CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO P2195 OR P2196)
READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (TEST VALUE OF A/F SENSOR)
READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (OUTPUT VOLTAGE OF A/F SENSOR)
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P2195 OR P2196)
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P2195 OR P2196)
INSPECT AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE)
INSPECT INTEGRATION RELAY (EFI MAIN RELAY)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (A/F SENSOR - ECM)
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P2195 OR P2196)
DTC P2195 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2196 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Signal Stuck Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DESCRIPTION
- HINT:
- Although the DTC titles say oxygen sensor, these DTCs relate to the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor.
- Sensor 1 refers to the sensor mounted in front of the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and located near the engine assembly.
The A/F sensor is of the planar type and is integrated with the heater, which heats the solid electrolyte (zirconia element). This heater is controlled by the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the exhaust gas temperature is low), a current flows into the heater to heat the sensor, in order to facilitate accurate air-fuel ratio detection. In addition, the sensor and heater portions are narrower than the conventional type. The heat generated by the heater is conducted to the solid electrolyte through the alumina, therefore the sensor activation is accelerated.
In order to obtain a high purification rate of the carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon (HC) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) components in the exhaust gas, a TWC is used. For the most efficient use of the TWC, the air-fuel ratio must be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric level.
*: Value changes inside the ECM. Since the A/F sensor is the current output element, a current is converted into a voltage inside the ECM. Any measurements taken at the A/F sensor or ECM connectors will show a constant voltage.

| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P2195 | Conditions (a) and (b) continue for 10 seconds or more (2 trip detection logic): (a) A/F sensor voltage more than 3.8 V (b) Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor voltage 0.15 V or more |
|
| While fuel-cut operation performed (during vehicle deceleration), A/F sensor current 3.6 mA or more for 3 seconds (2 trip detection logic) |
| |
| P2196 | Conditions (a) and (b) continue for 10 seconds or more (2 trip detection logic): (a) A/F sensor voltage less than 2.8 V for 10 seconds (b) HO2 sensor voltage less than 0.6 V |
|
| While fuel-cut operation performed (during vehicle deceleration), A/F sensor current less than 1.0 mA for 3 seconds (2 trip detection logic) |
|
- HINT:
- When either of these DTCs is set, check the A/F sensor output voltage by selecting the following menu items on the intelligent tester: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / A/F Control System / AFS B1 S1.
- Short-term fuel trim values can also be read using the intelligent tester.
- The ECM regulates the voltages at the A1A+ and A1A- terminals of the ECM to a constant level. Therefore, the A/F sensor output voltage cannot be confirmed without using the intelligent tester.
- If the A/F sensor is malfunctioning, the ECM sets the DTC P2195 or P2196.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
- Sensor voltage detection monitor
Under the air-fuel ratio feedback control, if the A/F sensor output voltage indicates rich or lean for a certain period of time, the ECM determines that there is a malfunction in the A/F sensor. The ECM illuminates the MIL and sets a DTC.
Example:
If the A/F sensor output voltage is less than 2.8 V (very rich condition) for 10 seconds, despite the rear HO2 sensor output voltage being less than 0.6 V, the ECM sets DTC P2196. Alternatively, if the A/F sensor output voltage is more than 3.8 V (very lean condition) for 10 seconds, despite the rear HO2 sensor output voltage being 0.15 V or more, DTC P2195 is set.
- Sensor current detection monitor
A rich air-fuel mixture causes a low A/F sensor current, and a lean air-fuel mixture causes a high A/F sensor current. Therefore, the sensor output becomes low during acceleration, and it becomes high during deceleration with the throttle valve fully closed. The ECM monitors the A/F sensor current during fuel-cut and detects any abnormal current values.
If the A/F sensor output is 3.6 mA or more for more than 3 seconds of cumulative time, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction in the A/F sensor and sets DTC P2195 (high-side stuck). If the A/F sensor output is less than 1.0 mA for more than 3 seconds of cumulative time, the ECM sets DTC P2196 (low-side stuck).

WIRING DIAGRAM
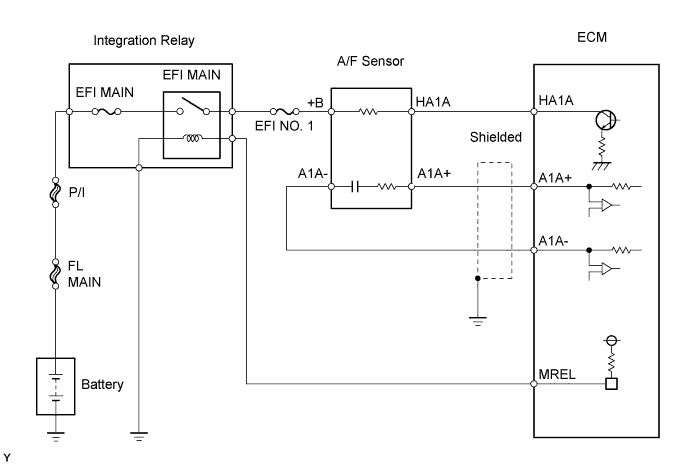
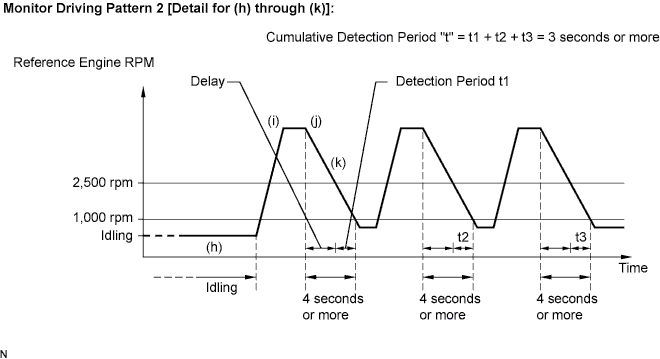
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
This confirmation driving pattern is used in the "PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN" procedure of the following diagnostic troubleshooting procedure.
- (a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- (b) Turn the ignition switch on (IG).
- (c) Turn the tester ON.
- (d) Clear DTCs (RAV4_ACA30 RM000000PDK0AJX.html).
- (e) Start the engine, and warm it up until the ECT reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
- (f) On the intelligent tester, select the following menu items to check the fuel-cut status: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / Idle Fuel Cut.
- (g) Drive the vehicle at between 38 mph (60 km/h) and 75 mph (120 km/h) for at least 10 minutes.
- (h) Change the transmission to 2nd gear.
- (i) Drive the vehicle at proper vehicle speed to perform fuel-cut operation (refer to the following HINT).
- HINT:
- Fuel-cut is performed when the following conditions are met:
- Accelerator pedal fully released.
- Engine speed is 2,500 rpm or more (fuel injection returns at 1,000 rpm).
- (j) Accelerate the vehicle to 40 mph (64 km/h) or more by depressing the accelerator pedal for at least 10 seconds.
- (k) Soon after performing step (j) above, release the accelerator pedal for at least 4 seconds without depressing the brake pedal, in order to execute fuel-cut control.
- (l) Allow the vehicle to decelerate until the vehicle speed declines to less than 6 mph (10 km/h).
- (m) Repeat steps from (h) through (k) above at least 3 times in one driving cycle.
- CAUTION:
- Strictly observe posted speed limits, traffic laws, and road conditions when performing these drive patterns.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- Intelligent tester only:
- Malfunctioning areas can be identified by performing the Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor function provided in the Active Test. The Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor function can help to determine whether the Air-fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor, Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor and other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning.
- (a) Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- (b) Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
- (c) Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
- (d) On the tester, select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor.
- (e) Perform the Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor operation with the engine idling (press the RIGHT or LEFT button to change the fuel injection volume).
- (f) Monitor the output voltages of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS B1 S1 and O2S B1 S2) displayed on the tester.
- HINT:
- The Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor operation lowers the fuel injection volume by 12.5% or increases the injection volume by 25%.
- The sensors react in accordance with increases and decreases in the fuel injection volume.
- Standard:
Tester Display
(Sensor)Injection Volume Status Voltage AFS B1 S1
(A/F)+25% Rich Less than 3.0 -12.5% Lean More than 3.35 O2S B1 S2
(HO2)+25% Rich More than 0.5 -12.5% Lean Less than 0.4
- NOTICE:
- The A/F sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the HO2 sensor (sensor 2) output has a maximum output delay of approximately of 20 seconds.
| Case | A/F Sensor (Sensor 1) Output Voltage | HO2 Sensor (Sensor 2) Output Voltage | Main Suspected Trouble Area |
| 1 |  |  | - |
| 2 |  |  |
|
| 3 |  |  |
|
| 4 |  |  |
|
- Following the Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor procedure enables technicians to check and graph the voltage outputs of both the A/F and HO2 sensors.
- To display the graph, select the following menu items on the tester: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor / Enter / View / AFS B1 S1 and O2S B1 S2.
- HINT:
- DTC P2A00 may be set when the air-fuel ratio is stuck rich or lean.
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. Freeze frame data records the engine condition when malfunctions are detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
- A low A/F sensor voltage could be caused by a rich air-fuel mixture. Check for conditions that would cause the engine to run rich.
- A high A/F sensor voltage could be caused by a lean air-fuel mixture. Check for conditions that would cause the engine to run lean.
| 1.CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO P2195 OR P2196) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch on (IG).
Turn the tester ON.
Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read DTCs.
- Result:
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to P2195 or P2196 A P2195 or P2196 and other DTCs B
- HINT:
- If any DTCs relating to the A/F sensor (DTCs for the A/F sensor heater or A/F sensor admittance) are output, troubleshoot those DTCs first.
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (TEST VALUE OF A/F SENSOR) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch on (IG) and turn the tester ON.
Clear DTCs (RAV4_ACA30 RM000000PDK0AJX.html).
Drive the vehicle in accordance with the drive pattern described in the CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN.
Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / Monitor Status.
Check that the status of O2S(A/FS) Monitor is Complete.
If the status is still Incomplete, drive the vehicle according to the driving pattern again.- HINT:
- Available indicates that the component has not been monitored yet.
- Complete indicates that the component is functioning normally.
- Incomplete indicates that the component is malfunctioning.
Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / A/F Control System / AFS B1 S1.
Check the test value of the A/F sensor output current during fuel-cut (Refer to the Monitor Driving Pattern 2 [Detail for (h) through (k)] in the CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN).
- Result:
Test Value Proceed to Within normal range (1.0 mA or more, and less than 3.6 mA) A Outside normal range (Less than 1.0 mA, or 3.6 mA or more) B
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 3.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (OUTPUT VOLTAGE OF A/F SENSOR) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine.
Turn the tester ON.
Warm up the A/F sensor at an engine speed of 2,500 rpm for 90 seconds.
On the tester, select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / A/F Control System / Snapshot / AFS B1 S1 and Engine Speed.
Check the A/F sensor voltage 3 times, when the engine is in each of the following conditions:
- (1) While idling (check for at least 30 seconds)
- (2) At an engine speed of approximately 2,500 rpm (without any sudden changes in engine speed)
- (3) Raise the engine speed to 4,000 rpm and then quickly release the accelerator pedal so that the throttle valve is fully closed.
- Standard voltage:
Condition A/F Sensor Voltage Variation Reference (1) and (2) Remains at approximately 3.3 V Between 3.1 V and 3.5 V (3) Increases to 3.8 V or more This occurs during engine deceleration
(when fuel-cut performed)
- (1) While idling (check for at least 30 seconds)
- HINT:
- For more information, see the diagrams below.

- If the output voltage of the A/F sensor remains at approximately 3.3 V (see Malfunction Condition diagram) under any conditions, including those above, the A/F sensor may have an open circuit. (This will also happen if the A/F sensor heater has an open circuit.)
- If the output voltage of the A/F sensor remains at either approximately 3.8 V or more, or 2.8 V or less (see Malfunction Condition diagram) under any conditions, including those above, the A/F sensor may have a short circuit.
- The ECM stops fuel injection (fuel cut) during engine deceleration. This causes a lean condition and result in a momentary increase in the A/F sensor output voltage.
- The ECM must establish a closed throttle valve position learning value to perform fuel cut. If the battery terminal has been reconnected, the vehicle must be driven over 10 mph (16 km/h) to allow the ECM to learn the closed throttle valve position.
- When the vehicle is driven:
The output voltage of the A/F sensor may be below 2.8 V during fuel enrichment. For the vehicle, this translates to a sudden increase in speed with the accelerator pedal fully depressed when trying to overtake another vehicle. The A/F sensor is functioning normally. - The A/F sensor is a current output element; therefore, the current is converted into a voltage inside the ECM. Measuring the voltage at the connectors of the A/F sensor or ECM will show a constant voltage result.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN |
| NEXT | |
| 5.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P2195 OR P2196) |
Read DTCs using the intelligent tester.
Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
- Result:
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to P2195 or P2196 A No output B
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 6.REPLACE AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
| NEXT | |
| 7.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN |
| NEXT | |
| 8.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P2195 OR P2196) |
Read DTCs using the intelligent tester.
Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
- Result:
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to No output A P2195 or P2196 B
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||
| 9.INSPECT AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE) |
 |
Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
Measure the resistance of the A/F sensor connector.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition HA1A (1) - +B (2) 1.8 Ω to 3.4 Ω at 20°C (68°F) HA1A (1) - A1A- (4) 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 10.INSPECT INTEGRATION RELAY (EFI MAIN RELAY) |
Remove the integration relay from the engine room relay block.
Inspect the EFI MAIN fuse.
Remove the EFI MAIN fuse from the integration relay.
Measure the EFI MAIN fuse resistance.
- Standard resistance:
- Below 1 Ω
Reinstall the EFI MAIN fuse.

Inspect the EFI MAIN relay.
Measure the EFI MAIN relay resistance.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition 1C-1 - 1A-4 10 kΩ or higher Below 1 Ω
(Apply battery voltage between terminals 1A-2 and 1A-3)
Reinstall the integration relay.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
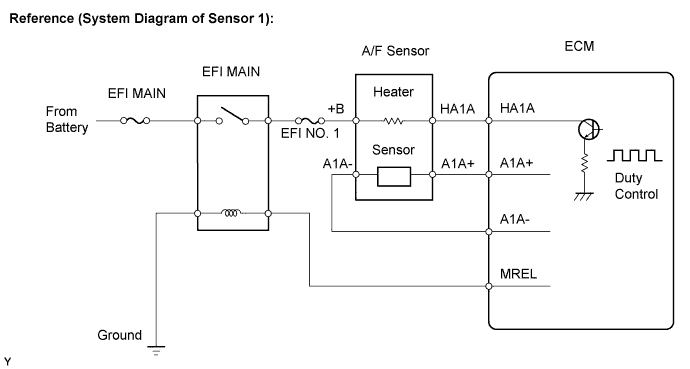
| 11.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (A/F SENSOR - ECM) |
 |
Disconnect the B7 A/F sensor connector.
Turn the ignition switch on (IG).
Measure the voltage between the +B terminal of the A/F sensor connector and body ground.
- Standard voltage:
Tester Connection Specified Condition +B (B7-2) - Body ground 9 to 14 V
Turn the ignition switch off.
Disconnect the B32 ECM connector.
Measure the resistance.
- Standard resistance (Check for open):
Tester Connections Specified Conditions HA1A (B7-1) - HA1A (B32-109) Below 1 Ω A1A+ (B7-3) - A1A+ (B32-112) Below 1 Ω A1A- (B7-4) - A1A- (B32-113) Below 1 Ω
- Standard resistance (Check for short):
Tester Connections Specified Conditions HA1A (B7-1) or HA1A (B32-109) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A1A+ (B7-3) or A1A+ (B32-112) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A1A- (B7-4) or A1A- (B32-113) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the ECM connector.
Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 12.REPLACE AIR-FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
| NEXT | |
| 13.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN |
| NEXT | |
| 14.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P2195 OR P2196) |
Read DTCs using the intelligent tester.
Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
- Result:
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to No output A P2195 or P2196 B
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||