Fuel Supply Pump (W/ Dpf) -- Installation |
- NOTICE:
- When replacing the injectors (including shuffling the injectors between the cylinders), common rail or cylinder head, it is necessary to replace the injection pipes with new ones.
- When replacing the fuel supply pump, common rail, cylinder block, cylinder head, cylinder head gasket or timing gear case, it is necessary to replace the fuel inlet pipe with a new one.
- After removing the injection pipes and fuel inlet pipe, clean them with a brush and compressed air.
| 1. INSTALL FUEL SUPPLY PUMP ASSEMBLY |
Check that the injection gear in the timing gear case moves back and forth smoothly.
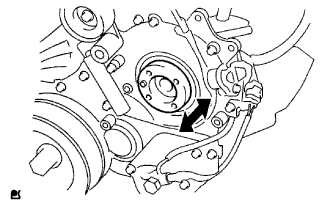 |
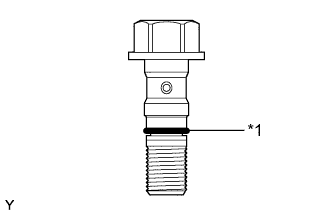
Install a new O-ring to the fuel supply pump.
Apply a light coat of engine oil to the O-ring.
Align the groove of the injection gear with the set key on the drive shaft.
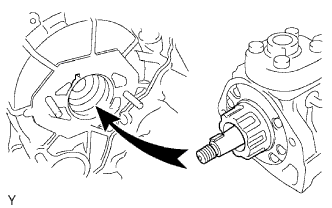 |
Install the fuel supply pump with the 2 nuts.
- Torque:
- 21 N*m{214 kgf*cm, 15 ft.*lbf}
Install a new O-ring before tightening the set nut.
Using SST, hold the crankshaft pulley and install the set nut.
- SST
- 09213-58014
09330-00021
- Torque:
- 64 N*m{650 kgf*cm, 47 ft.*lbf}
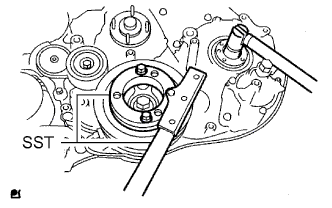 |
Install the pump drive shaft pulley and No. 2 camshaft timing pulley flange with the 4 bolts.
- Torque:
- 31 N*m{316 kgf*cm, 23 ft.*lbf}
Move the pump drive shaft pulley back and forth to check the thrust clearance of the injection pump drive shaft.
- Standard thrust clearance:
- 0.15 to 0.55 mm (0.00590 to 0.0217 in.)
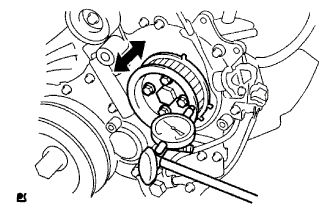 |
Connect the fuel temperature sensor connector and suction control valve connector to the fuel supply pump.
Connect the 2 fuel hoses.
| 2. INSTALL NO. 2 FUEL PIPE |
Apply a light coat of fuel to the O-ring of the fuel check valve.
Text in Illustration *1 O-Ring
 |
Temporarily install the No. 2 fuel pipe with the 3 bolts.
Text in Illustration *1 Gasket *2 No. 1 Fuel Pipe 
Bolt 
Supply Pump Hollow Screw 
Fuel Check Valve 
Union Bolt
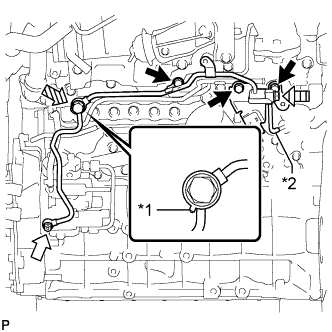 |
Install a new gasket to the No. 1 fuel pipe and temporarily install the union bolt.
Temporarily install a new gasket and the fuel check valve.
- NOTICE:
- When temporarily installing the fuel check valve, position the gasket as shown in the illustration.
Temporarily install a new gasket and the supply pump hollow screw.
Using a 6 mm hexagon wrench, tighten the supply pump hollow screw.
- Torque:
- 21 N*m{214 kgf*cm, 15 ft.*lbf}
Tighten the 3 bolts, fuel check valve and union bolt.
- Torque:
- for bolt:
- 20 N*m{204 kgf*cm, 15 ft.*lbf}
- for fuel check valve:
- 32 N*m{321 kgf*cm, 23 ft.*lbf}
- for union bolt:
- 21 N*m{214 kgf*cm, 15 ft.*lbf}
- NOTICE:
- When tightening the fuel check valve, replace the gasket if it becomes deformed.
| 3. INSTALL WIRING HARNESS CLAMP BRACKET |
Install the wiring harness clamp bracket with the bolt.
- Torque:
- 13 N*m{128 kgf*cm, 9 ft.*lbf}
Attach the wire harness clamp.
| 4. INSTALL NO. 4 INJECTION PIPE SUB-ASSEMBLY |
- NOTICE:
- When replacing an injector, it is necessary to replace the 4 injection pipes with new ones.
- Keep the joints of the injection pipe clean.
Temporarily install the No. 4 injection pipe with the union nuts.
Install the 2 No. 2 injection pipe clamps with the bolt and nut.
- Torque:
- 5.0 N*m{51 kgf*cm, 44 in.*lbf}
Using a 17 mm union nut wrench, tighten the injection pipe union nut on the common rail side.
- Torque:
- 35 N*m{357 kgf*cm, 26 ft.*lbf}
- NOTICE:
- Use the formula to calculate special torque values for situations where a union nut wrench is combined with a torque wrench (HILUX_TGN26 RM000004QR1006X.html).
Using a 17 mm union nut wrench, tighten the injection pipe union nuts on the injector side.
- Torque:
- 35 N*m{357 kgf*cm, 26 ft.*lbf}
- NOTICE:
- Use the formula to calculate special torque values for situations where a union nut wrench is combined with a torque wrench (HILUX_TGN26 RM000004QR1006X.html).
| 5. INSTALL ELECTRIC EGR CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY WITH NO. 2 EGR VALVE AND EGR COOLER |
| 6. INSTALL TIMING BELT |
| 7. INSTALL RADIATOR ASSEMBLY |
| 8. CONNECT CABLE TO NEGATIVE BATTERY TERMINAL |
- NOTICE:
- When disconnecting the cable, some systems need to be initialized after the cable is reconnected (HILUX_TGN26 RM000004QR3009X.html).
| 9. ADD ENGINE COOLANT |
Tighten the radiator drain cock plug by hand.
Tighten the cylinder block drain cock plug.
- Torque:
- 8.0 N*m{82 kgf*cm, 71 in.*lbf}
Fill the radiator with TOYOTA Super Long Life Coolant (SLLC) to the B line of the radiator reservoir.
- Standard capacity:
- 9.8 liters (10.4 US qts, 8.6 Imp. qts)
- NOTICE:
- Never use water as a substitute for engine coolant.
- HINT:
- TOYOTA vehicles are filled with TOYOTA SLLC at the factory. In order to avoid damage to the engine cooling system and other technical problems, only use TOYOTA SLLC or similar high quality ethylene glycol based non-silicate, non-amine, non-nitrite, non-borate coolant with long-life hybrid organic acid technology (coolant with long-life hybrid organic acid technology consists of a combination of low phosphates and organic acids).
- Please contact your TOYOTA dealer for further details.
Press the inlet and outlet radiator hoses several times by hand, and then check the level of the coolant.
If the coolant level drops below the B line, add TOYOTA SLLC to the B line.
Install the radiator reservoir cap.
Using a wrench, install the vent plug.
- Torque:
- 2.0 N*m{20 kgf*cm, 17 in.*lbf}
Bleed air from the cooling system.
Warm up the engine until the thermostat opens. While the thermostat is open, circulate the coolant for several minutes.
Maintain the engine speed at 2500 to 3000 rpm.
Press the inlet and outlet radiator hoses several times by hand to bleed air.
- CAUTION:
- When pressing the radiator hoses:
- Wear protective gloves.
- Be careful as the radiator hoses are hot.
- Keep your hands away from the radiator fan.
Stop the engine and wait until the coolant cools down to ambient temperature.
- CAUTION:
- Do not remove the radiator reservoir cap while the engine and radiator are still hot. Pressurized, hot engine coolant and steam may be released and cause serious burns.
After the coolant cools down, check that the coolant level is at the F line.
If the coolant level is below the F line, add TOYOTA SLLC to the F line.
| 10. BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM |
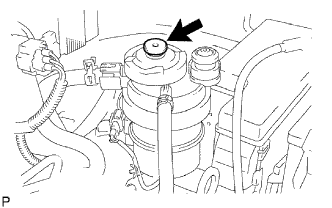
Using the hand pump mounted on the fuel filter cap, bleed the air from the fuel system. Continue pumping until the pump resistance increases.
- NOTICE:
- Hand pump pumping speed: Max. 2 strokes/ sec.
- The hand pump must be pushed with a full stroke during pumping.
- When the fuel pressure at the supply pump inlet port reaches a saturated pressure, the hand pump resistance increases.
- If pumping is interrupted during the air bleeding process, fuel in the fuel line may return to the fuel tank. Continue pumping until the hand pump resistance increases.
- If the hand pump resistance does not increase despite consecutively pumping 200 times or more, there may be a fuel leak between the fuel tank and fuel filter, the hand pump may be malfunctioning, or the vehicle may have run out of fuel.
- If air bleeding using the hand pump is incomplete, the common rail pressure does not rise to the pressure range necessary for normal use, and the engine cannot be started.
 |
Check if the engine starts.
- NOTICE:
- Even if air bleeding using the hand pump has been completed, the starter may need to be cranked for 10 seconds or more to start the engine.
- Do not crank the engine continuously for more than 20 seconds. The battery may be discharged.
- Use a fully-charged battery.
When the engine can be started, proceed to the next step.
If the engine cannot be started, bleed the air again using the hand pump until the hand pump resistance increases (refer to the procedures above). Then start the engine.
Turn the ignition switch off.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the intelligent tester on.
Clear the DTCs (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000PDK0X3X.html).
Start the engine.*1
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Test the Fuel Leak.*2
Text in Illustration *a Reference
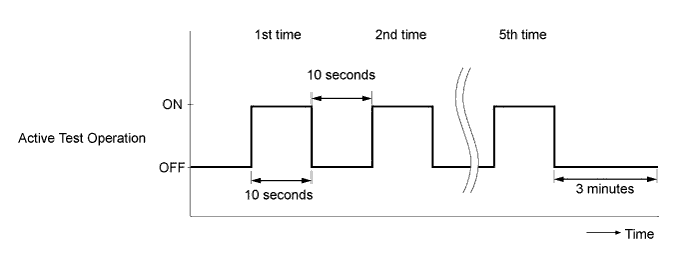
(Active Test Operation)
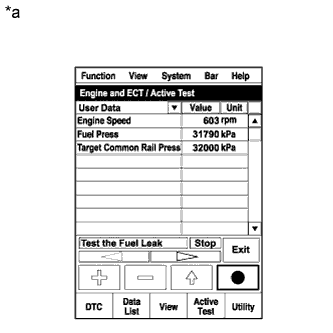 |
Perform the following test 5 times with on/off intervals of 10 seconds: Active Test / Test the Fuel Leak.*3
Allow the engine to idle for 3 minutes or more after performing the Active Test for the fifth time.
- HINT:
- When the Active Test "Test the Fuel Leak" is used to change the pump control mode, the actual fuel pressure inside the common rail drops below the target fuel pressure when the Active Test is off, but this is normal and does not indicate a pump malfunction.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / DTC.
Read Current DTCs.
Clear the DTCs (HILUX_TGN26 RM000000PDK0X3X.html).
- HINT:
- It is necessary to clear the DTCs, as DTC P1604 or P1605 may be stored when air is bled from the fuel system after replacing or repairing fuel system parts.
Repeat steps *1 to *3.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / DTC.
Read Current DTCs.
- OK:
- No DTCs are output.
| 11. PERFORM FUEL SUPPLY PUMP INITIALIZATION |
| 12. INSPECT FOR COOLANT LEAK |
- CAUTION:
- Do not remove the radiator reservoir cap while the engine and radiator are still hot. Pressurized, hot engine coolant and steam may be released and cause serious burns.
- NOTICE:
- Before each inspection, turn the A/C switch off.
Fill the radiator with coolant and attach a radiator cap tester.
Warm up the engine.
Using the radiator cap tester, increase the pressure inside the radiator to 118 kPa (1.2 kgf/cm2, 17 psi), and check that the pressure does not drop.
If the pressure drops, check the hoses, radiator and water pump for leaks. If no external leaks are found, check the heater core, cylinder block and head.
| 13. INSPECT FOR FUEL LEAK |
Perform the Active Test.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Turn the intelligent tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test.
Perform the Active Test.
Intelligent Tester Display Test Part Control Range Diagnostic Note Test the Fuel Leak Pressurize common rail interior and check for fuel leaks Stop/Start - The fuel pressure inside the common rail increases to the specified value and the engine speed increases to 2000 rpm when the Active Test is performed.
- The above conditions are maintained while the Active Test is being performed.
- The fuel pressure inside the common rail increases to the specified value and the engine speed increases to 2000 rpm when the Active Test is performed.