INSPECT AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE)
INSPECT ENGINE ROOM JUNCTION BLOCK (A/F RELAY)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (A/F SENSOR - ECM)
DTC P2238 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Pumping Current Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2239 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Pumping Current Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2241 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Pumping Current Circuit Low (Bank 2 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2242 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Pumping Current Circuit High (Bank 2 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2252 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Reference Ground Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2253 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Reference Ground Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2255 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Reference Ground Circuit Low (Bank 2 Sensor 1) |
DTC P2256 Oxygen (A/F) Sensor Reference Ground Circuit High (Bank 2 Sensor 1) |
DESCRIPTION
- HINT:
- Although the DTC titles include oxygen sensor, these DTCs relate to the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor.
- Sensor 1 refers to the sensor mounted in front of the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and located near the engine assembly.
The A/F sensor is the planar type and is integrated with the heater, which heats the solid electrolyte (zirconia element). This heater is controlled by the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the exhaust gas temperature is low), a current flows into the heater to heat the sensor, in order to facilitate accurate oxygen concentration detection. In addition, the sensor and heater portions are narrower than the conventional type. The heat generated by the heater is conducted to the solid electrolyte through the alumina, therefore the sensor activation is accelerated.
A three-way catalytic converter (TWC) is used in order to convert the carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon (HC), and nitrogen oxide (NOx) into less harmful substances. To allow the TWC to function effectively, it is necessary to keep the air-fuel ratio of the engine near the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio.
*: Value changes inside the ECM. Since the A/F sensor is the current output element, a current is converted to a voltage inside the ECM. Any measurements taken at the A/F sensor or ECM connectors will show a constant voltage.

| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P2238 P2241 |
(1 trip detection logic): (a) AF+ voltage is 0.5 V or less (b) (AF+) - (AF-) = 0.1 V or less
(2 trip detection logic) |
|
| P2239 P2242 | AF+ voltage is more than 4.5 V for 5.0 seconds or more (2 trip detection logic) |
|
| P2252 P2255 | AF- voltage is 0.5 V or less for 5.0 seconds or more (2 trip detection logic) |
|
| P2253 P2256 | AF- voltage is more than 4.5 V for 5.0 seconds or more (2 trip detection logic) |
|
- HINT:
- DTCs P2238, P2239, P2252 and P2253 indicate malfunctions related to the bank 1 A/F sensor circuit.
- DTCs P2241, P2242, P2255 and P2256 indicate malfunctions related to the bank 2 A/F sensor circuit.
- Bank 1 refers to the bank that includes cylinder No. 1.
- Bank 2 refers to the bank that includes cylinder No. 2.
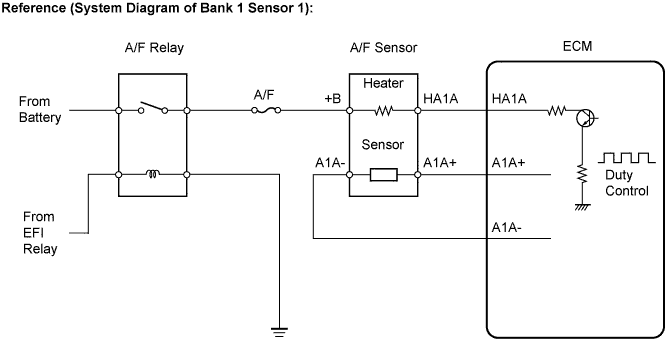
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P2195 (Link).INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- Intelligent tester only:
- Malfunctioning areas can be identified by performing "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" provided in the Active Test. "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" can help to determine whether the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor, Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor and other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning.
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Start the engine and turn the tester on.
- Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
- On the tester, enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor.
- Perform "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" with the engine in an idling condition (press the RIGHT or LEFT button to change the fuel injection volume).
- Monitor the output voltages of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS B1 S1 and O2S B1 S2 or AFS B2 S1 and O2S B2 S2) displayed on the tester.
- HINT:
- "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" lowers the fuel injection volume by 12.5 % or increases the injection volume by 25 %.
- Each sensor reacts in accordance with increases and decreases in the fuel injection volume.
| Tester Display (Sensor) | Injection Volume | Status | Voltage |
| AFS B1S1 or AFS B2S1 (A/F) | +25 % | Rich | Less than 3.0 V |
| AFS B1S1 or AFS B2S1 (A/F) | -12.5 % | Lean | More than 3.35 V |
| O2S B1S2 or O2S B2S2 (HO2) | +25 % | Rich | More than 0.55 V |
| O2S B1S2 or O2S B2S2 (HO2) | -12.5 % | Lean | Less than 0.4 V |
- NOTICE:
- The Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
| Case | A/F Sensor (Sensor 1) Output Voltage | HO2 Sensor (Sensor 2) Output Voltage | Main Suspected Trouble Areas | ||
| 1 | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  | - |
| Output Voltage More than 3.35 V Less than 3.0 V |  | Output Voltage More than 0.55 V Less than 0.4 V |  | ||
| 2 | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  |
|
| Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Output Voltage More than 0.55 V Less than 0.4 V |  | ||
| 3 | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  |
|
| Output Voltage More than 3.35 V Less than 3.0 V |  | Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
| 4 | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  | Injection Volume +25 % -12.5 % |  |
|
| Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
- Performing "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" enables technicians to check and graph the output voltages of both the A/F and HO2 sensors.
- The following A/F Control procedure enables the technician to check and graph the voltage output of both the heated oxygen sensors. To display the graph, select the following menu item on the tester: View Line/Graph.
- HINT:
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of a malfunction (CAMRY_ACV40 RM000000PDS01FX.html).
| 1.INSPECT AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE) |
Disconnect the C15 or C35 A/F sensor connector.
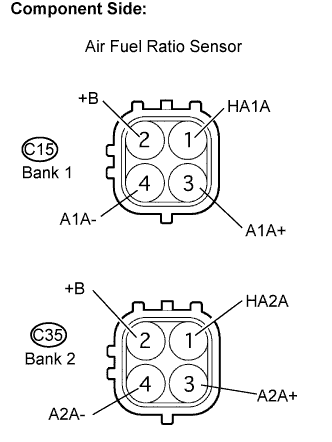 |
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard resistance:
- Bank 1 sensor 1:
Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition HA1A (1) - +B (2) 20°C (68°F) 1.8 to 3.4 Ω HA1A (1) - A1A- (4) - 10 kΩ or higher - Bank 2 sensor 1:
Tester Connection Condition Specified Condition HA2A (1) - +B (2) 20°C (68°F) 1.8 to 3.4 Ω HA2A (1) - A2A- (4) - 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 2.INSPECT A/F FUSE |
Remove the A/F fuse from the engine room junction block.
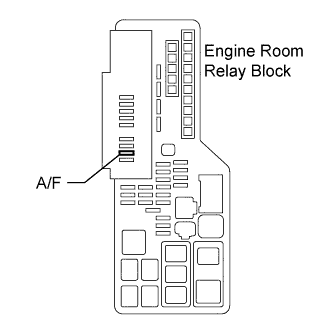 |
Measure the A/F fuse resistance.
- Standard resistance:
- Below 1 Ω
Reinstall the A/F fuse.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 3.INSPECT ENGINE ROOM JUNCTION BLOCK (A/F RELAY) |
Remove the engine room junction block from the engine room R/B.
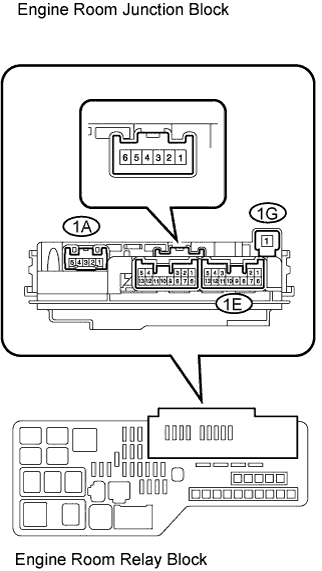 |
Inspect the A/F relay.
Measure the A/F relay resistance.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition 1G-1 - 1A-4 10 kΩ or higher 1G-1 - 1A-4 Below 1 Ω
(Apply battery voltage between terminals 1E-6 and 1E-11)
Reinstall the engine room junction block.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (A/F SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the C15 and C35 A/F sensor connectors.
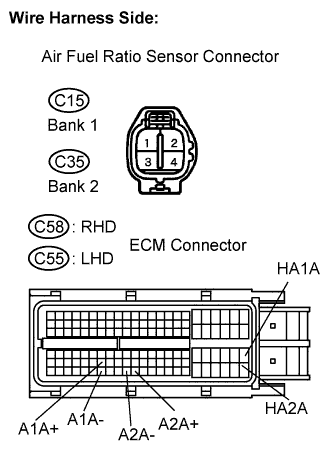 |
Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard voltage:
Tester Connection Specified Condition +B (C15-2) - Body ground 9 to 14 V +B (C35-2) - Body ground 9 to 14 V
Turn the ignition switch off.
Disconnect the C58 (RHD) or C55 (LHD) ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard resistance (Check for open):
- RHD:
Tester Connection Specified Condition HA1A (C15-1) - HA1A (C58-86) Below 1 Ω A1A+ (C15-3) - A1A+ (C58-93) Below 1 Ω A1A- (C15-4) - A1A- (C58-116) Below 1 Ω HA2A (C35-1) - HA2A (C58-109) Below 1 Ω A2A+ (C35-3) - A2A+ (C58-120) Below 1 Ω A2A- (C35-4) - A2A- (C58-119) Below 1 Ω - LHD:
Tester Connection Specified Condition HA1A (C15-1) - HA1A (C55-86) Below 1 Ω A1A+ (C15-3) - A1A+ (C55-93) Below 1 Ω A1A- (C15-4) - A1A- (C55-116) Below 1 Ω HA2A (C35-1) - HA2A (C55-109) Below 1 Ω A2A+ (C35-3) - A2A+ (C55-120) Below 1 Ω A2A- (C35-4) - A2A- (C55-119) Below 1 Ω
- Standard resistance (Check for short):
- RHD:
Tester Connection Specified Condition HA1A (C15-1) or HA1A (C58-86) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A1A+ (C15-3) or A1A+ (C58-93) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A1A- (C15-4) or A1A- (C58-116) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher HA2A (C35-1) or HA2A (C58-109) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A2A+ (C35-3) or A2A+ (C58-120) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A2A- (C35-4) or A2A- (C58-119)- Body ground 10 kΩ or higher - LHD:
Tester Connection Specified Condition HA1A (C15-1) or HA1A (C55-86) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A1A+ (C15-3) or A1A+ (C55-93) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A1A- (C15-4) or A1A- (C55-116) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher HA2A (C35-1) or HA2A (C55-109) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A2A+ (C35-3) or A2A+ (C55-120) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher A2A- (C35-4) or A2A- (C55-119)- Body ground 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the ECM connector.
Reconnect the A/F sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||