Ecd System (W/ Egr Cooler) -- System Description |
| ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM |
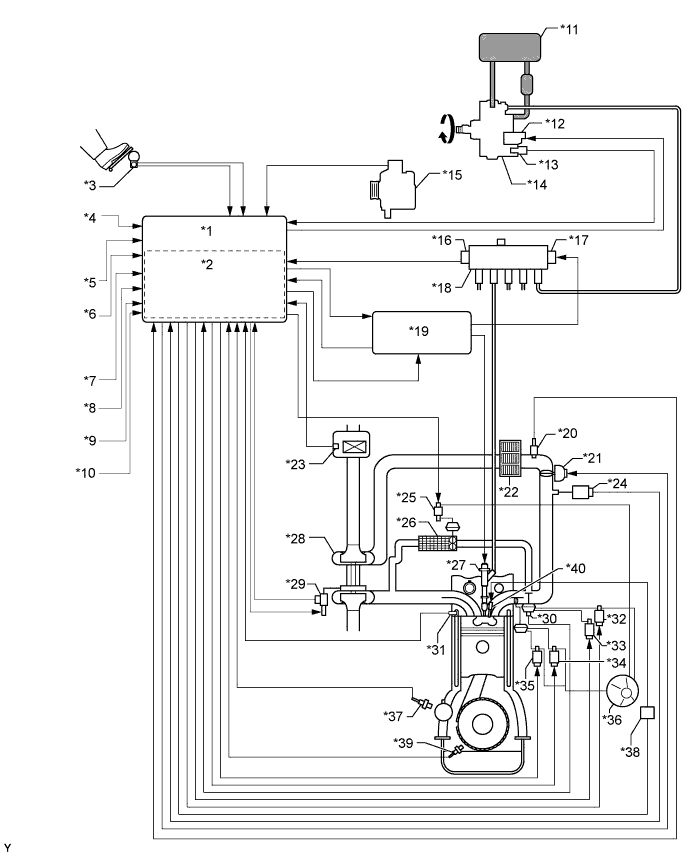
| *1 | ECM | *2 | Atmospheric Pressure Sensor |
| *3 | Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor | *4 | Ignition Switch Signal |
| *5 | Starter Signal | *6 | Vehicle Speed Signal |
| *7 | DLC3 | *8 | Battery Voltage |
| *9 | Other Signal | *10 | Stop Light Switch |
| *11 | Fuel Tank | *12 | Suction Control Valve |
| *13 | Fuel Temperature Sensor | *14 | Fuel Supply Pump Assembly |
| *15 | Generator | *16 | Fuel Pressure Sensor |
| *17 | Pressure Discharge Valve | *18 | Common Rail Assembly |
| *19 | Injector Driver | *20 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor |
| *21 | Diesel Throttle Body Assembly | *22 | Intercooler |
| *23 | Mass Air Flow Meter | *24 | Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor |
| *25 | Vacuum Switching Valve (for EGR Bypass Valve) | *26 | EGR Cooler |
| *27 | Injector Assembly | *28 | Turbocharger Sub-assembly |
| *29 | DC motor, Nozzle Vane Position Sensor | *30 | EGR Valve Position Sensor |
| *31 | Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor | *32 | Electric Vacuum Regulating Valve Assembly |
| *33 | Vacuum Switching Valve (for EGR Cut) | *34 | Vacuum Switching Valve (for No. 1 Swirl Control Valve) |
| *35 | Vacuum Switching Valve (for No. 2 Swirl Control Valve) | *36 | Vacuum Pump |
| *37 | Camshaft Position Sensor | *38 | Glow Plug Relay (GLOW) |
| *39 | Crankshaft Position Sensor | *40 | Glow Plug |
| COMMON RAIL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION |
Common rail system:
The common rail system uses high-pressure fuel for improved fuel economy. This system also provides robust engine power, while suppressing engine vibration and noise.
This system stores fuel in the common rail, which is pressurized and supplied with fuel by the supply pump. By storing fuel at high pressure, the common rail system can provide fuel at stable fuel injection pressures, regardless of engine speed or engine load.
The ECM, using the injector driver, provides an electric current to the solenoid valve in each injector assembly to regulate the fuel injection timing and volume. The ECM also monitors the internal fuel pressure of the common rail using the fuel pressure sensor. The ECM causes the supply pump to supply the fuel necessary to obtain the target fuel pressure.
In addition, this system uses a solenoid valve inside each injector assembly to open and close the fuel passages. Therefore, both fuel injection time and fuel injection volume can be precisely regulated by the ECM.
The common rail system allows a two-stage fuel injection process. In order to soften combustion shock, this system performs "pilot injection" prior to the main fuel injection. This helps to reduce engine vibration and noise.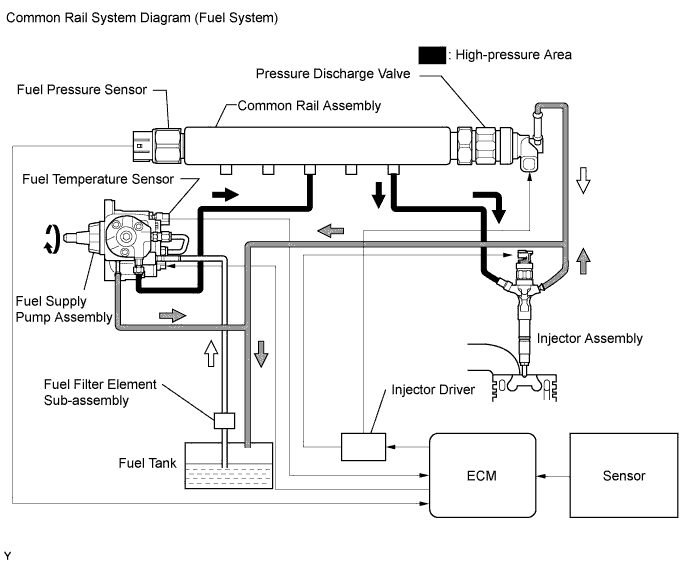
Common rail system components:
Component Description Common rail assembly Stores high-pressure fuel supplied by fuel supply pump assembly Fuel supply pump assembly Operated by crankshaft.
Supplies high-pressure fuel to common rail assembly.Injector assembly Injects fuel into combustion chamber based on signals from ECM Fuel pressure sensor Monitors internal fuel pressure of common rail assembly and sends signals to ECM Pressure discharge valve Opens based on signals from ECM when sudden deceleration occurs, or when ignition switch is off to prevent fuel pressure from becoming too high Suction control valve Adjusts fuel volume supplied to common rail and regulates internal fuel pressure based on signals from ECM Check valve Maintains pressure of fuel that discharges from injector Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) table for the common rail system:
- HINT:
- This table indicates typical DTC combinations for each malfunction.
*: There may be no DTCs stored depending on the condition of the malfunction.Trouble Area Malfunction DTC No. Injector assembly Open or short in injector circuit P0200, P0093* Stuck open P0093 Stuck closed - Fuel pressure sensor Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit or pressure sensor output fixed P0087, P0190, P0191, P0192, P0193 Pressure discharge valve Open or short in pressure discharge valve circuit P1271, P1272, P0088*, P0093*, P1229* Stuck open P0093 Stuck closed P1272, P0088* Suction control valve Open or short in suction control valve circuit P0627, P1229, P0088* Stuck open P1229, P0088* Stuck closed - Injector driver Faulty injector driver P0093*, P0200*, P1271*, P1272* Common rail system (Fuel system) Fuel leaks in high-pressure area P0093 Diagnostic trouble code description for the common rail system:
DTC No. Description P0087 Fuel pressure sensor output does not change P0088 Internal fuel pressure too high (200 MPa [2,039 kgf/cm2, 29,007 psi] or higher) P0093 Fuel leaks in high-pressure areas P0190 Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit (output voltage is too low or too high) P0191 Fuel pressure sensor out of range (Low output) P0192 Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit (output voltage is too low) P0193 Open or short in fuel pressure sensor circuit (output voltage is too high) P0200 Open or short in injector driver or injector circuit P0627 Open or short in suction control valve circuit P1229 Fuel overfeed P1271 Open or short in pressure discharge valve circuit P1272 Closed malfunction of the pressure discharge valve
| INJECTION CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION |
The ECM determines the injection volume and injection timing based on signals from the accelerator position sensor, crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sensor. The injector driver controls the injector assemblies based on signals from the ECM. The injector driver also controls the suction control valve installed on the supply pump to help regulate fuel pressure.
The feed pump is used to pump fuel from the fuel tank to the supply pump.

| SUPPLY PUMP OPERATION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION |

| SUCTION CONTROL VALVE OPERATION SYSTEM DESCRIPTION |
- HINT:
- The ECM controls the suction control valve operation to regulate the fuel volume that is produced by the supply pump for the common rail. This control is performed to regulate the internal fuel pressure of the common rail so that it reaches the targeted injection pressure.
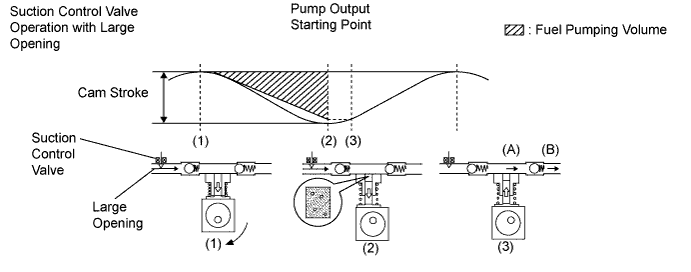
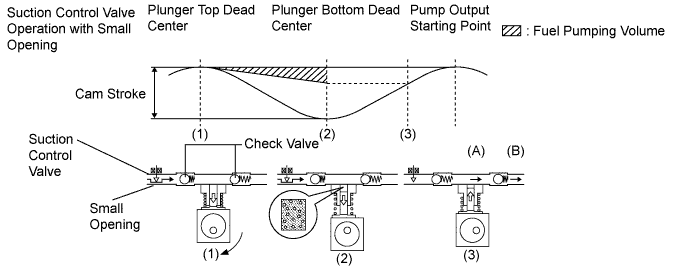
When the suction control valve opening is small:
When the opening of the suction control valve is small, the volume of supplied fuel is small.
The suction volume becomes small due to the narrow path despite the plunger stroke being full. The difference between the geometrical volume and suction volume creates a vacuum.
Pump output will start when the fuel pressure at (A) becomes higher than the common rail pressure (B).
When the suction control valve opening is large:
When the opening of the suction control valve is large, the volume of supplied fuel is increased.
If the plunger stroke is full, the suction volume becomes large because of the wide path.
Pump output will start when the fuel pressure at (A) becomes higher than the common rail pressure (B).