READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (OUTPUT VOLTAGE OF HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR)
INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (CHECK FOR SHORT)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CHECK FOR SHORT)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (INJECTION VOLUME)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (CONTROL THE INJECTION VOLUME)
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (INJECTION VOLUME)
INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE)
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR - ECM)
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0136, P0137 OR P0138)
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0136 or P0138)
DTC P0136 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 2) |
DTC P0137 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2) |
DTC P0138 Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2) |
DESCRIPTION
- HINT:
- Sensor 2 refers to the sensor mounted behind the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and located far from the engine assembly.
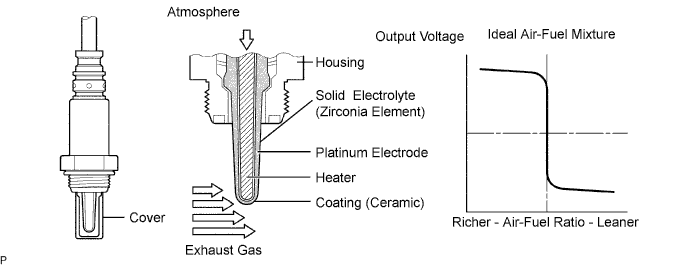
The HO2 sensor is located behind the TWC, and detects the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. Since the sensor is integrated with the heater that heats the sensing portion, it is possible to detect the oxygen concentration even when the intake air volume is low (the exhaust gas temperature is low).
When the air-fuel ratio becomes lean, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas is rich. The HO2 sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is lean (low voltage, i.e. less than 0.45 V).
Conversely, when the air-fuel ratio is richer than the stoichiometric air-fuel level, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas becomes lean. The HO2 sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is rich (high voltage, i.e. more than 0.45 V). The HO2 sensor has the property of changing its output voltage drastically when the air-fuel ratio is close to the stoichiometric level.
The ECM uses the supplementary information from the HO2 sensor to determine whether the air-fuel ratio after the TWC is rich or lean, and adjusts the fuel injection time accordingly. Thus, if the HO2 sensor is working improperly due to internal malfunctions, the ECM is unable to compensate for deviations in the primary air-fuel ratio control.
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P0136 |
|
|
| P0137 |
|
|
| P0138 |
|
|
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
- Active Air-Fuel Ratio Control
The ECM usually performs air-fuel ratio feedback control so that the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor output indicates a near stoichiometric air-fuel level. This vehicle includes active air-fuel ratio control in addition to regular air-fuel ratio control. The ECM performs active air-fuel ratio control to detect any deterioration in the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) and Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor malfunctions (refer to the diagram below).
Active air-fuel ratio control is performed for approximately 15 to 20 seconds while driving with a warm engine. During active air-fuel ratio control, the air-fuel ratio is forcibly regulated to become lean or rich by the ECM. If the ECM detects a malfunction, one of the following DTCs is set: DTC P0136 (abnormal voltage output), P0137 (open circuit) and P0138 (short circuit).
- Abnormal Voltage Output of HO2 Sensor (DTC P0136)
While the ECM is performing active air-fuel ratio control, the air-fuel ratio is forcibly regulated to become rich or lean. If the sensor is not functioning properly, the voltage output variation is small. For example, when the HO2 sensor voltage does not decrease to less than 0.21 V and does not increase to more than 0.59 V during active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM determines that the sensor voltage output is abnormal and sets DTC P0136.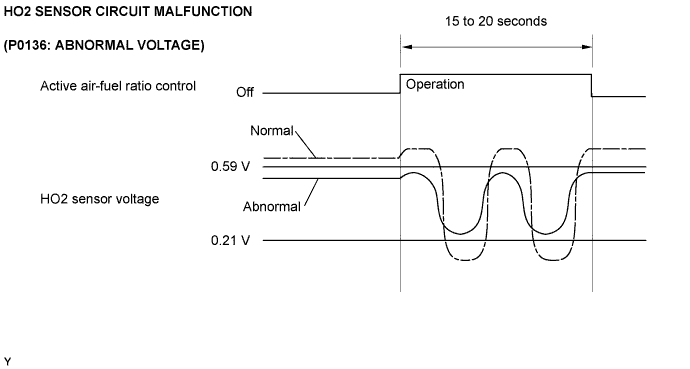
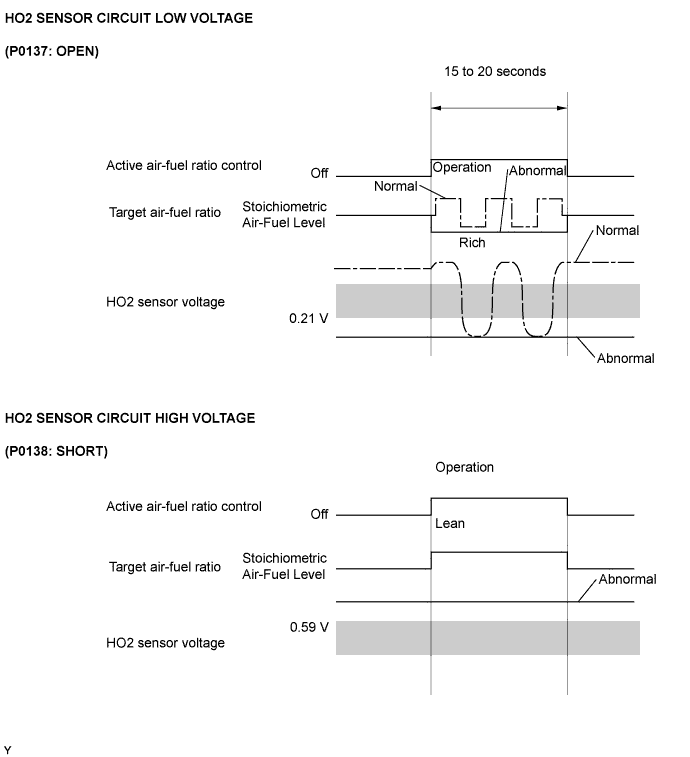
- Open or Short in Heated Oxygen (HO2) Sensor Circuit (DTC P0137 or P0138)
During active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM calculates the Oxygen Storage Capacity (OSC)* of the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) by forcibly regulating the air-fuel ratio to become rich or lean. If the HO2 sensor has an open or short, or the voltage output of the sensor decreases significantly, the OSC indicates an extraordinarily high value. Even if the ECM attempts to continue regulating the air-fuel ratio to become rich or lean, the HO2 sensor output does not change.
While performing active air-fuel ratio control, when the target air-fuel ratio is rich and the HO2 sensor voltage output is 0.21 V or less (lean), the ECM interprets this as an abnormally low sensor output voltage and sets DTC P0137. When the target air-fuel ratio is lean and the voltage output is 0.59 V or more (rich) during active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM determines that the sensor voltage output is abnormally high, and sets DTC P0138.- HINT:
- DTC P0138 is also set if the HO2 sensor voltage output is more than 1.2 V for 10 seconds or more.
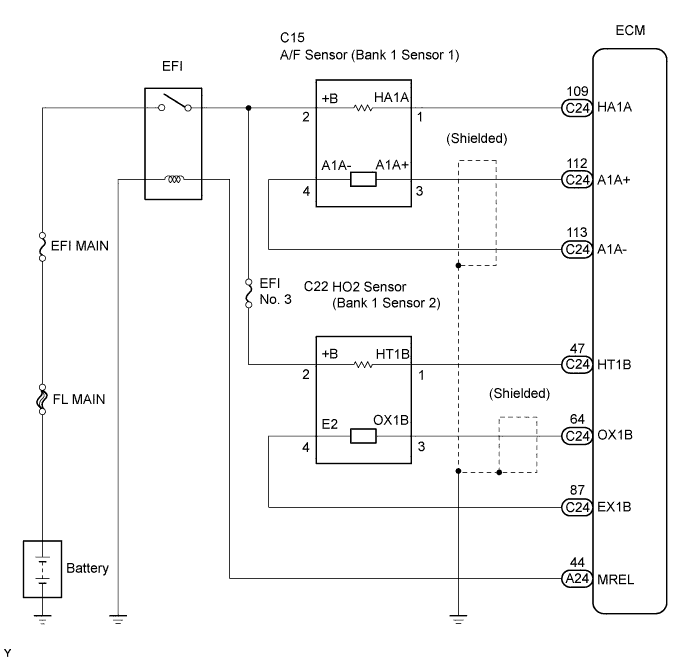
WIRING DIAGRAM
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
- HINT:
- This confirmation driving pattern is used in the "PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN" procedure of the following diagnostic troubleshooting procedure.
- Performing this confirmation pattern will activate the Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor monitor. (The catalyst monitor is performed simultaneously.) This is very useful for verifying the completion of the repair.
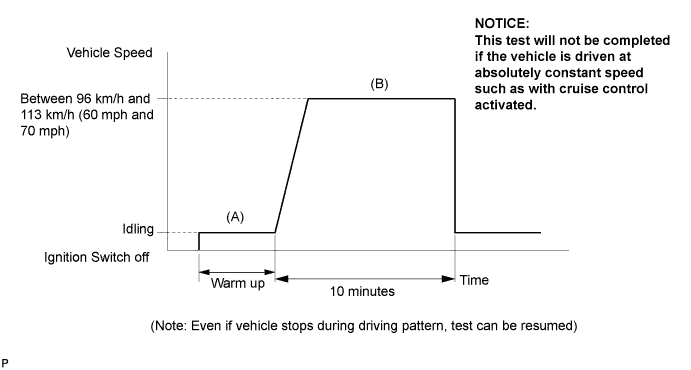
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.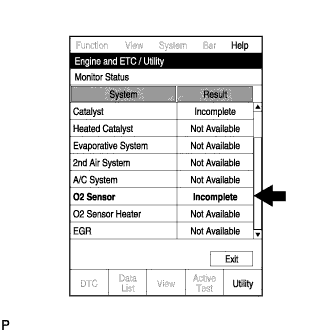
- Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
- Turn the tester on.
- Clear the DTCs (if set) (CAMRY_ACV40 RM000000PDK01RX.html).
- Enter the check mode (CAMRY_ACV40 RM000000PDL01VX.html).
- Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility.
- Check that "O2 Sensor" is "Incomplete".
- Start the engine and warm it up. (Proceed to "A")
- Drive the vehicle at between 96 km/h and 113 km/h (60 mph and 70 mph) for at least 10 minutes. (Proceed to "B")
- Note the state of the "Utility" items. Those items will change to "Complete" as the O2 Sensor monitor operates.
- On the tester, select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC and check if any DTCs (any pending DTCs) are set.
- HINT:
- If "O2 Sensor" does not change to "Complete", and any pending DTCs fail to set, extend the driving time.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
- HINT:
- Intelligent tester only:
- Malfunctioning areas can be identified by performing the "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" function provided in the Active Test. The "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" function can help determine whether the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor, Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor and other potential trouble areas are malfunctioning.
- The following instructions describe how to conduct the "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" operation using the intelligent tester.
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Start the engine and turn the tester on.
- Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
- On the tester, select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor.
- Perform the "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" operation with the engine idling (press the RIGHT or LEFT button to change the fuel injection volume).
- Monitor the voltage outputs of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS B1 S1 and O2S B1 S2) displayed on the tester.
- HINT:
- The "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" operation lowers the fuel injection volume by 12.5% or increases the injection volume by 25%.
- The sensors react in accordance with increases and decreases in the fuel injection volume.
- Standard:
Tester Display
(Sensor)Injection Volume Status Voltage AFS B1 S1
(A/F)+25% Rich Less than 3.0 -12.5% Lean More than 3.35 O2S B1 S2
(HO2)+25% Rich More than 0.5 -12.5% Lean Less than 0.4
- NOTICE:
- The A/F sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the HO2 sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
| Case | A/F Sensor (Sensor 1) Output Voltage | HO2 Sensor (Sensor 2) Output Voltage | Main Suspected Trouble Area | ||
| 1 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | - |
| Output Voltage More than 3.35 V Less than 3.0 V |  | Output Voltage More than 0.5 V Less than 0.4 V | 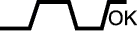 | ||
| 2 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  |
|
| Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Output Voltage More than 0.5 V Less than 0.4 V | 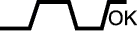 | ||
| 3 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  |
|
| Output Voltage More than 3.35 V Less than 3.0 V |  | Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
| 4 | Injection volume +25% -12.5% |  | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  |
|
| Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
- Following the "Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor" procedure enables technicians to check and graph the voltage outputs of both the A/F and HO2 sensors.
- To display the graph, select the following menu items on the tester: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor / Enter / View / AFS B1 S1 and O2S B1 S2.
- HINT:
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
- If the OX1B wire from the ECM connector is short-circuited to the +B wire, DTC P0138 will be set.
| 1.READ OUTPUT DTC |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
- Result:
Result Proceed to P0138 is output A P0137 is output B P0136 is output C P0136, P0137 or P0138 and other DTCs are output D
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.READ VALUE USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (OUTPUT VOLTAGE OF HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / All Data / O2S B1S2.
Allow the engine to idle.
Read the heated oxygen sensor output voltage while idling.
- Result:
Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage Proceed to 1.0 V or higher A Below 1.0 V B
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 3.INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (CHECK FOR SHORT) |
Disconnect the heated oxygen sensor connector.
 |
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition +B (2) - OX1B (3) 10 kΩ or higher +B (2) - E2 (4) 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the heated oxygen sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 4.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CHECK FOR SHORT) |
Turn the ignition switch off and wait for 5 minutes.
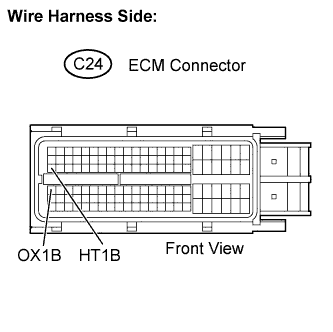 |
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition HT1B (C24-47) - OX1B (C24-64) 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the ECM connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||
| 5.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (INJECTION VOLUME) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine.
Turn the tester on.
Warm up the engine.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume.
Change the fuel injection volume using the tester and monitor the voltage output of the air fuel ratio and heated oxygen sensors displayed on the tester.
- HINT:
- Change the fuel injection volume within the range of -12% to +12%. The injection volume can be changed in fine gradations within this range.
- The air fuel ratio sensor is displayed as AFS Voltage B1S1, and the heated oxygen sensor is displayed as O2S B1S2 on the tester.
- The air fuel ratio sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the heated oxygen sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
Result Tester Display (Sensor) Voltage Variation Proceed to AFS Voltage B1S1 Alternates between higher than and below 3.3 V OK Remains at higher than 3.3 V NG Remains at below 3.3 V NG - HINT:
- A normal heated oxygen sensor voltage (O2S B1S2) reacts in accordance with increases and decreases in fuel injection volumes. When the air fuel ratio sensor voltage remains at either below or higher than 3.3 V despite the heated oxygen sensor indicating a normal reaction, the air fuel ratio sensor is malfunctioning.

|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 6.INSPECT AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
- HINT:
- This air fuel ratio sensor test is to check the air fuel ratio sensor current during the fuel-cut. When the sensor is normal, the sensor current will be below 3 mA in this test.
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
Turn the tester on.
Clear DTCs.
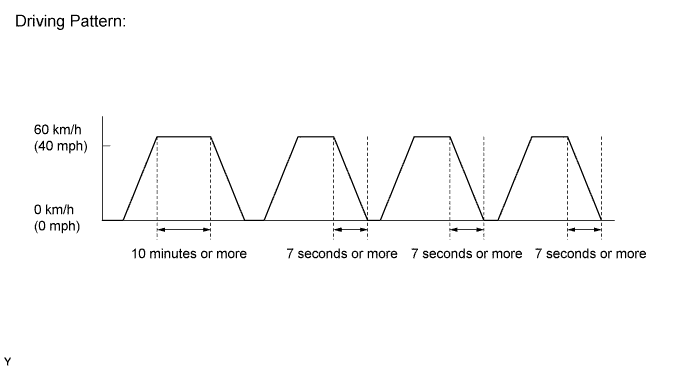
Drive the vehicle according to the drive pattern listed below.
Warm up the engine.
Drive the vehicle at 60 km/h (40 mph) or more for 10 minutes or more.
Stop the vehicle.
Accelerate the vehicle to 60 km/h (40 mph) or more and decelerate for 7 seconds or more. Perform this 3 times.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Data List / A/F Control System / AFS Current B1S1.
Read the value of the air fuel ratio sensor current while the fuel-cut operation is being performed.
- Standard current:
- Below 3.0 mA
- HINT:
- To measure the air fuel ratio sensor current precisely, perform the fuel-cut operation as long as possible.
- If it is difficult to measure the air fuel ratio sensor current, use the snapshot function of the intelligent tester.
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| 7.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (CONTROL THE INJECTION VOLUME) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine.
Turn the tester on.
Warm up the engine.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume / All Data / O2S B1S2.
Change the fuel injection volume using the tester, monitoring the voltage output of the heated oxygen sensors displayed on the tester.
- HINT:
- Change the fuel injection volume within the range of -12% to +12%. The injection volume can be changed in fine gradations within this range.
- The air fuel ratio sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the heated oxygen sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
- Standard voltage:
- Fluctuates between 0.4 V or less and 0.5 V or higher.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 8.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING INTELLIGENT TESTER (INJECTION VOLUME) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine.
Turn the tester on.
Warm up the engine.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume.
Change the fuel injection volume using the tester and monitor the voltage output of the air fuel ratio and heated oxygen sensors displayed on the tester.
- HINT:
- Change the fuel injection volume within the range of -12% to +12%. The injection volume can be changed in fine gradations within this range.
- The air fuel ratio sensor is displayed as AFS Voltage B1S1, and the heated oxygen sensor is displayed as O2S B1S2 on the tester.
- The air fuel ratio sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the heated oxygen sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20 seconds.
Result Tester Display (Sensor) Voltage Variation Proceed to AFS Voltage B1S1 Alternates between higher than and below 3.3 V OK Remains at higher than 3.3 V NG Remains at below 3.3 V NG - HINT:
- A normal heated oxygen sensor voltage (O2S B1S2) reacts in accordance with increases and decreases in fuel injection volumes. When the air fuel ratio sensor voltage remains at either below or higher than 3.3 V despite the heated oxygen sensor indicating a normal reaction, the air fuel ratio sensor is malfunctioning.

|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||
| 9.CHECK FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAK |
Check for exhaust gas leakage.
- OK:
- No gas leakage.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 10.INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE) |
Disconnect the C22 Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor connector.
 |
Measure the resistance between the terminals of the HO2 sensor connector.
- Standard resistance:
Tester Connection Specified Condition HT1B (1) - +B (2) 11 to 16 Ω at 20°C (68°F) HT1B (1) - E2 (4) 10 kΩ or higher
Reconnect the HO2 sensor connector.
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 11.CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR - ECM) |
Disconnect the heated oxygen sensor connector.
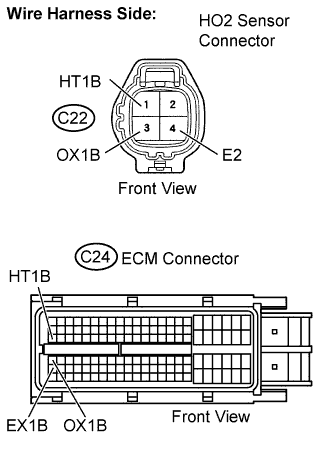 |
Disconnect the ECM connector.
Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
- Standard resistance (Check for open):
Tester Connection Specified Condition HT1B (C22-1) - HT1B (C24-47) Below 1 Ω OX1B (C22-3) - OX1B (C24-64) Below 1 Ω E2 (C22-4) - EX1B (C24-87) Below 1 Ω
- Standard resistance (Check for short):
Tester Connection Specified Condition HT1B (C22-1) or HT1B (C24-47) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher OX1B (C22-3) or OX1B (C24-64) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E2 (C22-4) or EX1B (C24-87) - Body ground 10 kΩ or higher
|
| ||||
| OK | |
| 12.REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
Replace the heated oxygen sensor.
| NEXT | |
| 13.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN |
Perform Confirmation Driving Pattern.
| NEXT | |
| 14.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0136, P0137 OR P0138) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
Turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
- Result:
Display (DTC Output) Proceed to P0136, P0137 or P0138 is output A DTC is not output B
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||
| 15.REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
Replace the air fuel ratio sensor.
| NEXT | |
| 16.PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN |
Perform Confirmation Driving Pattern.
| NEXT | |
| 17.CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0136 or P0138) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
Turn the tester on.
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read the DTCs.
- Result:
Result Proceed to P0136 or P0138 is output A DTC is not output B
|
| ||||
| A | ||
| ||