +/-3 mm3/st and Injection Volume is more than 10 mm3/st B* Injection Feedback Val #1 to #8 is within the range +/-3 mm3/st and Injection Volume is 10 mm3/st or less C
- HINT:
- *: When case "B" occurs usually symptoms may be noticeable, such as difficult starting, rough idling, knocking or black smoke at high common rail pressure.
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 21.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER |
- HINT:
- Use this Active Test to determine the malfunctioning cylinder.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Control the Cylinder #1 to #8 Fuel Cut.
- HINT:
| NEXT | |
| 22.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER |
- HINT:
- Use this Active Test to help determine whether a cylinder has compression loss or not.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Check the Cylinder Compression / Data List / Compression / Engine Speed of Cyl #1 to #8.
Check the engine speed during the Active Test.
- OK:
- If the values of Engine Speed Cyl #1 to #8 are within +/-10 rpm of each other.
- HINT:
- When cranking, if the speed of a cylinder is approximately 100 rpm more than the other cylinders, there is probably a loss of compression in that cylinder.
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| 23.CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER |
- HINT:
- Measure the compression of the cylinder that had a high speed during the Active Test "Check the Cylinder Compression".
Check the cylinder compression pressure ().
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 24.REPLACE FUEL INJECTOR OF MALFUNCTIONING CYLINDER |
- HINT:
- The injector is determined to be faulty as the corresponding cylinder is malfunctioning, but has no compression loss.
| NEXT | ||
| ||
| 25.CHECK TEMPERATURE WHEN STARTING TROUBLE OCCURS |
Check the temperature when starting trouble occurs.
| Result | Proceed to |
| Difficult to start only for cold engine. | A |
| Difficult to start both for cold and warmed up engine. | B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 26.INSPECT ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR |
Inspect the engine coolant temperature sensor ().
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 27.INSPECT GLOW PLUG ASSEMBLY (RESISTANCE) |
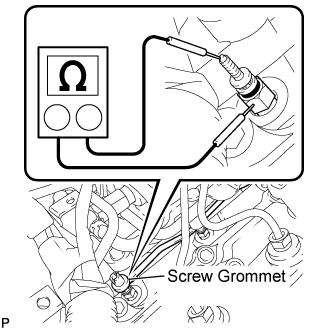
Disconnect the glow plug connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Resistance:
Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition Glow plug terminal - Body ground 20°C (68°F) Approximately 1 Ω
- HINT:
- If any of the glow plugs has an open circuit, the engine power will be insufficient only when the engine is cold.
- NOTICE:
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 28.INSPECT INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE |
Read the injector compensation code ().
- OK:
- Compensation codes stored in the ECM match compensation codes of the installed fuel injectors.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 29.CHECK FUEL QUALITY |
Check that fuel with cetane number is used.
| NEXT | |
| 30.CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
Check whether the difficulty starting has been successfully repaired by starting the engine.
| NEXT | ||
| ||
| 31.CHECK SNAPSHOT |
- HINT:
- When all Data List values are OK and Fuel Press is higher than Target Common Rail Pressure, perform the following inspection.
| NEXT | |
| 32.INSPECT INJECTOR DRIVER (EDU POWER SOURCE) |

Disconnect the C73 and C74 No. 1 injector driver (EDU) connectors.
Disconnect the C75 and C76 No. 2 injector driver (EDU) connectors.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard Voltage:
No. 1 Tester Connection Switch Condition Specified Condition C74-8 (+B) - C73-1 (GND) Ignition switch ON 11 to 14 V
- Standard Voltage:
No. 2 Tester Connection Switch Condition Specified Condition C76-8 (+B) - C75-1 (GND) Ignition switch ON 11 to 14 V
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 33.INSPECT FUEL INJECTOR |
- HINT:
- If there is no initial combustion during cranking, there may be air in the injectors.
| NEXT | ||
| ||